Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature region
for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature region北条 公伸*; 廣田 貴俊*; 名越 康人*; 深堀 拓也*; 清水 万真*; 下平 昌樹; 小川 琢矢*; 八代醍 健志*; 大畑 充*; 南 二三吉*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/07
加圧熱衝撃事象における延性-脆性遷移温度域の原子炉圧力容器の破壊挙動を予測するため、日本溶接協会規格(WES)として塑性拘束補正係数 を導入した評価手法の策定を目指している。WESでは当該評価手法として、簡易法と詳細法の2種類を定める予定である。簡易法による塑性拘束補正係数
を導入した評価手法の策定を目指している。WESでは当該評価手法として、簡易法と詳細法の2種類を定める予定である。簡易法による塑性拘束補正係数 の算出では、材料の降伏応力、降伏比、ワイブル形状母数をパラメータとした式を用いる。また、塑性拘束補正係数
の算出では、材料の降伏応力、降伏比、ワイブル形状母数をパラメータとした式を用いる。また、塑性拘束補正係数 は評価対象の欠陥寸法や構造物の板厚にも依存する。本研究では、様々な原子炉圧力容器を対象として簡易法による塑性拘束補正係数
は評価対象の欠陥寸法や構造物の板厚にも依存する。本研究では、様々な原子炉圧力容器を対象として簡易法による塑性拘束補正係数 を求めるため、構造物の板厚や亀裂寸法、降伏比やワイブル形状母数を変化させた感度解析を実施した。また、加圧熱衝撃事象は温度変化を伴う事象であることから、ワイブル形状母数等の温度依存性に関する検討も行った。
を求めるため、構造物の板厚や亀裂寸法、降伏比やワイブル形状母数を変化させた感度解析を実施した。また、加圧熱衝撃事象は温度変化を伴う事象であることから、ワイブル形状母数等の温度依存性に関する検討も行った。
名越 康人*; 深堀 拓也*; 岡田 裕*; 高橋 昭如*; 下平 昌樹; 上田 貴志*; 小川 琢矢*; 八代醍 健志*; 高橋 由紀夫*; 大畑 充*
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/03
日本溶接協会CAF小委員会では、塑性拘束効果を考慮した破壊評価手法ガイドラインの策定を目指している。この評価手法では、脆性破壊を評価するためのBereminモデルと延性亀裂成長を評価するためのGTNモデルを用いる。そこで、これらの評価モデルの適用性を検証するため、CAF小委員会の参加機関によるベンチマーク解析が行われた。ベンチマーク解析は、各機関が有する有限要素解析コードを用い、2種類の低合金鋼(A及びB)の破壊試験に対して実施されてきた。本発表では、低合金鋼Bに対する解析結果を報告する。Bereminモデルにおいて、一般的なワイブル形状母数(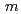 = 10, 20, 30)を用いた場合、各機関で計算されたワイブル応力が概ね一致することを確認した。また、Toughness Scaling Modelに基づいて、塑性拘束度が異なる2種類の試験片を用いてワイブル形状母数
= 10, 20, 30)を用いた場合、各機関で計算されたワイブル応力が概ね一致することを確認した。また、Toughness Scaling Modelに基づいて、塑性拘束度が異なる2種類の試験片を用いてワイブル形状母数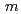 を算出した。算出されたワイブル形状母数
を算出した。算出されたワイブル形状母数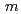 は解析機関によりばらつきはあったものの、最終的に算出されるワイブル応力は一致することを確認した。GTNモデルに関して、評価に用いるパラメータを1T-C(T)試験片の室温での荷重-変位関係に基づいて最適化した。最適化されたパラメータを用いてGTNモデルに基づき評価されたJ-R曲線が各機関で一致することを確認した。
は解析機関によりばらつきはあったものの、最終的に算出されるワイブル応力は一致することを確認した。GTNモデルに関して、評価に用いるパラメータを1T-C(T)試験片の室温での荷重-変位関係に基づいて最適化した。最適化されたパラメータを用いてGTNモデルに基づき評価されたJ-R曲線が各機関で一致することを確認した。
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; Li, Y.; 眞崎 浩一*; 高越 大輝*; 永井 政貴*; 南日 卓*; 村上 健太*; 関東 康祐*; 八代醍 健志*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.22-00484_1 - 22-00484_13, 2023/08
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code, PASCAL, has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency for failure probability and failure frequency evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and thermal transients. To strengthen the applicability of PASCAL, considerable efforts on verifications of the PASCAL code have been made in the past years. As a part of the verification activities, a working group consisted of different organizations from industry, universities and institutes, was established in Japan. In the early phase, the working group focused on verifying the PFM analysis functions for RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) subjected to pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. Recently, the PASCAL code has been improved in order to run PFM analyses for both RPVs in PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients. Simultaneously, the working group initiated a verification plan for the improved PASCAL through independent PFM analyses by different organizations. Concretely, verification analyses for a PWR-type RPV subjected to PTS transients and a BWR-type RPV subjected to a low-temperature over pressure transient were performed using PASCAL. This paper summarizes those verification activities, including the verification plan, analysis conditions and results. Based on the verification studies, the reliability of PASCAL for probabilistic integrity assessments of Japanese RPVs was confirmed with confidence.
廣田 貴俊*; 名越 康人*; 北条 公伸*; 岡田 裕*; 高橋 昭如*; 勝山 仁哉; 上田 貴志*; 小川 琢矢*; 八代醍 健志*; 大畑 充*; et al.
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/07
In order to establish a guideline for fracture evaluation by considering plastic constraint in the ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) region, the CAF (Constraint-Based Assessment of Fracture in Ductile-Brittle Transition Temperature Region) subcommittee has been launched in 2018 in the Japan Welding Engineering Society. In the committee, fracture tests are conducted using C(T), SE(B), and 50mm-thick flat plate with a surface flaw subjected to bending load or tensile load to verify fracture evaluation methods. Since simulation results are easily affected by analysis conditions, benchmark analysis is essential for the potential users of the guideline. Therefore, benchmark analyses are executed on brittle and ductile damages by Beremin and Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman (GTN) models implemented in the finite element (FE) codes. The benchmark analyses are carried out in four steps; Step 0 is to confirm the output of FE codes in each member with the same input data and the same FE model. Step 1 is to confirm the result of Weibull stress analysis for C(T) specimens tested at -125 C. The Weibull parameter, m, was fixed in this step. At step 2, sensitivity analyses are conducted on Weibull stresses in different conditions. The outputs by the GTN model are also confirmed. At the final step, the fracture simulation will be run for flat plate specimens with less plastic constraint than the standard fracture toughness specimen. As the results of the benchmark analyses up to step 2, a significant difference is not observed in the Weibull stress computed by committee members with the same input data and FE model and it is confirmed that the effects of element type, nonlinear deformation theory employed in FE analysis. For the calculation of the Weibull parameter m by using the fracture toughness test results and the developed programs by committee members, the converged values of m show good agreement among them.
C. The Weibull parameter, m, was fixed in this step. At step 2, sensitivity analyses are conducted on Weibull stresses in different conditions. The outputs by the GTN model are also confirmed. At the final step, the fracture simulation will be run for flat plate specimens with less plastic constraint than the standard fracture toughness specimen. As the results of the benchmark analyses up to step 2, a significant difference is not observed in the Weibull stress computed by committee members with the same input data and FE model and it is confirmed that the effects of element type, nonlinear deformation theory employed in FE analysis. For the calculation of the Weibull parameter m by using the fracture toughness test results and the developed programs by committee members, the converged values of m show good agreement among them.