Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawase, Keigo; Kando, Masaki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Daito, Izuru; Kondo, Shuji; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Chen, L.*; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
Nuclear Physics Review, 26(Suppl.), p.94 - 99, 2009/07
We constructed MeV- and sub-MeV-photon sources by means of Compton backscattering with a laser light and an electron beam at SPring-8 and KPSI-JAEA. MeV-photon source consists of a continuous-wave optically-pumped far infrared laser and an 8-GeV stored electron beam. Sub-MeV-photon source consists of a Nd:YAG pulse-laser and an 150-MeV electron beam accelerated by a microtron. Both source have been succeeded backscattered photon generation. In this talk, I will present characteristics and future prospects of these photon sources.
 -ray generation from backward Compton scattering at SPring-8
-ray generation from backward Compton scattering at SPring-8Kawase, Keigo; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Okajima, Shigeki*; Shoji, Masazumi*; Suzuki, Shinsuke*; Tamura, Kazuhiro*; Yorita, Tetsuhiko*; Okuma, Haruo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 592(3), p.154 - 161, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:76.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)A test experimental line at SPring-8 has been constructed for the generation of backward Compton scattered (BCS)  -ray by head-on collision between an 8 GeV electron beam and a far-infrared (FIR) laser. For the FIR laser, we use a continuous-wave methanol laser optically pumped by a carbon dioxide (
-ray by head-on collision between an 8 GeV electron beam and a far-infrared (FIR) laser. For the FIR laser, we use a continuous-wave methanol laser optically pumped by a carbon dioxide (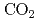 ) laser. The FIR laser output power achieved is 1.6 W at maximum for 118.8
) laser. The FIR laser output power achieved is 1.6 W at maximum for 118.8  m lasing; this value is the highest in the case of this type of laser. As a result of the direct measurement, the generated BCS
m lasing; this value is the highest in the case of this type of laser. As a result of the direct measurement, the generated BCS  -ray flux was found to be about
-ray flux was found to be about 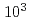 photons/s. This value is consistent with the estimation calculated by taking into account the input laser power and the transmittance of the laser transport system.
photons/s. This value is consistent with the estimation calculated by taking into account the input laser power and the transmittance of the laser transport system.
 (
(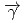 ,
,
 )
) and
and  (
(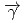 ,
,
 )
)
 reactions for
reactions for 
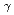 =1.5-2.4 GeV
=1.5-2.4 GeVZegers, R. G. T.*; Sumihama, Mizuki*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Dat , S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(9), p.092001_1 - 092001_4, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 = +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutron
= +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutronNakano, Takashi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Date, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(1), p.012002_1 - 012002_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:1023 Percentile:99.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kasagi, Jirota*; Kinoshita, Tadashi*; Yorita, Tetsuhiko*; Yamazaki, Hirohito*; Harada, Hideo; Shigetome, Yoshialki
PNC TY8601 97-001, 12 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
Satoh, Daiki; Abe, Shinichiro; Kanda, Hiroki*; Nagayama, Keiichi*; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Yorita, Tetsuhiko*; Zhao, H.*; Matsui, Shotaro*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
The Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) at Osaka University is planning to increase the intensity of the high-energy white neutron field that can be used to analyze semiconductor soft errors caused by cosmic ray-derived neutrons. Using the PHITS code, we had designed and installed a neutron-producing target, beam dumps, collimators, etc., applicable to the 392 MeV proton beam with 10 times higher intensity (about 10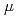 A) than the current one. In this study, the accuracy of the PHITS simulations was confirmed based on the data measured at the real facility. The simulation geometry was constructed according to the drawings of the facility. The INCL model and JENDL-5 were used for the radiation transport simulations. Neutron and gamma-ray dose rates were measured at several locations using the Wendi-2 and DARWIN monitors. As a result, PHITS well reproduced the neutron fluence rates at the semiconductor irradiation location, and the simulated values agreed with the measured neutron and gamma-ray dose rates within 5 and 15%, respectively, behind the shielding.
A) than the current one. In this study, the accuracy of the PHITS simulations was confirmed based on the data measured at the real facility. The simulation geometry was constructed according to the drawings of the facility. The INCL model and JENDL-5 were used for the radiation transport simulations. Neutron and gamma-ray dose rates were measured at several locations using the Wendi-2 and DARWIN monitors. As a result, PHITS well reproduced the neutron fluence rates at the semiconductor irradiation location, and the simulated values agreed with the measured neutron and gamma-ray dose rates within 5 and 15%, respectively, behind the shielding.