Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Hiroki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Sawabe, Yuki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072019_1 - 072019_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)In J-PARC 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron, the synchronized data system using reflective memory has been constructed. In order to support the requirement of using larger size data in high intensity beam operation in the future, a new synchronized data generation method has been proposed. The new method implements in the measurement system the functions performed by the high-level computer in the current system, thereby realizing synchronized data generation using data transfer via LAN. In this study, we have constructed a test bench for the new synchronized data system that implements the proposed method and verified its performance. This result leads to the development of the new synchronized data system based on data transfer via LAN. In this paper, we describe the outline of the new synchronized data generation method and the results of performance tests.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.937 - 941, 2023/11
In the J-PARC 3GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), the 400 MeV H beam is changed to H
beam is changed to H beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced at KEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced at KEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takahashi, Hiroki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Chimura, Motoki; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Hayashi, Naoki; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Sawabe, Yuki*; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.839 - 843, 2023/11
In the J -PARC 3GeV synchrotron accelerator (RCS), a new signal processing system for beam monitors is been developing to replace the existing system for the main beam monitors that monitor the stability of the accelerator: beam loss monitor, beam position monitor and beam current monitor. The new system will consist of a TAG server and an ADC module that can be used commonly for the three main monitors. The main design concepts of the new system are: (1) the TAG server divides various beam J-PARC tag information to each ADC module, (2) the ADC module converts acquisition data from beam monitors to digital signals by ADC and performs high-speed analysis by FPGA with switching analysis methods to suit each monitor, (3) the ADC module periodically outputs the analysis data with tag information by packing the signal processing data of all shots for about 10 seconds, and also outputs any one shot data on-demand, and (4) the raw waveform data, the latest four shots of FFT-related data in the process of analysis and bunch data for each cycle are stored in the internal memory of the ADC module, and the data can be read out as needed. In this presentation, we will report on the progress of the data acquisition test of tag information reading and beam monitor signals using the prototype under development.
Watanabe, Kazuhiko*; Niki, Kazuaki*; Takahashi, Hiroki; Yamamoto, Noboru*; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Fukuta, Shimpei*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.844 - 847, 2023/11
J-PARC Personnel Protection System (PPS) acquires and displays data using by PPS Data System. PPS Data System has been using SCADA software, but it has become difficult to handle increased data due to the limited number of signals. Then, it became necessary to build PPS Data System using different software. Therefore, we decided to construct a new system using EPICS, which has been used in the J-PARC control system. On the other hand, PPS is a system that guarantees the safety of personnel, so it cannot be shut down for long periods of time. In addition, it is the most important safety system and must maintain high reliability and stability, so it would be dangerous to update the entire system in a short period of time. Therefore, we decided to divide the PPS Data System by function and replace it with the new system partially while operating the current system. This allows us to verify the operation of the updated parts and correct any problems without compromising the functionality of the PPS, and to construct a new system with high reliability and stability. This presentation will provide an overview of the new system, the updating process, and the progress.
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Okabe, Kota; Okita, Hidefumi; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hotchi, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 68th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2023) (Internet), p.147 - 152, 2023/10
 particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linac
particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linacTamura, Jun; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Liu, Y.*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1049, p.168033_1 - 168033_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac is a high-intensity accelerator in which beam loss is a critical issue. In the J-PARC linac, H beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H
beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H
linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H
particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H
linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H particles were separated from the H
particles were separated from the H beam, and the intensity profiles of the H
beam, and the intensity profiles of the H particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H
particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H
particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H
particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
Saha, P. K.; Okabe, Kota; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hotchi, Hideaki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2420, p.012040_1 - 012040_7, 2023/01
Saha, P. K.; Okabe, Kota; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1 - 5, 2023/01
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.629 - 633, 2023/01
In the J-PARC 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), a 400 MeV H beam injected from the linac is exchange to an H
beam injected from the linac is exchange to an H beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3 GeV. The charge exchange foils mainly used in the RCS are HBC foil (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil), which are made by adding a small amount of boron to carbon rods and using them as electrodes by the arc deposition method. Since 2018, foils produced by JAEA have been used for user operation. So far, no major problems have occurred due to the foils. Meanwhile, the beam power of the RCS has been gradually increased from 500 kW to 830 kW since 2018. As beam power increases, the foil issues were identified to achieve the RCS design power of 1 MW. In this paper, we will report on the recent foil usage status and issue in the user operation.
beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3 GeV. The charge exchange foils mainly used in the RCS are HBC foil (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil), which are made by adding a small amount of boron to carbon rods and using them as electrodes by the arc deposition method. Since 2018, foils produced by JAEA have been used for user operation. So far, no major problems have occurred due to the foils. Meanwhile, the beam power of the RCS has been gradually increased from 500 kW to 830 kW since 2018. As beam power increases, the foil issues were identified to achieve the RCS design power of 1 MW. In this paper, we will report on the recent foil usage status and issue in the user operation.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Nomura, Masahiro; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Fujirai, Kosuke; Kamiya, Junichiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.277 - 281, 2023/01
The J-PARC 3GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) is aiming to provide the proton beam of very high power for neutron experiments and the main ring synchrotron. We have continued the beam commissioning and the output power from RCS have been increasing. In recent years, we have been trying continuous supply of 1-MW high-intensity beam, which is the design value, to a neutron target. We tried to operate continuously for over 40 hours in June 2020. However, some trouble occurred and the operation was frequently suspended. In June 2021, we tried again 1-MW operation but it was suspended due to deterioration of the cooling water performance. Last summer shutdown period, we recovered performance of the cooling water system and retried in this June. In the final case, the outside temperature became extremely high. We could not keep 1-MW power, whereas 600 kW beam was delivered in stable.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Toyama, Takeshi*; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro
Proceedings of 13th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 22) (Internet), p.1663 - 1666, 2022/07
Ceramic breaks are used in synchrotrons for many purposes. For example, they are inserted between the Multi-Wire Profile Monitors (MWPMs) on the injection line at the rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) in J-PARC to completely prevent the wall currents accompanying beams from affecting the MWPMs. On the other hand, from the viewpoint of suppressing beam impedances and the radiation fields from the ceramic breaks, it would be preferable that the inner surface of the ceramic break is coated with titanium nitride (TiN), or covered over capacitors. In this report, we measure the radiation fields from the ceramic break with and without capacitors as well as the beam profile and investigate the effect of the ceramic break on the measurements.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Kamiya, Junichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tani, Norio; Kotoku, Hirofumi*; Horino, Koki*; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Takeda, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Kazami
JAEA-Technology 2021-019, 105 Pages, 2021/11
Since a user operation startup, the 3 GeV synchrotron accelerator (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron: RCS) gradually reinforced the beam power. As a result, the surface dose rate of the apparatus located at the beam injection area of the RCS, such as the magnet, vacuum chambers, beam monitors, etc., increases year by year. The beam injection area has many apparatuses which required manual maintenance, so reducing worker's dose is a serious issue. To solve this problem, we have organized a task force for the installation of the shield. The task force has aimed to optimize the structure of the radiation shield, construct the installation procedure with due consideration of the worker's dose suppression. As the examination result of the shield design, we have decided to adopt removal shielding that could be installed quickly and easily when needed. We carried out shield installation work during the 2020 summer maintenance period. The renewal work required to install the shielding has been carried out in a under high-dose environment. For this reason, reducing the dose of workers was an important issue. So, we carefully prepared the work plan and work procedure in advance. During the work period, we implemented various dose reduction measures and managed individual dose carefully. As a result, the dose of all workers could be kept below the predetermined management value. We had installed removal shielding at the beam injection area in the 2020 summer maintenance period. We confirmed that this shield can contribute to the reduction of the dose during work near the beam injection area. It was a large-scale work to occupy the beam injection area during almost of the summer maintenance period. However, it is considered very meaningful for dose suppression in future maintenance works.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamada, Naoto*; Yamagata, Ryohei*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.850 - 854, 2021/10
no abstracts in English
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Kamiya, Junichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tani, Norio; Kotoku, Hirofumi*; Horino, Koki*; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Takeda, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Kazami
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.238 - 242, 2021/10
Since a user operation startup, the 3GeV synchrotron accelerator (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron: RCS) gradually reinforced the beam power. As a result, the surface dose rate of the apparatus located at the beam injection area of the RCS increases year by year. The beam injection area has many apparatuses which required manual maintenance, so reducing worker's dose is a serious issue. To solve this problem, we have decided to adopt removal shielding that could be installed quickly and easily when needed. We carried out shield installation work during the 2020 summer maintenance period. The installation work of the shield has been carried out in a under high-dose environment. For this reason, reducing the dose of workers was an important issue. So, we carefully prepared the work plan and work procedure in advance. During the work period, we implemented various dose reduction measures and managed individual dose carefully. As a result, the dose of all workers could be kept below the predetermined management value. We had installed removal shielding at the beam injection area in the 2020 summer maintenance period. We confirmed that this shield can contribute to the reduction of the dose during work near the beam injection area.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Otsu, Satoru*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.494 - 498, 2021/10
J-PARC 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) provides more than 700 kW proton beam to the neutron target. In order to investigate the influence of the radiation, we intend to evaluate the radiations such as the neutron and gamma-rays, which are generated due to the proton beam loss. If the amount of beam loss is excessive, it becomes difficult to identify the individual neutron and gamma ray. Therefore, we investigated the signal rate of the extraction point of RCS. Preliminary result indicated that we can enough distinguish the neutron and gamma-ray by the liquid scintillator.
Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Okabe, Kota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Fumihiko; Hotchi, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 21) (Internet), p.590 - 593, 2021/08
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Saha, P. K.; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Fujirai, Kosuke; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Suganuma, Kazuaki
EPJ Techniques and Instrumentation (Internet), 8(1), p.9_1 - 9_9, 2021/07
The 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex supplies a high-intensity proton beam for neutron experiments. Various parameters are monitored to achieve a stable operation, and it was found that the oscillations of the charge-exchange efficiency and cooling water temperature were synchronized. We evaluated the orbit fluctuations at the injection point using a beam current of the injection dump, which is proportional to the number of particles that miss the foil and fail in the charge exchange, and profile of the injection beam. The total width of the fluctuations was approximately 0.072 mm. This value is negligible from the user operation viewpoint as our existing beam position monitors cannot detect such a small signal deviation. This displacement corresponds to a 1.63 10
10 variation in the dipole magnetic field. Conversely, the magnetic field variation in the L3BT dipole magnet, which was estimated by the temperature change directly, is 4.08
variation in the dipole magnetic field. Conversely, the magnetic field variation in the L3BT dipole magnet, which was estimated by the temperature change directly, is 4.08 10
10 . This result suggested that the change in the cooling water temperature is one of the major causes of the efficiency fluctuation.
. This result suggested that the change in the cooling water temperature is one of the major causes of the efficiency fluctuation.
 -state of a
-state of a  hypernucleus,
hypernucleus, 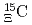
Yoshimoto, Masahiro*; Fujita, Manami; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Ichikawa, Yudai; Ichikawa, Masaya; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2021(7), p.073D02_1 - 073D02_19, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:81.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Naoki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Okabe, Kota; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamamoto, Masanobu; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011018_1 - 011018_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English