Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 29(2), p.63 - 81, 2022/12
The understanding of the swelling phenomenon of montmorillonite is essential to predict the physical and chemical behavior of clay-based barriers in radioactive waste disposal systems. This study investigated the key factors controlling crystalline swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. On the basis of the comparisons between MD simulated and experimental results, the water content in the interlayer in five homoionic (Na , K
, K , Cs
, Cs , Ca
, Ca and Sr
and Sr ) montmorillonite was strongly correlated to the hydration number and the preference of an outer- or inner-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The detailed analysis for these results offer insights that the hydration number is controlled by the hydration free energy, the volume and the distribution of each interlayer counter-ion. The systematic MD simulations with virtually variable parameters clarified that the hydration free energy and the charge of interlayer counter- ions compete as influencing factors, and the control the formation rate of an outer-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The empirical relationships between these key factors will allow essential insights into predicting the swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions.
) montmorillonite was strongly correlated to the hydration number and the preference of an outer- or inner-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The detailed analysis for these results offer insights that the hydration number is controlled by the hydration free energy, the volume and the distribution of each interlayer counter-ion. The systematic MD simulations with virtually variable parameters clarified that the hydration free energy and the charge of interlayer counter- ions compete as influencing factors, and the control the formation rate of an outer-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The empirical relationships between these key factors will allow essential insights into predicting the swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions.
 Cs
Cs , and
, and  I
I in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approaches
in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approachesFukatsu, Yuta; Yotsuji, Kenji*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 211, p.106176_1 - 106176_10, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:88.36(Chemistry, Physical)Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
Applied Clay Science, 204, p.106034_1 - 106034_13, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:98 Percentile:99.75(Chemistry, Physical)Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Sakuma, Hiroshi*
Nendo Kagaku, 58(1), p.8 - 25, 2019/00
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were conducted to investigate physical properties of water and cations in montmorillonite interlayer nanopores. The swelling behaviors and hydration states were firstly evaluated as functions of interlayer cations and layer charge. The diffusion coefficients of water and cations in interlayer nanopores were decreased in comparison with those in bulk water and came closer to those in bulk water when basal spacing increased. The viscosity coefficients of interlayer water estimated indicated a significant effect of viscoelectricity at 1- and 2-layer hydration states and higher layer charge of montmorillonite. These trends from MD calculations were confirmed to be consistent with existing measured data and previous MD simulation. In addition, model and parameter related to viscoelectric effect used in the diffusion model was refined based on comparative discussion between MD simulations and measurements. The series of MD calculations could provide atomic level understanding for the developments and improvements of the diffusion model for compacted montmorillonite.
Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suehara, Shigeru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Fujii, Naoki*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Honda, Akira
Clays and Clay Minerals, 65(4), p.252 - 272, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.29(Chemistry, Physical)Structure and stability of montmorillonite edge faces (110), (010), (100), and (130) of the layer charges y = 0.5 and 0.33 are investigated by the first-principles electronic calculations based on the density functional theory. Stacking and single layer models are tested for understanding the effect of stacking on the stability of montmorillonite edge faces. Most stacking layers stabilize the edge faces by making hydrogen bonds between the layers; therefore, the surface energy of stacking layers is reduced rather than the single layer model. This indicates that the surface energy of edge faces should be estimated depending on the swelling conditions. Lowest surface energies of (010) and (130) edge faces were realized by the presence of Mg ions on the edge faces. These edge faces have a strong adsorption site for cations due to local negative charge of the edges.
Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 92, p.286 - 297, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)Diffusion and adsorption behavior of uranyl (UO ) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO
) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO , K
, K , CO
, CO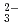 and Cl
and Cl and H
and H O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO
O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H
is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO
O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO CO
CO and UO
and UO (CO
(CO )
) can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO
can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO and K
and K were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO
were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO might be smaller than that of K
might be smaller than that of K . Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
. Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Okubo, Takahiro*
CMS Workshop Lectures, Vol.21, p.251 - 257, 2016/06
We have developed integrated sorption and diffusion model (ISD model) for assessment of diffusion parameters consistent with sorption processes in compacted bentonite. The ISD model gives consistent consideration to porewater chemistry, sorption and diffusion processes in compacted bentonite. The diffusion component based on the electric double layer theory and the homogeneous pore model in the ISD model accounts consistently for cation De overestimation and anion exclusion in narrow pores. The current ISD model can quantitatively account for diffusion of monovalent cations and anions, however, the model predictions disagree with diffusion data for multivalent cation and complex species. To improve the applicability of the model, it is necessary to consider the atomic level interactions between solute, solvent or clay mineral, and try that we apply the current ISD model to heterogeneous pore structure. In this study we try the application of the current ISD model to multiple pore structure. As results of numerical analysis of these models, the salinity dependence of effective diffusivity for the multi-pore model is comparatively smaller than that for the homogeneous pore model and the current diffusion model is improved.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro; Yotsuji, Kenji; Ishii, Yasuo; Takahashi, Hiroaki*
CMS Workshop Lectures, Vol.21, p.241 - 250, 2016/00
Sorption and diffusion of radionuclides in argillaceous rocks are key processes in the safe geological disposal. The diffusion and sorption behavior of Ni(II), Am(III) and Se(IV) in mudstone from the Horonobe URL were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusivities obtained by the through-diffusion experiments were in the sequence of Cs , Ni
, Ni , HTO, I
, HTO, I , Se(SeO
, Se(SeO
 ), Am(Am(CO
), Am(Am(CO )
) ) by comparison with the previous study. The distribution coefficient values were consistent with those obtained by batch sorption tests. These results were interpreted by the clay-based modeling approach coupling the thermodynamic sorption model assuming key contributions of clays (smectite and illite) and the diffusion model assuming the electrical double layer theory and the simplified pore model with size distribution. This clay-based model could provide reasonable account of observed trends and could be basically applicable for various radionuclides.
) by comparison with the previous study. The distribution coefficient values were consistent with those obtained by batch sorption tests. These results were interpreted by the clay-based modeling approach coupling the thermodynamic sorption model assuming key contributions of clays (smectite and illite) and the diffusion model assuming the electrical double layer theory and the simplified pore model with size distribution. This clay-based model could provide reasonable account of observed trends and could be basically applicable for various radionuclides.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Ochs, M.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(10), p.1191 - 1204, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:83.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model for compacted bentonites was developed based on the consistent combination of (1) the porewater chemistry model, (2) the thermodynamic sorption model (TSM), and (3) the diffusion model based on the electrical double layer (EDL) theory. This ISD model was successfully tested for various actinides with a complex chemistry (Np(V), Am(III), U(VI) under conditions where carbonate complexes are formed), by using published diffusion and sorption data (
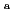 ,
, 
 ,
, 
 ) as a function of partial montmorillonite density. Quantitative agreements were observed as same as monovalent cations (Cs
) as a function of partial montmorillonite density. Quantitative agreements were observed as same as monovalent cations (Cs , Na
, Na ), anions (Cl
), anions (Cl , I
, I , TcO
, TcO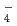 ) previously reported. The ISD model could be therefore seen to be able to predict sorption and diffusion behavior of various complex radionuclides in compacted bentonites.
) previously reported. The ISD model could be therefore seen to be able to predict sorption and diffusion behavior of various complex radionuclides in compacted bentonites.
Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Nishimaki, Yuichiro*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1665, p.123 - 129, 2014/07
The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model has been developed to quantify these processes in compacted bentonite. The ISD model assuming averaged narrow porespace and the electric double layer (EDL) theory could give quantitative agreement with diffusion data of monovalent cations and anions under wide range of conditions. However, the systematic disagreements were observed for multivalent cations, anions and complex species. In this study, the excluded volume effect and the dielectric saturation effect were introduced into the current ISD model and the modified Poisson-Boltzmann equations were numerically solved. The ionic distributions were influenced at the near surface, however, these changes were canceled by averaging for the porespace. As a result, these modified models had little effect on the effective diffusivity. On the other hand, the modified model considering hydrated ions with the effective electric charge could give good reproducibility of diffusion data.
 , Na
, Na , I
, I and HTO in compacted sodium montmorillonite as a function of porewater salinity; Integrated sorption and diffusion model
and HTO in compacted sodium montmorillonite as a function of porewater salinity; Integrated sorption and diffusion modelTachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 132, p.75 - 93, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:102 Percentile:94.25(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Sorption and diffusion of radionuclides in compacted bentonite are key processes in the safe geological disposal. The effects of porewater salinity on diffusion and sorption of Cs , Na
, Na , I
, I and HTO in compacted montmorillonite were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) in montmorillonite (dry density of 800 kg/m
and HTO in compacted montmorillonite were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) in montmorillonite (dry density of 800 kg/m ) were measured under different salinities (0.01-0.5 M). The De showed cation excess and anion exclusion effects, which were influenced by salinity. The Kd values for Cs
) were measured under different salinities (0.01-0.5 M). The De showed cation excess and anion exclusion effects, which were influenced by salinity. The Kd values for Cs and Na
and Na were sensitive to salinity. The Da trends of Cs
were sensitive to salinity. The Da trends of Cs and Na
and Na are mostly independent on salinity. These results were interpreted by the integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model coupling the ion exchange model and the EDL diffusion model in narrow pores. This ISD model was further applied to diffusion data of monovalent cations and anions in compacted bentonite, performed well for a wide range of compaction.
are mostly independent on salinity. These results were interpreted by the integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model coupling the ion exchange model and the EDL diffusion model in narrow pores. This ISD model was further applied to diffusion data of monovalent cations and anions in compacted bentonite, performed well for a wide range of compaction.
 in compacted sodium montmorillonite as a function of porewater salinity
in compacted sodium montmorillonite as a function of porewater salinityTachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji
Proceedings of 5th International Meeting on Clays in Natural and Engineered Barriers for Radioactive Waste Confinement (USB Flash Drive), p.899 - 900, 2012/10
Sorption and diffusion of radionuclides in compacted bentonite are key processes in the safe geological disposal. The effects of porewater salinity on Sr diffusion and sorption in compacted montmorillonite were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Sr in montmorillonite compacted to dry density of 800 kg/m were measured under four different salinities (0.01-0.5 M NaCl). The De decreased drastically with increasing porewater salinity. The Kd values decreased with increasing salinity, which are consistent with Kd values obtained by batch sorption. These results were interpreted by the ISD model coupling the thermodynamic sorption model and the EDL diffusion model in narrow pores. The ISD model can be basically applicable for divalent cations, however is needed to modify for better agreement at low salinity conditions by considering additional factors.
were measured under four different salinities (0.01-0.5 M NaCl). The De decreased drastically with increasing porewater salinity. The Kd values decreased with increasing salinity, which are consistent with Kd values obtained by batch sorption. These results were interpreted by the ISD model coupling the thermodynamic sorption model and the EDL diffusion model in narrow pores. The ISD model can be basically applicable for divalent cations, however is needed to modify for better agreement at low salinity conditions by considering additional factors.
Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Nishimaki, Yuichiro*
Proceedings of 5th International Meeting on Clays in Natural and Engineered Barriers for Radioactive Waste Confinement (USB Flash Drive), p.427 - 428, 2012/10
We have developed integrated sorption and diffusion model (ISD model) for assessment of diffusion parameters consistent with sorption processes in compacted bentonite. Conventional ISD model is unsatisfactory because for multivalent cation/anion and complex ion model predictions disagree with experimental data, and because the model contains additional non-physical fitting parameter. Accordingly we extract the factors influencing the assessment from fundamental assumptions of the conventional ISD model. In this study we incorporated the excluded volume effect and the dielectric saturation effect into ISD model. As results of numerical analysis of these models the considering factors influence hardly the effective diffusivity. Therefore it does not mean that the disagreement with experimental data are caused by considering factors in this report.
Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Nishimaki, Yuichiro*
JAEA-Research 2011-047, 105 Pages, 2012/02
We have developed integrated sorption and diffusion model (ISD model) for assessment of diffusion parameters consistent with sorption processes in compacted bentonite. Conventional ISD model is unsatisfactory because for multivalent cation/anion and complex ion model predictions disagree with experimental data, and because the model contains additional non-physical fitting parameter. Accordingly we extract the factors influencing the assessment from fundamental assumptions of the conventional ISD model. In this report we incorporated the excluded volume effect, the dielectric saturation effect and the fluctuation potential effect caused by ion-ion electrostatic interaction into ISD model. As results of numerical analysis of these models the considering factors influence hardly the effective diffusivity. Therefore it does not mean that the disagreement with experimental data are caused by considering factors in this report.
 , I
, I and HTO in samples of the argillaceous Wakkanai Formation from the Horonobe URL, Japan; Clay-based modeling approach
and HTO in samples of the argillaceous Wakkanai Formation from the Horonobe URL, Japan; Clay-based modeling approachTachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Seida, Yoshimi*; Yui, Mikazu
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(22), p.6742 - 6759, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:81.43(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Diffusion and sorption behaviors of Cs , I
, I and HTO in samples of the Wakkanai Formation from Horonobe URL were investigated as a function of ionic strength (IS) of synthetic groundwater by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments. The
and HTO in samples of the Wakkanai Formation from Horonobe URL were investigated as a function of ionic strength (IS) of synthetic groundwater by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments. The 
 values showed cation excess and anion exclusion effects, which were strongly dependent on IS;
values showed cation excess and anion exclusion effects, which were strongly dependent on IS; 
 for Cs
for Cs decreased as IS increased,
decreased as IS increased, 
 for I
for I showed the opposite dependency and
showed the opposite dependency and 
 for HTO showed no dependence. The Kd values for Cs determined by through-diffusion and batch experiments were in good agreement and decreased with IS as a result of competitive ion exchange. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted based on the clay-based modeling approach in assuming the clay components of illite and smectite control diffusion and sorption mechanisms. The model predicted the
for HTO showed no dependence. The Kd values for Cs determined by through-diffusion and batch experiments were in good agreement and decreased with IS as a result of competitive ion exchange. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted based on the clay-based modeling approach in assuming the clay components of illite and smectite control diffusion and sorption mechanisms. The model predicted the 
 and Kd trends obtained by the series of experiments reasonably well, implying the key contribution of the clay particle and nano-size pore for ionic migration.
and Kd trends obtained by the series of experiments reasonably well, implying the key contribution of the clay particle and nano-size pore for ionic migration.
Tachi, Yukio; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ochs, M.*; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Seida, Yoshimi; Yamada, Norikazu*; Yui, Mikazu
Radiochimica Acta, 98(9-11), p.711 - 718, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:86.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Diffusion and sorption of radionuclides in compacted bentonite are the key processes in the safe geological disposal. The effects of carbonate and salinity on Np(V) diffusion and sorption in compacted montmorillonite were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusion coefficients (
 ) and distribution coefficients (
) and distribution coefficients (
 ) of Np in montmorillonite compacted to dry density of 800 kg/m
) of Np in montmorillonite compacted to dry density of 800 kg/m were measured under four conditions with different salinities (0.05/0.5 M NaCl) and carbonate concentrations (0/0.01 M NaHCO
were measured under four conditions with different salinities (0.05/0.5 M NaCl) and carbonate concentrations (0/0.01 M NaHCO ). The
). The 
 for carbonate-free conditions decreased as salinity increased, and those for carbonate conditions showed the opposite dependency. The
for carbonate-free conditions decreased as salinity increased, and those for carbonate conditions showed the opposite dependency. The 
 decreased by one order of magnitude under high carbonate condition. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted by coupling the thermodynamic aqueous speciation, the thermodynamic sorption model based on ion exchange and surface complexation, and the diffusion model based on electrical double layer theory in narrow pores. The mechanistic model could be useful in predicting the sorption and diffusion behavior of complex species in compacted systems.
decreased by one order of magnitude under high carbonate condition. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted by coupling the thermodynamic aqueous speciation, the thermodynamic sorption model based on ion exchange and surface complexation, and the diffusion model based on electrical double layer theory in narrow pores. The mechanistic model could be useful in predicting the sorption and diffusion behavior of complex species in compacted systems.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Ochs, M.*; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2009-069, 83 Pages, 2010/03
This report presents the prototype model/database for integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD2009) in bentonite systems as basis for performance assessment (PA) of geological disposal. The sorption model is based on a relatively simple 1-site surface complexation/diffuse layer model in combination with 1-site ion exchange model. The model parameters for surface chemistry/sorption are evaluated based on existing datasets for Na-montmorillonite, which covers key geochemical conditions, in consistent way. The diffusion model based on homogeneous pore structure and electrical double layer theory was developed and coupled with batch-based sorption model, then was validated by using data in compacted montmorillonite. The sorption and diffusion models were also tested by applying data in bentonite systems. The model and related parameters developed for key radionuclides such as Cs, Np(V), Ni, Am, etc. are integrated to ISD2009 database, which could be useful in future PA exercise.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Seida, Yoshimi; Yui, Mikazu
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1193, p.545 - 552, 2009/05
Diffusion of Cs and I in compacted montmorillonite were examined from the viewpoints of mechanistic understanding of salinity effects. The effective diffusivity and capacity factor for Cs and I were measured in compacted montmorillonite saturated with 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl by through-diffusion experiments, coupled with multiple curve analysis including tracer depletion, breakthrough, and depth concentration curves. The De values obtained for Cs decreased as salinity increased, and those for I showed the opposite dependency. The distribution coefficient of Cs decreased as salinity increased. The diffusion and sorption parameters for Cs were also obtained by in-diffusion and batch sorption experiments, showing good agreement with those by the through-diffusion. The diffusion model based on electrical double layer theory predicted the salinity dependence of De reasonably well, the apparent diffusivity which includes sorption effect was also interpreted by the sorption coupled model.
Yotsuji, Kenji*; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(2), p.166 - 176, 2008/06
To clarify the dissolution mechanism of clay minerals, the basal and edge surface structures of dioctahedral 2:1 phyllosilicate was optimized using semi-empirical molecular orbital method. The stability of the surface structure was estimated by the bond length, bond strength and the bond energy on bonds of interest along the basal and edge surfaces. The optimized basal surface structure of montmorillonite resides at a local minimum on the potential energy surface, because each normal mode for the optimized structure has real vibrational frequency. The ideal (010)-type edge surface of pyrophyllite was initialized using crystal chemical methods. The edge surface structure that was protonated allowing for pH-dependency was optimized. On optimized edge surfaces structural relaxation occurred in all pH-conditions, then it was found that Si-O bonds in the silanol groups were stronger, and Al-O bonds in the aluminol groups were weaker, than corresponding bonds in the bulk structures, respectively. The rate-determining step is thought to be governed by hydrolysis of outer Si-O bonds on edge surfaces in alkaline dissolution of pyrophyllite and by hydrolysis of Al-O bonds in bridging Si-O-Al bonds on edge surfaces in acid dissolution.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Seida, Yoshimi*
no journal, ,
Diffusion and sorption behaviors of Cs+, I- and HTO in samples of the Wakkanai Formation from Horonobe URL were investigated as a function of salinity of synthetic groundwater by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments. The Kd values for Cs determined by through-diffusion and batch experiments were in good agreement and decreased with salinity as a result of competitive ion exchange. The De values showed cation excess and anion exclusion effects, which were strongly dependent on IS; De for Cs+ decreased as salinity increased, De for I- showed the opposite dependency and De for HTO showed no dependence. Sorption and diffusion behaviors were interpreted based on the clay-based modeling approach in assuming the clay components of illite and smectite control diffusion and sorption mechanisms. The model predicted the De and Kd trends obtained by the series of experiments reasonably well, implying the key contribution of the clay particle and nano-size pore for ionic migration.