Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,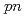 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Tang, C.*; Song, Q.*; Chang, C.-Z.*; Xu, Y.*; Onuma, Yuichi; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Liu, Y.*; Yuan, W.*; Yao, Y.*; Moodera, J. S.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 4(6), p.eaas8660_1 - eaas8660_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:83.43(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Pace, D. C.*; Austin, M. E.*; Bass, E. M.*; Budny, R.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hillesheim, J. C.*; Holcomb, C. T.*; Gorelenkova, M.*; Grierson, B. A.*; McCune, D. C.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 20(5), p.056108_1 - 056108_18, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:81.13(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Energetic ion transport due to microturbulence is investigated in MHD-quiescent plasmas by way of neutral beam injection in the DIII-D tokamak. A range of on-axis and off-axis beam injection scenarios are employed to vary relevant parameters such as the character of the background microturbulence and the value of Eb/Te, where Eb is the energetic ion energy and Te the electron temperature. In all cases it is found that any transport enhancement due to microturbulence is too small to observe experimentally. These transport effects are modeled using numerical and analytic expectations that calculate the energetic ion diffusivity due to microturbulence. It is determined that energetic ion transport due to coherent modes, including possible reductions in neutral beam current drive, is a considerably larger effect and should therefore be considered more important for ITER.
Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Skobelev, I.*; Fortov, V. E.*; Boldarev, A.*; Gasilov, V.*; Chen, L. M.*; Zhang, L.*; Yan, W.*; Yuan, D.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.181 - 201, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)
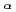 X-ray emission from intense femtosecond laser-solid interactions
X-ray emission from intense femtosecond laser-solid interactionsXu, M. H.*; Chen, L.-M.; Li, Y.-T.*; Yuan, X.-H.*; Liu, Y.-Q.*; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Tajima, Toshiki; Wang, Z.-H.*; Wei, Z.-Y.*; Zhao, W.*; et al.
Acta Physica Sinica, 56(1), p.353 - 358, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.87(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The characteristics of 
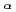 X-ray sources generated by p-polarized femtosecond laser-solid interactions are experimentally studied in the relativistic regime. By use of knife-edge image technique and a single-photon-counting X-ray CCD camera, we obtain the source size, the spectrum and the conversion efficiency of the
X-ray sources generated by p-polarized femtosecond laser-solid interactions are experimentally studied in the relativistic regime. By use of knife-edge image technique and a single-photon-counting X-ray CCD camera, we obtain the source size, the spectrum and the conversion efficiency of the 
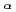 X-ray sources. The experimental results show that the conversion efficiency of
X-ray sources. The experimental results show that the conversion efficiency of 
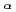 photons reaches an optimum value 7.08
photons reaches an optimum value 7.08 10
10 /sr at the laser intensity of 1.6
/sr at the laser intensity of 1.6 10
10 W/cm
W/cm , which is different from the Reich's simulation results. We find that about 10% of laser energy is converted into the forward hot electrons at the laser intensity of 1.6
, which is different from the Reich's simulation results. We find that about 10% of laser energy is converted into the forward hot electrons at the laser intensity of 1.6 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.