Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oizumi, Akito; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 223, p.111677_1 - 111677_12, 2025/12
This study aims to provide a new rational physical protection (PP) design method by using 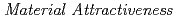 (
(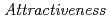 ) and to design a rational PP system for a site of the transuranium fuel cycle with accelerator-drive systems (ADSs cycle) using the new method. First, the new rational PP design method with different PP design requirements for each
) and to design a rational PP system for a site of the transuranium fuel cycle with accelerator-drive systems (ADSs cycle) using the new method. First, the new rational PP design method with different PP design requirements for each 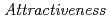 was generalized based on the definitions of a national standard method defined by the US Department of Energy, the joint US-Japan study, and the International Atomic Energy Agency. A new PP categorization of Uranium (U), including U-234, which is abundant in the ADS cycle, was also developed based on
was generalized based on the definitions of a national standard method defined by the US Department of Energy, the joint US-Japan study, and the International Atomic Energy Agency. A new PP categorization of Uranium (U), including U-234, which is abundant in the ADS cycle, was also developed based on 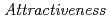 . Second, a PP design was conducted for a general BWR site with MOX fuel and the ADS cycle site by using the new rational method. It was clarified that the highest overall
. Second, a PP design was conducted for a general BWR site with MOX fuel and the ADS cycle site by using the new rational method. It was clarified that the highest overall 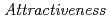 of the items within the ADS cycle site was lower than that of the MOX fuel assembly within the BWR site. The BWR site was determined to be Category I requiring the inner area. The PP design requirement level of the ADS cycle site was determined to be Category II, which does not require an inner area, while the ADS cycle site would have been classified as Category I if the PP design had been conducted using the conventional method.
of the items within the ADS cycle site was lower than that of the MOX fuel assembly within the BWR site. The BWR site was determined to be Category I requiring the inner area. The PP design requirement level of the ADS cycle site was determined to be Category II, which does not require an inner area, while the ADS cycle site would have been classified as Category I if the PP design had been conducted using the conventional method.
Dei, Shuntaro; Shibata, Masahito*; Negishi, Kumi*; Sugiura, Yuki; Amano, Yuki; Bateman, K.*; Wilson, J.*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kagami, Saya; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
Results in Earth Sciences (Internet), 3, p.100097_1 - 100097_16, 2025/12
Interactions between cement and host rock in geological repositories for radioactive waste will result in a chemically disturbed zone, which may potentially affect the long-term safety. This paper investigates the chemical evolution at the interface between cement (Ordinary Portland Cement: OPC and Low Alkaline Cement: LAC) and mudstone after 11 years of in situ reactions at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The study combines various analytical techniques to identify the key reactions at the cement-rock interface, including cement dissolution, precipitation of secondary minerals such as calcite and C-(A-)S-H phases, cation exchange in montmorillonite and reduced porosity in mudstone. The study also highlights the effects of cement-mudstone interactions on radionuclide migration, such as reduction of diffusivity due to reduced porosity and enhancement of sorption due to incorporation into secondary minerals in the altered mudstone.
Otsuka, Naohiko*; Devi, V.*; Iwamoto, Osamu
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 225, p.111903_1 - 111903_18, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0 C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS method
C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS methodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Sharma, A.*; Kumar, R.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Pellegrini, M.*; Yokoyama, Ryo*; Okamoto, Koji*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 250, p.127343_1 - 127343_17, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0 C
CPham, V. H.; Kurata, Masaki; Nagae, Yuji; Ishibashi, Ryo*; Sasaki, Masana*
Corrosion Science, 255, p.113098_1 - 113098_9, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0Wada, Yuki; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hibiki, Takashi*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 249, p.127219_1 - 127219_16, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0Luu, V. N.; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Udagawa, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114222_1 - 114222_15, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0Kubo, Kotaro; Mori, Kenji*; Muramatsu, Ken
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114176_1 - 114176_14, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0Aoki, Takeshi; Shimizu, Atsushi; Ishii, Katsunori; Morita, Keisuke; Mizuta, Naoki; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Noguchi, Hiroki; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 220, p.111503_1 - 111503_7, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Aiming to establish coupling technologies between a high temperature gas cooled reactor and a hydrogen production plant, JAEA has initiated the HTTR Heat Application Test Project and is conducting the safety design and the safety analysis for the licensing of the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility. The present study proposed a relative evaluation methodology for the demarcation of applicable laws and design standards for the nuclear hydrogen production system and applied it to the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility. The evaluation results showed that a candidate applying the High Pressure Gas Safety Act to the Heat Application Test Facility (hydrogen production plant) and design standards established under the High Pressure Gas Safety Act to the steam reformer did not show the lowest category in any of the metrics, and was proposed as the most superior demarcation option for the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility.
Soma, Shu; Ishigaki, Masahiro*; Shibamoto, Yasuteru
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 219, p.111455_1 - 111455_12, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yildirim, A. C.*; Mei, H.*; Toda, Kanako*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*
Applied Clay Science, 274, p.107853_1 - 107853_9, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Wang, Z.; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Duan, G.*
Journal of Computational Physics, 537, p.114072_1 - 114072_29, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe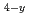 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cao, T.*; Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; 10 of others*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 940, p.148534_1 - 148534_16, 2025/09
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyYamashita, Takayuki*; Koga, Norimitsu*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Fujii, Hidetoshi*; Umezawa, Osamu*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Ichiba, Yuta*
Radiation Measurements, 187, p.107486_1 - 107486_8, 2025/09
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Miwa, Shuhei
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 218, p.111433_1 - 111433_10, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tamura, Yukiko*; Arakawa, Masato*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Fujinami, So*; Shibata, Motoki*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Yamada, Masako*; Seto, Hideki*; et al.
Polymer, 333, p.128662_1 - 128662_8, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0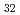 (Al, Zn)
(Al, Zn)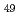 Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorder
Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorderShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Abe, Rion*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Wang, Y.*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 265, p.116730_1 - 116730_7, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management
JAEA-Review 2025-006, 126 Pages, 2025/07
This report describes the activities of Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management (DDWM) in Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) in the period from April 1, 2023 to March 31, 2024. The report covers organization and missions of DDWM, outline and operation/maintenance of facilities which belong to DDWM, treatment and management of radioactive wastes, decommissioning activities, and related research and development activities which were conducted in DDWM. In FY2023 radioactive wastes generated from R&D activities in NSRI were treated safely. They were about 156 m of combustible solid wastes and 84 m
of combustible solid wastes and 84 m of noncombustible solid wastes and 295 m
of noncombustible solid wastes and 295 m of liquid wastes. After adequate treatment, 837 waste packages (in 200 L drum equivalent) were generated. The total amounts of accumulated waste packages were 118,664 as of the end of FY2023 due to efforts of the restitution of waste packages to the Japan Radioisotope Association and volume reduction treatments of the stored waste packages. Decommissioning activities were carried out for the JAEA's Reprocessing Test Facility. As for the R&D activities, studies on radiochemical analyses of wastes for disposal were continued. In order to pass the conformity review on the New Regulatory Requirements for waste management facilities, the Approval of the design and construction method was applied sequentially for the Nuclear Regulation Authority. The ministry of the Environment and Tokai-mura office requested JAEA to dispose of the contaminated soil generated by the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The monitoring work at the playground was conducted during this period.
of liquid wastes. After adequate treatment, 837 waste packages (in 200 L drum equivalent) were generated. The total amounts of accumulated waste packages were 118,664 as of the end of FY2023 due to efforts of the restitution of waste packages to the Japan Radioisotope Association and volume reduction treatments of the stored waste packages. Decommissioning activities were carried out for the JAEA's Reprocessing Test Facility. As for the R&D activities, studies on radiochemical analyses of wastes for disposal were continued. In order to pass the conformity review on the New Regulatory Requirements for waste management facilities, the Approval of the design and construction method was applied sequentially for the Nuclear Regulation Authority. The ministry of the Environment and Tokai-mura office requested JAEA to dispose of the contaminated soil generated by the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The monitoring work at the playground was conducted during this period.