Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 他4名*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) equi-atomic multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties from cryogenic to room temperatures. At room temperature, deformation is dominated by dislocation slip, while at cryogenic temperatures (CTs), reduced stacking fault energy enhances strain hardening with twinning. This study uses in-situ neutron diffraction to analyze the temperature-dependent deformation behavior of Al (CoNiV)
(CoNiV)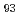 , a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
, a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:98.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanoprecipitates and nanoscale retained austenite (RA) with suitable stability play crucial roles in determining the yield strength (YS) and ductility of ultrahigh strength steels (UHSSs). However, owing to the kinetics incompatibility between nanoprecipitation and austenite reversion, it is highly challenging to simultaneously introduce high-density nanoprecipitates and optimized RA in UHSSs. In this work, through the combination of austenite reversion treatment (ART) and subsequent flash austenitizing (FA), nanoscale chemical heterogeneity was successfully introduced into a low-cost UHSS prior to the aging process. This chemical heterogeneity involved the enrichment of Mn and Ni in the austenite phase. The resulting UHSS exhibited dual-nanoprecipitation of Ni(Al,Mn) and (Mo,Cr) C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
Li, L.*; 宮本 吾郎*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; 諸岡 聡; 及川 勝成*; 友田 陽*; 古原 忠*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation (DT) of austenite ( ) to ferrite (
) to ferrite ( ) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with
) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with  +
+ duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in
duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in  +
+ two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.
two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.  to
to  DT during isothermal compression and
DT during isothermal compression and  to
to  reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between
reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between  and
and  was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft
was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft  phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the
phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the  to
to  transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 徐 平光; 行武 栄太郎*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 59(14), p.5831 - 5853, 2024/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:73.30(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnesium alloy AZ31, which has undergone high-pressure torsion processing, was subjected to in situ annealing micro-beam synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction and compared to the as-received rolled sheet material that was investigated through in situ neutron diffraction. While the latter only exhibits thermal expansion and minor recovery, the nanostructured specimen displays a complex evolution, including recovery, strong recrystallization, phase transformations, and various regimes of grain growth. Nanometer-scale grain sizes, determined using Williamson-Hall analysis, exhibit seamless growth, aligning with the transition to larger grains, as assessed through the occupancy of single grain reflections on the diffraction rings. The study uncovers strain anomalies resulting from thermal expansion, segregation of Al atoms, and the kinetics of vacancy creation and annihilation. Notably, a substantial number of excess vacancies were generated through high-pressure torsion, and maintained for driving the recrystallization and forming highly activated volumes for diffusion and phase precipitation during heating. The unsystematic scatter observed in the Williamson-Hall plot indicates high dislocation densities following severe plastic deformation, which significantly decreases during recrystallization. Subsequently, dislocations reappear during grain growth, likely in response to torque gradients in larger grains. It is worth noting that the characteristics of unsystematic scatter differ for dislocations created at high and low temperatures, underscoring the strong temperature dependence of slip system activation.
 neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinement
neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinementMao, W.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 諸岡 聡; Gao, S.*; 川崎 卓郎; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 176, p.69 - 82, 2024/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:59.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-24Ni-0.3C(wt.%)準安定オーステナイト鋼の降伏応力は、平均結晶粒径が35 m(粗粒[CG])から0.5
m(粗粒[CG])から0.5 m(超微細粒[UFG])に減少すると3.5倍(158
m(超微細粒[UFG])に減少すると3.5倍(158 551MPa)に増加したが、引張伸びは大きく維持された(0.87
551MPa)に増加したが、引張伸びは大きく維持された(0.87 0.82)。結晶粒径が力学特性と変形機構に及ぼす影響を定量的に明らかにするため、室温での引張変形中にCGとUFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C鋼のその場中性子回折測定を行った。CGとUFG試料における塑性変形の初期段階は転位すべりによって支配され、変形後期には変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)も生じた。結晶粒の微細化により、DIMTの開始応力が大きく増加し、ひずみに関するDIMTの速度が抑制されることがわかった。結果として、(i)結晶粒微細化によりオー ステナイトが安定化し、DIMTに対して最も安定な結晶粒である
0.82)。結晶粒径が力学特性と変形機構に及ぼす影響を定量的に明らかにするため、室温での引張変形中にCGとUFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C鋼のその場中性子回折測定を行った。CGとUFG試料における塑性変形の初期段階は転位すべりによって支配され、変形後期には変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)も生じた。結晶粒の微細化により、DIMTの開始応力が大きく増加し、ひずみに関するDIMTの速度が抑制されることがわかった。結果として、(i)結晶粒微細化によりオー ステナイトが安定化し、DIMTに対して最も安定な結晶粒である 111
111 //LD(LD:負荷方向)オーステナイト粒でのDIMTの開始が大幅に遅れた。その結果、UFG試験片の
//LD(LD:負荷方向)オーステナイト粒でのDIMTの開始が大幅に遅れた。その結果、UFG試験片の 111
111 //LDオーステナイト粒のほとんどはマルテンサイトに変態しなかった。(ii)結晶粒の微細化は、マルテンサイト変態の自己促進効果も抑制した。それにもかかわらず、UFG試験片の変態速度が低いDIMTは、CG試験片のより応力を増加させるのに効率がよく、変形中に均一な変形を維持するのに適していた。以上の現象は、UFG準安定オーステナイト鋼の優れた強度と延性の両立に相互に寄与している。
//LDオーステナイト粒のほとんどはマルテンサイトに変態しなかった。(ii)結晶粒の微細化は、マルテンサイト変態の自己促進効果も抑制した。それにもかかわらず、UFG試験片の変態速度が低いDIMTは、CG試験片のより応力を増加させるのに効率がよく、変形中に均一な変形を維持するのに適していた。以上の現象は、UFG準安定オーステナイト鋼の優れた強度と延性の両立に相互に寄与している。
Liu, X. J.*; 徐 平光; 城 鮎美*; Zhang, S. Y.*; 菖蒲 敬久; 行武 栄太郎*; 秋田 貢一*; Zolotoyabko, E.*; Liss, K.-D.*
Journal of Materials Science, 57(46), p.21446 - 21459, 2022/12
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:33.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In situ time/temperature-resolved synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction is applied to study heat-mediated structural changes and phase transformations in rolled sheets of AZ91 and AZ31 magnesium alloys. Azimuthal diffraction intensities along the Debye-Scherrer rings (AT-plots) are used to obtain information on grain recovery and recrystallization temperatures as well as temperature-assisted grain rotations. The azimuthally integrated diffraction intensities, plotted as functions of the scattering vector (QT-plots), provide vital data on the temperature-dependent lattice parameters of the Mg/Al matrix and intermetallic precipitates, as well as on the evolution of the precipitates' volume fraction. It was found that in AZ31, the main precipitates are of the AlMn type, which is rather stable in the investigated temperature range (up to 773 K). In contrast, in AZ91, the major intermetallic precipitates, Al Mg
Mg , undergo complete dissolution above 600 K. It is caused by the enhanced diffusion of Al into the Mg/Al matrix, which according to the Al-Mg phase diagram, can adopt more Al at elevated temperatures. This diffusion is revealed by the proportional diminishing of the matrix lattice parameter (chemical strain), allowing us to quantify the Al content in the matrix. Fast temperature-dependent manipulation with intermetallic content in the Mg/Al alloy can, in principle, be used for controlling its mechanical properties.
, undergo complete dissolution above 600 K. It is caused by the enhanced diffusion of Al into the Mg/Al matrix, which according to the Al-Mg phase diagram, can adopt more Al at elevated temperatures. This diffusion is revealed by the proportional diminishing of the matrix lattice parameter (chemical strain), allowing us to quantify the Al content in the matrix. Fast temperature-dependent manipulation with intermetallic content in the Mg/Al alloy can, in principle, be used for controlling its mechanical properties.
Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; Wang, L.*; Tang, B.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 加藤 秀実*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 129, p.251 - 260, 2022/12
被引用回数:37 パーセンタイル:95.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Owing to their attractive structure and mechanical properties, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) and medium-entropy alloys (MEAs) have attracted considerable research interest. The strength of HEAs/MEAs with a single face-centered cubic (FCC) phase, on the other hand, requires improvement. Therefore, in this study, we demonstrate a strategy for increasing the room-temperature strength of FCC-phase HEAs/MEAs by tuning cryo-pre-straining-induced crystal defects via the temperature-dependent stacking fault energy-regulated plasticity mechanism. Through neutron diffraction line profile analysis and electron microscope observation, the effect of the tuned defects on the tensile strength was clarified. This study discussed the possibility of developing single-phase high-performance HEAs by tuning pre-straining-induced crystal defects.
Yang, J.*; Ren, W.*; Zhao, X.*; 菊地 龍弥*; Miao, P.*; 中島 健次; Li, B.*; Zhang, Z.*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 99, p.55 - 60, 2022/02
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:53.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)物性測定と中性子散乱を組み合わせることにより、面心立方高エントロピー合金CrMnFeCoNiの磁気および熱輸送特性を調べた。DCおよびAC帯磁率は、温度領域全体で反強磁性および強磁性相互作用が共存する常磁性挙動を示し、それぞれ、常磁性から反強磁性への遷移、反強磁性から強磁性への遷移、およびスピン凍結に対応して、約80, 50、および20Kで3つの異常が見られる。電気伝導率と熱伝導率はNiに比べて大幅に低下しており、格子熱伝導率の温度依存性はガラスのようなプラトーを示す。非弾性中性子散乱測定は弱い非調和性を示唆し、熱輸送は欠陥散乱によって支配されると思われる。
 ZnSnS
ZnSnS thin films induced by 200 MeV Xe swift heavy ions irradiation
thin films induced by 200 MeV Xe swift heavy ions irradiationKhoualed, M.*; Boutebakh, F. Z.*; Chettah, A.*; 雨倉 宏*; 石川 法人; Ghemid, S.*; Attaf, N.*; Aida, M. S.*
Journal of Materials Science; Materials in Electronics, 32(20), p.25516 - 25527, 2021/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:27.19(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)太陽電池の吸収層としての候補材である半導体Cu ZnSnS
ZnSnS に、200MeV Xeの高速重イオンを照射して、紫外・可視分光法を用いて照射影響としての光学特性変化を評価し、X線回折法,ラマン分光法により結晶構造変化を評価した。その結果、吸収端エネルギーは、短い波長側にシフトし、バンドギャップは広がる方向に変化することが分かった。結晶性の劣化の挙動から、イオントラックの寸法が計測でき、サーマルスパイクモデルに基づいた計算予測と一致することが分かった。
に、200MeV Xeの高速重イオンを照射して、紫外・可視分光法を用いて照射影響としての光学特性変化を評価し、X線回折法,ラマン分光法により結晶構造変化を評価した。その結果、吸収端エネルギーは、短い波長側にシフトし、バンドギャップは広がる方向に変化することが分かった。結晶性の劣化の挙動から、イオントラックの寸法が計測でき、サーマルスパイクモデルに基づいた計算予測と一致することが分かった。
早川 頌*; 土井原 康平*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 愛知 正温*; 鈴木 克幸*
Journal of Materials Science, 54(17), p.11509 - 11525, 2019/09
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:54.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed molecular dynamics simulations to evaluate the effects of stacking fault energy (SFE) on interactions between a screw dislocation and spherical voids in face-centered cubic (fcc) metals. It was observed that the frequency of the cross-slips is a critical factor affecting the interaction, with primarily three different interaction morphologies being observed: (1) the two partial dislocations detach from the void independently with a time lag, (2) the two partial dislocations detach from the void almost simultaneously on a single slip plane, and (3) the two partial dislocations detach from the void almost simultaneously while involving more than one cross-slip and a jog formation. The magnitude of the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) increases in the order mentioned above. The CRSS values for interaction morphology (2), which was observed most frequently in this study, were in good agreement with those predicted analytically by adjusting the parameters dependent on the SFE. Based on the obtained results, we discussed the applicability of the analytical model for void hardening in fcc metals. The results of this work contribute significantly to the modeling of mechanical property degradation in irradiated metals.
早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 川畑 友弥*; 鈴木 克幸*
Journal of Materials Science, 54(16), p.11096 - 11110, 2019/08
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:43.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed molecular dynamics simulations of displacement cascades in FCC metals under Poisson's deformation using interatomic potentials differing in stacking fault energy (SFE), in order to investigate the effect of tensile strain on the SFE dependence of defect formation processes. There was no clear SFE dependence of the number of residual defects and the size distribution of defect clusters under both no strain and the applied strain, while the strain enhanced the defect formation to a certain extent. We also observed that the strain affected the formations of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters depending on their size and the Burgers vector. These results were consistent with the analysis based on the defect formation energies. Meanwhile, the number of SIA perfect loops was higher at lower SFE under both no strain and the applied strain, leading to an increase in the ratio of glissile SIA clusters with a decrease in SFE. Further, the absolute number of SIA perfect loops was increased by the applied strain, while the SFE dependence of the number of SIA perfect loops was not affected. These findings were associated with the difference in formation energy between an SIA perfect loop and an SIA Frank loop. The insights extracted from this study significantly contribute to the modeling of microstructural evolution in nuclear materials under irradiation, especially for low SFE metals such as austenitic stainless steels.
 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO
徳田 誠*; 真下 茂*; Khandaker, J. I.*; 緒方 裕大; 峯 洋二*; 速水 真也*; 吉朝 朗*
Journal of Materials Science, 51(17), p.7899 - 7906, 2016/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:6.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report the effect of a strong gravitational field on oriented crystalline perovskite-type manganese oxide La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (LSMO). A strong gravitational field can change in crystalline state and the enhancement of usual diffusion. We subjected oriented crystalline La
(LSMO). A strong gravitational field can change in crystalline state and the enhancement of usual diffusion. We subjected oriented crystalline La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO with different grain and grain-boundary (GBs) Sr concentrations to a strong gravitational field and investigated the resulting changes in the A-site cation diffusion and physical properties of the material. The quantitative analysis at the grain and GBs indicated that cation diffusion was more enhanced than the annealed one. The temperature dependence of the magnetic susceptibility of the gravity samples changed with the Sr concentration in the grains. The temperature dependence of the resistivity curves of the gravity sample showed several abrupt changes, which corresponded to phase transitions at the grains and GBs, which may be caused by composition changes.
with different grain and grain-boundary (GBs) Sr concentrations to a strong gravitational field and investigated the resulting changes in the A-site cation diffusion and physical properties of the material. The quantitative analysis at the grain and GBs indicated that cation diffusion was more enhanced than the annealed one. The temperature dependence of the magnetic susceptibility of the gravity samples changed with the Sr concentration in the grains. The temperature dependence of the resistivity curves of the gravity sample showed several abrupt changes, which corresponded to phase transitions at the grains and GBs, which may be caused by composition changes.
 , C-SiO
, C-SiO , and C-SiC-SiO
, and C-SiC-SiO nanotubes
nanotubes田口 富嗣; 社本 真一
Journal of Materials Science, 47(10), p.4363 - 4369, 2012/05
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:10.70(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)簡便な熱処理により、3種類の複合ナノチューブ(SiC-SiO , C-SiO
, C-SiO 及びC-SiC-SiO
及びC-SiC-SiO ナノチューブ)の合成に成功した。これら多層複合ナノチューブは、金属,半導体及び絶縁体と異なった電気特性を有する物質から合成されていた。特に、金属,半導体及び絶縁体から構成されているC-SiC-SiO
ナノチューブ)の合成に成功した。これら多層複合ナノチューブは、金属,半導体及び絶縁体と異なった電気特性を有する物質から合成されていた。特に、金属,半導体及び絶縁体から構成されているC-SiC-SiO ナノチューブは、本研究により初めて合成された。これら多層複合ナノチューブは、ナノ電気・光学デバイスへの応用が期待される。
ナノチューブは、本研究により初めて合成された。これら多層複合ナノチューブは、ナノ電気・光学デバイスへの応用が期待される。
北 憲一郎; 成澤 雅紀*; 中平 敦*; 間渕 博*; 杉本 雅樹; 吉川 正人
Journal of Materials Science, 45(13), p.3397 - 3404, 2010/04
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:35.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ポリカルボシラン(PCS)にポリシロキサンの1種であるポリメチルフェニルシロキサン(PMPhS)を混合したポリマーブレンドを用いて、炭化ケイ素(SiC)系繊維を作製した。PCSに対してPMPhSは30mass%まで相溶し、そのポリマーブレンドは513K以上で加熱すると透明な液状ポリマーと化した。また、PMPhSを混合すると軟化点も低下した。PCSへのPMPhSの15mass%混合が、平均直径14.4 mの細径高分子繊維を得るために適した条件であり、1273Kで焼成した橋かけ高分子繊維のセラミック収率は85.5%であった。細径であるにもかかわらず、引張強度は1273K焼成後で0.78GPaを示すこのSiC系繊維を、さらに1673
mの細径高分子繊維を得るために適した条件であり、1273Kで焼成した橋かけ高分子繊維のセラミック収率は85.5%であった。細径であるにもかかわらず、引張強度は1273K焼成後で0.78GPaを示すこのSiC系繊維を、さらに1673 1773Kで焼成した場合、ナノ結晶粒からなる特有のミクロ構造を持つ多孔質なSiC系繊維が得られ、その表面積は70
1773Kで焼成した場合、ナノ結晶粒からなる特有のミクロ構造を持つ多孔質なSiC系繊維が得られ、その表面積は70 150m
150m /gであった。
/gであった。
北 憲一郎; 成澤 雅紀*; 中平 敦*; 間渕 博*; 伊藤 正義*; 杉本 雅樹; 吉川 正人
Journal of Materials Science, 45(1), p.139 - 145, 2010/01
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:37.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ポリカルボシラン(PCS)と高分子量のポリヒドロメチルシロキサン(PMHS-h)からポリマーブレンドを作製し、粘度測定,質量変化率,発生ガス量等を測定した。その中で、260 Cにおいて粘度が極小値を示す、PMHS-hを15mass%混合させたポリマーブレンドを選び、これを紡糸して熱酸化不融化後に1273Kで焼成した。得られたファイバーのSEM観察を行ったところ、ファイバー断面に均一に複数の孔が存在していた。引張強度は約2.14GPaを示した。このファイバーを1773Kでさらに焼成したところ、通常のSiCファイバー表面に形成されるはずの
Cにおいて粘度が極小値を示す、PMHS-hを15mass%混合させたポリマーブレンドを選び、これを紡糸して熱酸化不融化後に1273Kで焼成した。得られたファイバーのSEM観察を行ったところ、ファイバー断面に均一に複数の孔が存在していた。引張強度は約2.14GPaを示した。このファイバーを1773Kでさらに焼成したところ、通常のSiCファイバー表面に形成されるはずの -SiC結晶塊が観察されず、引張強度は0.56GPaと非常に高い値を示した。1273Kの焼成後に1773Kで再焼成する新手法をPMHS-hとPCSのポリマーブレンドに適用することにより、高強度・高耐熱性の複数孔を有するSiC系セラミックスファイバーが作製可能であることがわかった。
-SiC結晶塊が観察されず、引張強度は0.56GPaと非常に高い値を示した。1273Kの焼成後に1773Kで再焼成する新手法をPMHS-hとPCSのポリマーブレンドに適用することにより、高強度・高耐熱性の複数孔を有するSiC系セラミックスファイバーが作製可能であることがわかった。
 C
CChen, J.; Zhai, M.*; 浅野 雅春; Huang, L.*; 前川 康成
Journal of Materials Science, 44(14), p.3674 - 3681, 2009/07
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:58.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)放射線グラフト後加水分解することにより、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン高分子電解質膜を合成した。合成した電解質膜を燃料電池に組み込み、高温で長期耐久性を評価した。その結果、0.3A/cm の燃料電池密度で1000時間以上の耐久性があることが確認できた。同時に、そのセル電圧の劣化率も時間あたりわずかに18マイクロボルトであることがわかった。耐久性実験後、電解質膜と触媒層の劣化メカニズムを調べたところ、炭化水素系電解質膜では、高濃度酸素の環境で熱劣化が起こり、これが電圧低下につながることがわかった。また、触媒層では、白金微粒子の粗大化が起こり、これが電圧低下につながることもわかった。
の燃料電池密度で1000時間以上の耐久性があることが確認できた。同時に、そのセル電圧の劣化率も時間あたりわずかに18マイクロボルトであることがわかった。耐久性実験後、電解質膜と触媒層の劣化メカニズムを調べたところ、炭化水素系電解質膜では、高濃度酸素の環境で熱劣化が起こり、これが電圧低下につながることがわかった。また、触媒層では、白金微粒子の粗大化が起こり、これが電圧低下につながることもわかった。
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiation古澤 和也*; 北 恵里香*; 佐伯 俊彦*; 長澤 尚胤; 西 則雄*; 土橋 敏明*
Journal of Biomaterials Science; Polymer Edition, 19(9), p.1159 - 1170, 2008/09
デオキシリボ核酸(DNA)は発ガン性物質をインターカーション吸着する働きがあることから、このDNAを不溶化することによって、天然高分子由来の環境浄化材料を開発することが可能となる。そこで、本研究では食品加工残渣の鮭白子DNAを選定し、多糖類誘導体やタンパク質にブレンド後、放射線橋かけしてハイブリッドゲルを創製し、得られたゲルのゲル分率,膨潤度を調べるとともに、発ガン物質のモデル物質であるアクリジルオレンジを用いて吸着特性を評価した。カルボキシメチルセルロース,ゼラチン,アルブミンを用いた場合に効率よく橋かけし、50kGy照射でゲル分率が60%以上になり、その吸水特性は約200倍であることを見いだした。10kGy照射して得られたゼラチン/DNAゲルのアクリジルオレンジの吸着量は、DNA無添加に比べて10倍以上(1.8 g/g)に増加し、環境浄化材料としての有用性を確認できた。
g/g)に増加し、環境浄化材料としての有用性を確認できた。
Septiani, U.*; Chen, J.; 浅野 雅春; 前川 康成; 吉田 勝; 久保田 仁*
Journal of Materials Science, 42(4), p.1330 - 1335, 2007/02
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:48.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)電解質膜の開発において、耐久性の向上は重要な課題になっている。本論文では、ETFE膜にスチレンモノマーを放射線グラフトした後、スルホン化して得た高分子電解質膜の耐久性に及ぼす照射雰囲気の影響について検討した結果をまとめた。10kGy照射したETFE膜(50 m)にアルゴンガスをバブリングしたスチレンモノマー(40vol%)とトルエン(60vol%)の混合溶液を充填して50
m)にアルゴンガスをバブリングしたスチレンモノマー(40vol%)とトルエン(60vol%)の混合溶液を充填して50 Cでグラフト重合を行った。この前照射の場合、アルゴン雰囲気中及び酸素雰囲気中で行った。前照射・後グラフト重合法によるETFE膜へのスチレンをグラフト重合後、スルホン化して得た電解質膜の耐酸化性を検討した。耐酸化性試験には、1.0mmol/gのイオン交換容量を持つ電解質膜を用いた。耐酸化性は60
Cでグラフト重合を行った。この前照射の場合、アルゴン雰囲気中及び酸素雰囲気中で行った。前照射・後グラフト重合法によるETFE膜へのスチレンをグラフト重合後、スルホン化して得た電解質膜の耐酸化性を検討した。耐酸化性試験には、1.0mmol/gのイオン交換容量を持つ電解質膜を用いた。耐酸化性は60 C、3%過酸化水素水溶液中に電解質膜を浸漬した後の重量変化から評価した。その結果、アルゴン雰囲気下で照射して得た電解質膜の耐久性は、酸素雰囲気下で照射して得た電解質膜に比べて、2倍高いことがわかった。酸素雰囲気下で照射して得た電解質膜の耐久性が低い理由として、主鎖とグラフト鎖の間にあるエーテル結合に起因していると推察した。
C、3%過酸化水素水溶液中に電解質膜を浸漬した後の重量変化から評価した。その結果、アルゴン雰囲気下で照射して得た電解質膜の耐久性は、酸素雰囲気下で照射して得た電解質膜に比べて、2倍高いことがわかった。酸素雰囲気下で照射して得た電解質膜の耐久性が低い理由として、主鎖とグラフト鎖の間にあるエーテル結合に起因していると推察した。
出崎 亮; 杉本 雅樹; 吉川 正人; 田中 茂; 成澤 雅紀*; 岡村 清人*; 伊藤 正義*
Journal of Materials Science, 42(1), p.130 - 135, 2007/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:13.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)われわれは、液体のケイ素系ポリマーであるポリビニルシラン(PVS)から 線架橋を利用してSiC微小成型体を作製している。得られるSiC微小成型体の特性と焼成条件の間には密接な関係があるので、PVSのセラミックス化過程を調べ、最適な焼成条件を見いだすことが重要である。本報では、室温で
線架橋を利用してSiC微小成型体を作製している。得られるSiC微小成型体の特性と焼成条件の間には密接な関係があるので、PVSのセラミックス化過程を調べ、最適な焼成条件を見いだすことが重要である。本報では、室温で 線架橋されたPVSのセラミックス化過程をガス分析,熱重量分析,密度変化等の面から調べた。
線架橋されたPVSのセラミックス化過程をガス分析,熱重量分析,密度変化等の面から調べた。 線架橋PVSのセラミックス化は500K以上の温度で始まり、700-1100Kの温度域で急激な有機-無機変成が起こることが明らかになった。質量変化と密度変化の結果から、放射線架橋、及びその後の焼成過程におけるPVSの体積収縮率が80%であることを明らかにした。1573Kでの焼成によって得られたSiCについて、密度が2.50g/cm
線架橋PVSのセラミックス化は500K以上の温度で始まり、700-1100Kの温度域で急激な有機-無機変成が起こることが明らかになった。質量変化と密度変化の結果から、放射線架橋、及びその後の焼成過程におけるPVSの体積収縮率が80%であることを明らかにした。1573Kでの焼成によって得られたSiCについて、密度が2.50g/cm 、微小ビッカース硬さが31.6GPaであった。
、微小ビッカース硬さが31.6GPaであった。
Chen, J.; 浅野 雅春; 八巻 徹也; 吉田 勝
Journal of Materials Science, 41(4), p.1289 - 1292, 2006/02
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:57.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)電解質膜の耐久性を向上させるために、スチレンに代わるモノマーとして、スチレンの誘導体であるメチルスチレン(MeSt)及びt-ブチルスチレン(tBuSt)さらに架橋剤として、高密度の架橋構造の付与が期待できるジビニルベンゼン(DVB)を組合せた新規な電解質膜を放射線グラフト重合法により合成した。このようにして得た36%のグラフト率を持つ電解質膜は、ゴア膜に比べて高いプロトン導電性を持つことがわかった。また、膜の安定性は、スチレン/DVB膜に比べて3倍向上した。