Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
長谷川 邦夫; 山口 義仁; Udyawar, A.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 147(3), p.034501_1 - 034501_7, 2025/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)Fatigue crack growth thresholds and reference fatigue crack growth rate da/dN curves for ferritic steels in air environment are provided in Appendix Y of the ASME Code Section XI. Therein, the thresholds and da/dN are expressed as a function of stress ratio R; however, the R is not explicit, when R is negative. The thresholds are given as constant values for negative R. In addition, the ASME provides two equations for da/dN under negative R; however, the boundary between the two equations is not technically known. Thus, the dependency of negative R on da/dN is not well understood. Herein, revised threshold values for negative R are provided based on experimental data, and a new boundary between the two equations for da/dN is defined using crack opening behavior and the R dependency of da/dN based on a literature survey.
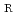 for negative stress ratios R based on trend in experimental data for fatigue crack growth rates of austenitic stainless steels for ASME code Section XI
for negative stress ratios R based on trend in experimental data for fatigue crack growth rates of austenitic stainless steels for ASME code Section XINegyesi, M.*; 山口 義仁; 長谷川 邦夫; Lacroix, V.*; Morley, A.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 147(2), p.021201_1 - 021201_7, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)Fatigue crack growth rates for stainless steels in air environment are provided by the ASME Code Section XI. When the stress ratio R is positive from 0 to 1, the scaling parameter SR increases with the increasing ratio R, and the crack growth rates increase with the increasing stress ratio R. When R is less than 0, the parameter SR=1. Hence, fatigue crack growth rates under negative R ratios are independent of stress ratios R according to the ASME Code Section XI. However, from the literature survey, experimental data reveal that the fatigue crack growth rates decreases with decreasing R ratios below zero. The objective of this paper is to assess fatigue crack growth rates under such negative stress ratios for stainless steels in air environment. An equation determined from trends in experimental data surveyed in this study is proposed for negative stress R ratios to calculate the parameter SR for the ASME Code Section XI.
月森 和之; 矢田 浩基
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 147, p.031901_1 - 031901_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)日本では、福島第一原子力発電所の事故以来、原子力プラントに対して厳しい安全対策が取られている。シビアアクシデント時において、放射性物質を内包する危機がそのバウンダリ機能を維持できるか否かが重要な関心事となる。本研究では、高速炉の1時冷却材を内包する容器等のバウンダリを構成する構造部材である鏡板とベローズに着目し、設計を超える過大な圧力を受けた場合の座屈、座屈後変形、さらにバウンダリの貫通破損(バウンダリ機能喪失)までの挙動を検討した。研究は、2013年度に始まり、段階的に進められたが、最終段階として、新たに提案する破損クライテリアの鏡板、ベローズへの適用結果を示すものである。
滝藤 聖崇; 奥田 幸彦; 西田 明美; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 146(6), p.061301_1 - 061301_12, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)In probabilistic risk assessment against earthquakes for nuclear power plants, developing a realistic response analysis method for the fragility assessment of piping systems considering input seismic motions exceeding the design assumptions is important. Piping systems typically exhibit complex three-dimensional shapes, and the arrangement and stiffness of the piping support structures significantly affect the response characteristics of the entire piping system. Therefore, developing a realistic response analysis method for piping systems, including support structures is necessary. In this study, a method is proposed for modeling the elastoplastic hysteresis characteristics of piping support structures to establish a seismic response analysis method for piping systems, including support structures. First, the authors proposed an elastoplastic spring model that can express the elastoplastic hysteresis characteristics of a piping support structure. Subsequently, using this model, the authors perform a simulation analysis for the loading test of a piping support structure. The analysis and test results correlated well, confirming the effectiveness of the proposal of the model.
渡壁 智祥; 高橋 英樹*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(5), p.051502_1 - 051502_11, 2023/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)設計条件を越える過酷な地震荷重を想定した場合の最終的な振る舞いを把握すること、また、現行設計が終局強度と比べてどの程度の余裕を見込んでいるかを明確にすることは耐震健全性を確実なものにするという観点から重要である。本研究では、高速炉用薄肉ティ配管を対象にした破壊試験や解析評価を通じて、破損様式、動的応答挙動、動的非弾性解析による破損予測の精度、既存設計規格に含まれる安全裕度について検討した。
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(2), p.021501_1 - 021501_9, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:13.27(Engineering, Mechanical)The fracture toughness in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is located under the weld overlay cladding on the inner surface of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV), was evaluated by considering the inhomogeneous microstructures of the HAZ. In this regard, 0.4T-C(T) specimens and Mini-C(T) specimens were manufactured to clarify the effect of the HAZ on fracture toughness. First, the fracture toughness was evaluated using 0.4T-C(T) specimens targeted on microstructural distribution due to the cladding bead location. The reference temperature (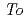 ) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12
) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12 C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The
C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The 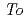 value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the
value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the 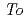 values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40
values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40 C
C 60
60 C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
東 喜三郎*; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(6), p.061303_1 - 061303_13, 2022/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.34(Engineering, Mechanical)In this paper, we investigate the influence of the stress intensity factor at the maximum point for a circumferential crack and an axial crack with a large aspect ratio in a cylinder. First, we obtained the influence coefficients Gi for the stress intensity factor at the surface point, the deepest point, and the maximum point by finite element analysis, and developed a series of closed-form Gi solutions. Then, we proposed methods for evaluating the stress intensity factor for a crack with a large aspect ratio in a manner that characterizes the influence of the solutions at the maximum point.
長谷川 邦夫; Strnadel, B.*; Li, Y.; Lacroix, V.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(6), p.061202_1 - 061202_6, 2022/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.22(Engineering, Mechanical)配管の肉厚が薄いとき、未貫通亀裂は貫通亀裂になりやすく、冷却材の漏洩の可能性が高まる。ASME Code Section XIでは、薄肉配管に対して貫通亀裂の最終許容角度が定められている。この最終許容角度は、もし未貫通亀裂が貫通亀裂になったとき、塑性崩壊しないように設けられている。この安定性を保つために貫通亀裂の塑性崩壊応力が許容応力と組み合わされている。しかしながら、薄肉配管の貫通亀裂の最終許容角度が求められない。この論文は貫通亀裂の塑性崩壊応力と未貫通亀裂の許容応力を比較する。これらの応力の比較により、貫通亀裂の最終許容応力式を導いた。この角度を、厳密解として表すとともに、オプションとして種々な運転状態における近似解で表すことができた。
長谷川 邦夫; Li, Y.; Strnadel, B.*; Udyawar, A.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(5), p.051305_1 - 051305_6, 2022/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.34(Engineering, Mechanical)周方向未貫通亀裂を有し曲げ応力を受ける配管の塑性崩壊応力はASME Code Section XIに用意された極限荷重評価法で推定される。極限荷重評価法を使って許容亀裂深さが決定され、ASME Code Section XIでは各運転状態における許容欠陥深さが表で用意されている。一方、未貫通亀裂が貫通するときの応力は局所近似極限荷重評価法で推定される。これらの評価法を用いて未貫通亀裂を有する配管の許容欠陥深さを検討した。これらの2つの評価法から各運転状態における許容欠陥深さを比較したところ、局所近似極限荷重評価法から得られる許容欠陥深さは、ほとんどの場合極限荷重評価法からえられる許容欠陥深さより小さいことが明らかになった。ASME Code Section XIで与えられる許容欠陥深さは亀裂の貫通に対して非安全であることが分かった。
真野 晃宏; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011506_1 - 011506_9, 2022/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.22(Engineering, Mechanical)これまで、沸騰水型原子炉(BWR)配管系のニッケル合金異材溶接継手において応力腐食割れ(SCC)による亀裂の存在が報告されており、そのような溶接継手に対する構造健全性評価が重要となっている。現在、影響因子の固有の不確実さを確率分布として考慮することで亀裂を有する機器の破損確率を定量的に評価できる確率論的破壊力学(PFM)評価手法が、より合理的な構造健全性評価手法として注目されており、原子力機構では、溶接継手を含む原子炉配管系を対象としたPFM解析コードPASCAL-SPの開発を進めている。本研究では、PASCAL-SPにBWRのニッケル合金異材溶接継手を対象とした解析機能を新たに導入した。また、改良したPASCAL-SPを用いて、異材溶接継手を対象に、漏えいの検知及び供用期間中検査が破損確率に及ぼす影響に関する感度解析を実施した。解析結果より、改良したPASCAL-SPは、異材溶接継手の破損確率を求め、供用期間中検査等の効果を定量的に評価できることから、構造健全性評価に有用であると結論付けた。
下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011304_1 - 011304_7, 2022/02
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.96(Engineering, Mechanical)JEAC4206-2016における原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価では、材料の破壊靭性が、想定欠陥であるクラッド下半楕円亀裂の先端における応力拡大係数よりも高いことが求められている。しかしながら、破壊靭性試験片と想定亀裂の亀裂深さやクラッドの有無といった違いにより、塑性拘束状態や破壊靭性評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、クラッド下亀裂が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響を調べるため、3点曲げ破壊靭性試験及び有限要素解析を実施した。その結果、クラッド下亀裂の塑性拘束が表面亀裂のそれに比べて弱いことを解析によって示した。さらに、クラッド下亀裂の弱い塑性拘束の影響により、クラッド下亀裂の破壊靭性が表面亀裂よりも見かけ上高くなることを実験及びローカルアプローチによって明らかにした。
長谷川 邦夫*; Dvo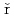
 k, D.*; Mare
k, D.*; Mare , V.*; Strnadel, B.*; Li, Y.
, V.*; Strnadel, B.*; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011303_1 - 011303_6, 2022/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:40.91(Engineering, Mechanical)周方向表面亀裂を有する配管が引張荷重を受ける場合の塑性崩壊応力は正味断面応力概念に基づく極限荷重評価法により見積もることができる。LLC-1と表示する極限荷重は軸方向の荷重のつり合いから求められ、LLC-2と表示する極限荷重は曲げモーメントと軸方向の荷重のつり合いから求められており、米国機械学会規格ASME Codeに採用されている。本論文では、この2種類の極限荷重による塑性崩壊応力を既存の試験結果と比較し、浅い亀裂の場合はLLC-1タイプの塑性崩壊応力は試験結果と比較的近く、深い亀裂の場合はLLC-2タイプの塑性崩壊応力は試験結果と比較的よく一致することを確認した。その結果、現行ASME Codeの極限荷重に基づく許容亀裂深さが保守的であることを確認した。
熊谷 知久*; 三浦 靖史*; 三浦 直樹*; Marie, S.*; Almahdi, R.*; 真野 晃宏; Li, Y.; 勝山 仁哉; 和田 義孝*; Hwang, J.-H.*; et al.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011509_1 - 011509_18, 2022/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.34(Engineering, Mechanical)延性材料の破壊挙動を予測するため、いくつかの延性破壊シミュレーション手法が提案されている。ただし、これらの手法には実機器への適用性に関する懸念がある。本研究では、パラメータの決定を含めたシミュレーション手法の予測能力を確認するため、実機器を想定した破壊試験に関する2つの問題を設定し、ベンチマーク解析を実施した。1つ目の問題は、周方向の表面亀裂及び貫通亀裂を有する配管に対する単調曲げ荷重負荷試験、2つ目の問題は、周方向貫通亀裂を有する配管に対する繰り返し曲げ荷重負荷試験である。ベンチマークの参加機関は、独自に選択した手法によって延性亀裂進展挙動を予測した。用いられた手法は、ボイド率基準を有するGurson-Tvergaard-Needleman(GTN)モデルに基づく有限要素法(FEM)、応力三軸度により修正される破壊ひずみ基準また破壊エネルギー基準に基づくFEM、Jまたは J基準に基づく拡張FEM及び弾塑性粒子法等である。単調曲げ荷重負荷試験に関しては、すべての手法によるシミュレーションの結果が配管の変形と亀裂進展の挙動を精度よく再現し、シミュレーション手法の実機器への適用性が確認された。一方、繰り返し曲げ荷重負荷試験におけるこれらの挙動については、ほとんどの手法で再現できなかった。今後材料の繰り返し硬化特性等を考慮したパラメータの決定手法についてさらなる検討が必要であることを確認した。
J基準に基づく拡張FEM及び弾塑性粒子法等である。単調曲げ荷重負荷試験に関しては、すべての手法によるシミュレーションの結果が配管の変形と亀裂進展の挙動を精度よく再現し、シミュレーション手法の実機器への適用性が確認された。一方、繰り返し曲げ荷重負荷試験におけるこれらの挙動については、ほとんどの手法で再現できなかった。今後材料の繰り返し硬化特性等を考慮したパラメータの決定手法についてさらなる検討が必要であることを確認した。
安藤 勝訓; 廣瀬 悠一*; 高野 雅仁*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(6), p.061505_1 - 061505_9, 2021/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:12.30(Engineering, Mechanical)本研究では、改良9Cr-1Mo鋼製の多孔板試験体の疲労及びクリープ疲労試験の行い、その結果を用いて種々の構造物の疲労およびクリープ疲労寿命の評価方法を比較・検証を行った。具体的には、多孔板試験体の試験では550 Cにおいて機械的繰り返し荷重を加え、孔の表面における亀裂の発生と伝播を観察するとともに、一連の有限要素解析に基づいて、種々の破損寿命評価方法により破損繰返し数を予測して、試験結果と予測結果の比較検証を行た。
Cにおいて機械的繰り返し荷重を加え、孔の表面における亀裂の発生と伝播を観察するとともに、一連の有限要素解析に基づいて、種々の破損寿命評価方法により破損繰返し数を予測して、試験結果と予測結果の比較検証を行た。
高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(5), p.051502_1 - 051502_8, 2021/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:25.22(Engineering, Mechanical)本研究では、照射脆化予測に取込むべき化学成分を特定し、原子炉圧力容器鋼の照射脆化予測の不確実性を評価した。日本の加圧水型原子炉の監視試験データに対してノンパラメトリックベイズ(BNP)法を用いた統計分析を行った。BNP法は入力データの複雑さと不確かさを考慮可能な機械学習手法である。脆化への影響が大きい入力変数の組合せを評価可能な統計的指標を導入し、中性子照射量, Cu, Ni, Si含有量の4つの変数の組合せが脆化予測に最も効果的であることを明らかにした。また、化学成分では脆化量に対してCu含有量の影響が最も大きく、Ni, Siの順番で影響が大きいことを示した。関連温度移行量( RT
RT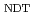 )をBNP法を用いて算出した結果、計算値と実測値の残差の標準偏差は8.4
)をBNP法を用いて算出した結果、計算値と実測値の残差の標準偏差は8.4 Cであり、現行の国内脆化予測法(JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補))と同等かそれ以上の予測性有していることを確認した。BNP法によって計算された
Cであり、現行の国内脆化予測法(JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補))と同等かそれ以上の予測性有していることを確認した。BNP法によって計算された RT
RT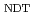 の事後分布の95%確信区間(入力データの不確実性を考慮した場合にデータが存在し得る範囲)は国内脆化予測法のマージンと同等かそれよりも小さく、JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補)において、適切なマージンが設定されていることを定量的に示した。
の事後分布の95%確信区間(入力データの不確実性を考慮した場合にデータが存在し得る範囲)は国内脆化予測法のマージンと同等かそれよりも小さく、JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補)において、適切なマージンが設定されていることを定量的に示した。
Li, Y.; 勝又 源七郎*; 眞崎 浩一; 林 翔太郎*; 板橋 遊*; 永井 政貴*; 鈴木 雅秀*; 関東 康祐*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(4), p.041501_1 - 041501_8, 2021/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:18.71(Engineering, Mechanical)It has been recognized that probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is a promising methodology in structural integrity assessments of pressure boundary components of nuclear power plants, because it can rationally represent the influencing parameters in their inherent probabilistic distributions without over conservativeness. A PFM analysis code PASCAL has been developed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to evaluate the through-wall cracking frequencies of domestic reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) transients. In this study, as a part of the verification activities, a working group was established with seven organizations from industry, universities and institutes. Through one year activities, the applicability of PASCAL for structural integrity assessments of domestic RPVs was confirmed with great confidence. This paper presents the details of the verification activities of the working group.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; 眞崎 浩一; 渡辺 正*; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(3), p.031704_1 - 031704_8, 2021/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)Structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is important for the safe operation of nuclear power plant. For an RPV in a pressurized water reactor (PWR), pressurized thermal shock (PTS) resulted from rapid coolant water injection due to a loss-of-coolant accident is an issue of particular concern. The coolant water temperature in the emergency core cooling system (ECCS) can influence the integrity of RPV subjected to PTS events; thus, this paper is focused on investigating the effect of coolant water temperature of ECCS on failure probability of an RPV. First, thermal-hydraulic (TH) analyses were conducted for a Japanese PWR model plant by using RELAP5, and different coolant water temperatures in ECCS were considered to investigate the effect of coolant water temperature on TH behaviors during a PTS event. Using the TH analysis results, probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analyses were performed for the RPV of the Japanese model plant. Based on the PFM analysis results, the effect of coolant water temperature on failure probability of the RPV was quantified.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 吉村 忍*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(2), p.021505_1 - 021505_8, 2021/04
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:6.02(Engineering, Mechanical)Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is considered to be a promising methodology in structural integrity assessments of pressure-boundary components in nuclear power plants since it can rationally represent the inherent probabilistic distributions for influence parameters without over-conservativeness. To strengthen the applicability of PFM methodology in Japan, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL4 which enables the failure frequency evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and thermal transients. PASCAL4 is expected to make a significant contribution to the probabilistic integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs. In this study, PFM analysis for a Japanese model RPV in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) was conducted using PASCAL4, and the effects of nondestructive examination (NDE) and neutron flux reduction on failure frequencies of the RPV were quantitatively evaluated. From the analysis results, it is concluded that PASCAL4 is useful for probabilistic integrity assessments of embrittled RPVs and can enhance the applicability of PFM methodology.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(5), p.051501_1 - 051501_10, 2020/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:16.76(Engineering, Mechanical)Structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) is essential for the safe operation of nuclear power plants. For RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs), the assessment should be performed by considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. To assess the structural integrity of an RPV, a traditional method is usually employed by comparing fracture toughness of the RPV material with the stress intensity factor ( ) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,
) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,  of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on
of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on  calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for
calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for  calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
山口 義仁; 長谷川 邦夫; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(4), p.041507_1 - 041507_6, 2020/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:5.70(Engineering, Mechanical)疲労亀裂進展中における亀裂の開閉口は、亀裂進展速度の評価において重要な現象である。ASME Code Section XIのAppendix A-4300は、負の応力比におけるフェライト鋼の疲労亀裂進展速度を算出する式について、負荷の大きさに応じて二つ提示している。一つは、負荷が小さい場合に、亀裂の閉口を考慮する式である。もう一つは、負荷が大きい場合に、亀裂の閉口を考慮しない式である。本研究では、フェライト鋼に対して、負荷の大きさを徐々に変えながら疲労亀裂進展試験を実施し、負荷の大きさが亀裂閉口に及ぼす影響を調査した。その結果、Appendix A-4300における疲労亀裂進展速度算出式を切り替える負荷の大きさと比較して、より小さい負荷で亀裂が閉口することを明らかにした。