Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
佐藤 優樹
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf046_1 - ncaf046_11, 2025/05
被引用回数:0Radioactive substances released during the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident were deposited on various equipment and building structures within the plant site. To minimize worker exposure and plan effective remediation strategies, accurately identifying the locations of these deposits is crucial. In response to this need, the current study presents a method to accurately determine the locations of multiple radiation sources in three dimensions and quantify their radioactivity levels. In particular, the method involves the application of an inverse estimation technique to data captured using a Compton camera. Here, the target region is first divided into multiple regions of interest. Image data are then acquired by placing a radiation source of known radioactivity in each region of interest. The resulting images are subsequently multiplied by each coefficient and summed to reproduce the image data of multiple unknown radiation sources. The radioactivity of each unknown radiation source is then derived based on the coefficients determined through inverse estimation.
辻 智也; 吉富 寛; 佐藤 文信*; 谷村 嘉彦
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf060_1 - ncaf060_15, 2025/00
An irradiation environment for dosemeters calibration in the fluorescence X-ray field was set up at the Facility of Radiation Standards of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) by re-establishing the fluorescence X-ray calibration field that was established in 1989. The reference air kerma rates were determined using reference ionization chambers (ICs) calibrated using X-ray narrow-spectrum series calibration field of the national metrology standard (NMS) in Japan. Since no X-ray calibration field using fluorescence X-rays is available in Japan, the measurements were corrected by factors that accounts for differences in the fluorescence X-ray calibration field energy and the X-ray narrow-spectrum series calibration field energy. The conversion coefficients and correction factors for air densities for the fluorescence X-ray calibration field, including those unavailable in the ISO 4037 standard series, were derived from the measured X-ray fluence rate spectra.
古渡 意彦*; 中上 晃一*; 土方 保和*; 山下 一太*; 平井 悠太*; 松崎 賢*; 盛武 敬*; 辻 智也; Zutz, H.*; Ketelhut, S.*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf061_1 - ncaf061_9, 2025/00
It is crucial to monitor healthcare workers' radiation exposure, especially given the increasing reliance on X-ray imaging technologies. In response to new evidence that the threshold for lens opacity is lower than previously thought, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has revised the annual dose limit for exposure to the lens of the eye. After the revision of the annual eye lens dose limit, the new survey on the dosemeter wearing rate was conducted in Japan. The result showed that despite the presence of monitoring protocols, the dosemeter wearing rate among healthcare workers was still low. Compliance often lacked robust verification measures, especially in smaller medical facilities. Active personal dosemeters (APDs) are commonly used in Japan, although studies suggest that they may underestimate exposure in certain settings, such as pulsed X-ray fields. Passive dosemeters, on the other hand, serve as legal dosemeters, offering a more accurate assessment of radiation exposure. This article addresses issues related to the monitoring of healthcare workers using APDs and clarifies concerns regarding the use of APDs by orthopedic surgeons during procedures involving high-dose X-ray exposure. A series of performance tests suggested that the APDs worn by orthopedic surgeons, who are often exposed to higher dose rates near patients, may underestimate radiation levels during procedures. This underestimation occurs because the surgeons are exposed to pulsed, scattered X-ray fields with energies ranging from 20 and 100 keV. The results also suggest monitoring techniques should be improved to ensure the safety of healthcare workers.
鯨岡 郁雄; 野口 芳宏*; 嶋田 和真; 廣内 淳; 高原 省五
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1561 - 1567, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)国産の放射線誘発がんリスクの推定モデルを実装した計算コードを開発するために、公開されている他国の既存の計算コード(RadRAT (U.S.NIH)、Blue Book Model (U.S.EPA)、Korean-Specific Model(FNC Technology Co, Ltd))と、これらのコードの基本となるBEIR VII(米国科学アカデミーの電離放射線の放射線健康リスクに関する報告書)を調査し、3つのコードとBEIR VIIモデルの計算結果を比較した。各コードとBEIR VIIで計算した全固形がんの生涯寄与リスクのうち、特にKorean-Specific Modelで計算した結果については、他と有意な差が認められた。この原因の一つはいくつかの組織や臓器のリスク移転に関するパラメータがコード間で異なっていることであり、このことは日本版コードの開発において慎重に検討されるべき課題の一つである。
古渡 意彦*; 吉富 寛; 谷 幸太郎*; 谷村 嘉彦; 栗原 治*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1574 - 1579, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)This study attempted the reconstruction of organ doses of victims who are highly exposed to gamma rays in non-homogeneous exposure accident by a sealed 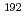 Ir source in Gilan, Iran. According to the accident report by International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), a victim was highly exposed on his right chest and the dose estimation by means of biodosimtry and clinical observation were carried out. However, dose reconstruction by means of physical dosimetry was not completely made. In this study, a series of Monte Carlo (MC) calculations employing the PHITS 3.24 incorporated with the Adult male Mesh-type Reference Computational Phantom was performed to estimate organ doses with reference to an actual radiation accident involved in the
Ir source in Gilan, Iran. According to the accident report by International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), a victim was highly exposed on his right chest and the dose estimation by means of biodosimtry and clinical observation were carried out. However, dose reconstruction by means of physical dosimetry was not completely made. In this study, a series of Monte Carlo (MC) calculations employing the PHITS 3.24 incorporated with the Adult male Mesh-type Reference Computational Phantom was performed to estimate organ doses with reference to an actual radiation accident involved in the 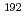 Ir sealed source, and to investigate issues on reconstruction of organ doses of victims who are highly exposed to radiation under non-homogeneous exposure accident. Calculated organ doses for the lungs, the red born marrow, and the small intestine by MC calculation were compared with experimental values taken from the literature and were within 23% in terms of mGy h
Ir sealed source, and to investigate issues on reconstruction of organ doses of victims who are highly exposed to radiation under non-homogeneous exposure accident. Calculated organ doses for the lungs, the red born marrow, and the small intestine by MC calculation were compared with experimental values taken from the literature and were within 23% in terms of mGy h /Ci for the Gilan case. The averaged whole body dose was estimated to be 0.31 Gy, which are less than one-tenth than that estimated by biodosimetry (3.1-4.1 Gy). In the IAEA Gilan report, the average whole body dose was assumed to be 2 Gy for rough estimation of physical dose, having a large discrepancy with those estimated by the MC calculation.
/Ci for the Gilan case. The averaged whole body dose was estimated to be 0.31 Gy, which are less than one-tenth than that estimated by biodosimetry (3.1-4.1 Gy). In the IAEA Gilan report, the average whole body dose was assumed to be 2 Gy for rough estimation of physical dose, having a large discrepancy with those estimated by the MC calculation.
清藤 一*; 横塚 恵莉*; 岡 壽崇; 北辻 章浩; 長澤 尚胤*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1656 - 1659, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)生物由来原料から作製した炭酸アパタイトへの Coガンマ線照射を行い、アラニンやフリッケ線量計に替わる線量計として利用可能か調べた。照射によって生成する炭酸ラジカルの収量は照射後に20%減衰したが、7日でほぼ一定になることがわかった。炭酸ラジカル収量と吸収線量の関係は、10Gyから1000Gyの範囲で線形関係にあり、炭酸アパタイトは化学線量計として利用可能であることが示された。
Coガンマ線照射を行い、アラニンやフリッケ線量計に替わる線量計として利用可能か調べた。照射によって生成する炭酸ラジカルの収量は照射後に20%減衰したが、7日でほぼ一定になることがわかった。炭酸ラジカル収量と吸収線量の関係は、10Gyから1000Gyの範囲で線形関係にあり、炭酸アパタイトは化学線量計として利用可能であることが示された。
 -ray visualization survey meter in high gamma and neutron background environment
-ray visualization survey meter in high gamma and neutron background environment坪田 陽一; 小林 賢二; 石井 達也; 平戸 未彩紀; 塩谷 聡; 中川 貴博
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1676 - 1680, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPS、1F)の廃止措置では、作業員が建屋内の構造物の撤去、放射能汚染の監視、建屋内の除染を行っている。作業員のスーツ表面の汚染を測定するため、高 ・
・ 線バックグラウンド環境下での
線バックグラウンド環境下での 核種の表面放射能汚染を測定・可視化できる手持ち式サーベイメータを開発した。
核種の表面放射能汚染を測定・可視化できる手持ち式サーベイメータを開発した。 核種を選択的に測定するために、薄膜ZnS:Agシンチレータ、多チャンネル光電子増倍管(MA-PMT)、MA-PMTの各チャンネルの個別増幅回路と計数回路からなる
核種を選択的に測定するために、薄膜ZnS:Agシンチレータ、多チャンネル光電子増倍管(MA-PMT)、MA-PMTの各チャンネルの個別増幅回路と計数回路からなる 線用の手持ち式サーベイメータを設計・試作した。
線用の手持ち式サーベイメータを設計・試作した。 線計数性能試験の結果、試作機は2.1
線計数性能試験の結果、試作機は2.1  10
10 cpmでも計数飽和せず、それを超える
cpmでも計数飽和せず、それを超える 線の計数が可能であることが示された。また、
線の計数が可能であることが示された。また、 線応答試験では、高強度の線源(1Sv/h以上と推定)に近接しても
線応答試験では、高強度の線源(1Sv/h以上と推定)に近接しても 線応答はなかった。今後は、軽量化・小型化を図るとともに、汚染環境下での実機検証を行い、可用性を高めていく計画である。
線応答はなかった。今後は、軽量化・小型化を図るとともに、汚染環境下での実機検証を行い、可用性を高めていく計画である。
北村 剛将; 岡 壽崇; 清藤 一*; 横塚 恵莉*; 長澤 尚胤*; 北辻 章浩
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1660 - 1665, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)歯の主成分であるヒドロキシアパタイトが、アラニン線量計やフリッケ線量計などでは測定が不可能な1Gy以下の低線量を測定可能な固体線量計として利用可能かを検討した。市販のヒドロキシアパタイトへ Coガンマ線を75Gyまで照射し、生成した炭酸ラジカルをESR分光計で測定した。炭酸ラジカル強度と吸収線量の関係(線量応答曲線)を調べたところ、未照射から75Gyまでの範囲で、両者はよい線形性を示した(
Coガンマ線を75Gyまで照射し、生成した炭酸ラジカルをESR分光計で測定した。炭酸ラジカル強度と吸収線量の関係(線量応答曲線)を調べたところ、未照射から75Gyまでの範囲で、両者はよい線形性を示した(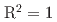 )。線量応答曲線を利用して検出下限値を推定したところ99.7mGyと見積もられ、本試料は1Gy以下の線量も計測可能であることがわかった。照射から8ヶ月経過後にも同様の測定を行い、炭酸ラジカル強度が変化しなかったことから、ラジカルの長期安定にも優れていることがわかった。これらの結果から、当該試料は新規線量計の候補材料として利用可能である。
)。線量応答曲線を利用して検出下限値を推定したところ99.7mGyと見積もられ、本試料は1Gy以下の線量も計測可能であることがわかった。照射から8ヶ月経過後にも同様の測定を行い、炭酸ラジカル強度が変化しなかったことから、ラジカルの長期安定にも優れていることがわかった。これらの結果から、当該試料は新規線量計の候補材料として利用可能である。
 Am gamma calibration field based on international standards and its conversion coefficients
Am gamma calibration field based on international standards and its conversion coefficients辻 智也; 吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦*; 谷村 嘉彦
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(15), p.1416 - 1424, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)A  Am gamma (
Am gamma ( )-ray calibration field that meets the requirements for a
)-ray calibration field that meets the requirements for a  -ray reference field as specified in the ISO 4037 standard series was established in the Facility of Radiation Standards of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The reference air kerma rates were measured using a reference ionization chamber (IC) calibrated by the N-80 quality X-ray calibration field of the national metrology standard in Japan and with a correction to account for differences in photon energy due to the calibration field. Conversion coefficients for the
-ray reference field as specified in the ISO 4037 standard series was established in the Facility of Radiation Standards of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The reference air kerma rates were measured using a reference ionization chamber (IC) calibrated by the N-80 quality X-ray calibration field of the national metrology standard in Japan and with a correction to account for differences in photon energy due to the calibration field. Conversion coefficients for the  Am
Am  -ray calibration field, including those not listed in the ISO 4037 standard series, were calculated based on the measured
-ray calibration field, including those not listed in the ISO 4037 standard series, were calculated based on the measured  -ray fluence rate spectra.
-ray fluence rate spectra.
遠藤 章
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(13), p.1266 - 1273, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)本研究では、外部中性子照射における周辺線量 、周辺線量当量
、周辺線量当量 及び実効線量の関係を、様々な作業場の163種類の中性子スペクトルを用いて分析した。その結果、実効線量の評価に対して、
及び実効線量の関係を、様々な作業場の163種類の中性子スペクトルを用いて分析した。その結果、実効線量の評価に対して、 は中性子のエネルギー分布によっては著しく過大あるいは過小評価する一方、
は中性子のエネルギー分布によっては著しく過大あるいは過小評価する一方、 は過大評価の場合でも適度な範囲内で合理的な推定値を与えることが明らかになった。本研究は、特に高エネルギー中性子が存在する環境における線量評価に対して、実用量の要件から見た
は過大評価の場合でも適度な範囲内で合理的な推定値を与えることが明らかになった。本研究は、特に高エネルギー中性子が存在する環境における線量評価に対して、実用量の要件から見た の限界と
の限界と の優位性を示した。
の優位性を示した。
渡部 浩司*; 佐藤 達彦; Yu, K. N.*; Zivkovic, M.*; Krstic, D.*; Nikezic, D.*; Kim, K. M.*; 山谷 泰賀*; 河地 有木*; 田中 浩基*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(2), p.130 - 142, 2024/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:46.61(Environmental Sciences)DynamicMCは、人体ファントムが単色線源に照射されたときの3次元線量分布を簡単に計算可能なGUIソフトウェアである。従来は、米国産放射線挙動解析コードMCNPと接続して使うよう設計されていた。本研究では、DynamicMCをPHITSと接続して使うように改良し、いくつかの新機能を付加した。具体的な改良点は以下の通りである。(1)単色のみならず放射性同位元素の崩壊により生じる様々なエネルギースペクトルを持つ線源に対応可能とした、(2)臓器吸収線量を計算可能とした、(3)複数の条件に対する平均線量を計算可能とした、(4)遮蔽物の影響を考慮可能とした。本改良により、DynamicMCは放射線防護の研究や教育など様々な目的で利用可能となった。
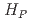 (0.07) for extremity dose monitoring of medical personnel
(0.07) for extremity dose monitoring of medical personnel古渡 意彦*; 吉富 寛; 永元 啓介*; 中上 晃一*; 盛武 敬*; 欅田 尚樹*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(15-16), p.1807 - 1812, 2023/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)An additional individual monitoring using ring badge must be made, when inhomogenous exposure around radiation workers' extremity were critical for radiation workers. The RPLD, the GD-302M and the GD-352M have a dimension of 13.0 mm in length and 2.8 mm in diameter for outer casing and will also be a promising candidate for individual monitoring of the extremities of medical personnel. We investigated the applicability of this commercially available RPLDs to extremity dose monitoring by performing a characterization of the dosemeters by experiments and Monte Carlo (MC) calculations. The results shows that the energy response of GD-352M fully meets the IEC requirement between 20 keV and 200 keV. We also found that no significant angular dependence of responses for each model was observed and orientation of irradiation hardly affected the response. In conclusion, we demonstrated the applicability of a small RPLD to the extremity monitoring in terms of 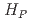 (0.07) for medical personnel.
(0.07) for medical personnel.
光安 優典*; 岡 壽崇; 高橋 温*; 木野 康志*; 奥津 賢一*; 関根 勉*; 山下 琢磨*; 清水 良央*; 千葉 美麗*; 鈴木 敏彦*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1620 - 1625, 2023/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:25.62(Environmental Sciences)ESRを用いた線量計測を行う際は、ESRスペクトルを複数成分でカーブフィットし、炭酸ラジカル強度だけを抽出する必要がある。複数成分を同時にフィッティングする従来の方法では、うまく解析が収束しない例が見られ、その場合、当該個体の線量推定が不可能になってしまう。そこで、我々は複数成分のうち、主要な炭酸ラジカルと有機物ラジカルを最初にフィットし、そのあとに残りの成分をフィットする新しいアルゴリズムを開発して、より多くの個体のESRスペクトルを解析可能にすることを検討している。新しいアルゴリズムで福島県で捕獲した野生ニホンザルの歯を解析したところ、従来の方法では解析できなかった個体の炭酸ラジカル強度も抽出でき、線量推定可能になった。
豊田 新*; 井上 一彦*; 山口 一郎*; 星 正治*; 廣田 誠子*; 岡 壽崇; 島崎 達也*; 水野 秀之*; 谷 篤史*; 保田 浩志*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1557 - 1564, 2023/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:25.62(Environmental Sciences)EPR(electron paramagnetic resonance, electron spin resonance (ESR)ともいう)線量計測法の汎用性評価のため、相互比較試験を行った。線量を推定するために必要な、数十から数百mGyの線量を与えた標準試料は、各参加機関が作成した。同様にして作成した試料に未知線量を与えたものとあわせた試料セットを測定した後、他の参加機関に送り、また、他の参加機関が作成した別の試料セットを測定するということを繰り返した。既知線量の試料で作成した検量線の傾きには若干の差が見られるが、未知線量試料の測定値の差は系統的であり、測定値ではなく試料に起因するところが大きいことが示唆された。詳細な解析結果も報告する予定である。
 particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector森下 祐樹; 佐川 直貴; 高田 千恵; 百瀬 琢麿; 高崎 浩司
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(13), p.1376 - 1383, 2023/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:46.61(Environmental Sciences)内部被ばく線量を評価するためには、二酸化プルトニウム(PuO )粒子の直径(放射能中央空気力学直径)を評価することが非常に重要である。本研究では、
)粒子の直径(放射能中央空気力学直径)を評価することが非常に重要である。本研究では、 線イメージング検出器を用いてPuO
線イメージング検出器を用いてPuO 粒子径を評価する手法を開発した。モンテカルロシミュレーションにより粒径の異なるPuO
粒子径を評価する手法を開発した。モンテカルロシミュレーションにより粒径の異なるPuO 粒子をモデル化し、粒径ごとのエネルギースペクトルの形状の変化を評価した。
粒子をモデル化し、粒径ごとのエネルギースペクトルの形状の変化を評価した。 PuO
PuO の場合とPuO
の場合とPuO (Puの同位体組成を含む)の場合をモデル化した。得られたパラメータから重回帰分析を行い、PuO
(Puの同位体組成を含む)の場合をモデル化した。得られたパラメータから重回帰分析を行い、PuO 粒子径を求めた。シミュレートされた直径と回帰モデルで得られた直径はよく一致した。アルファ粒子イメージング検出器を使用する利点は、個々の粒子のアルファエネルギースペクトルを測定できることであり、これにより粒子径分布の正確な測定が可能になる。
粒子径を求めた。シミュレートされた直径と回帰モデルで得られた直径はよく一致した。アルファ粒子イメージング検出器を使用する利点は、個々の粒子のアルファエネルギースペクトルを測定できることであり、これにより粒子径分布の正確な測定が可能になる。
古渡 意彦*; 窪田 卓見*; 吉富 寛; 欅田 尚樹*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(11), p.1239 - 1247, 2023/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)We performed an experimental investigation on occupational exposure of the eye lens and the extremity of radiation workers engaged in handling of highly activated materials in a small research accelerator facility. Using a simplified physical phantom to simulate the relevant inhomogeneous radiation exposure situations, the personal dose equivalents obtained at the eye lens and the extremities of radiation workers handling heavily radioactive converters were measured together with the dose measured by personal dosemeters worn on their trunk. Results of a mockup experiments and the Monte Carlo calculations suggest that the quantitative estimation of the eye lens doses can be estimated from the trunk dose, while the extremity doses vary considerably from the dose readings from the trunk, depending on the use of simple point-source or volume source geometry.
佐藤 優樹; 峯本 浩二郎*; 根本 誠*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(8-9), p.1021 - 1028, 2023/06
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:62.75(Environmental Sciences)Identifying and visualizing the radiation source location are important in reducing the exposure dose of workers at the decommissioning site of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and in improving the radiation protection functions in other sites where radiation sources are handled. In this paper, we developed the COMpton camera for Radiation Imaging System (COMRIS) to identify and visualize the radiation source location in 3D using output data from a Compton camera and a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) device as input data. Here, we presented COMRIS to visualize a  Cs-radiation source in a dark environment using data acquired by a commercial Compton camera and a LiDAR-based SLAM device mounted on a robot as input data. The radiation source image obtained using the Compton camera was drawn on the 3D work environment model acquired by the SLAM device, and the radiation source location was visible in 3D.
Cs-radiation source in a dark environment using data acquired by a commercial Compton camera and a LiDAR-based SLAM device mounted on a robot as input data. The radiation source image obtained using the Compton camera was drawn on the 3D work environment model acquired by the SLAM device, and the radiation source location was visible in 3D.
古渡 意彦*; 永元 啓介*; 中上 晃一*; 吉富 寛; 盛武 敬*; 欅田 尚樹*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(17), p.1303 - 1312, 2022/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:29.47(Environmental Sciences)We demonstrate a practical calibration method and its applicability for a commercially available radiophotoluminescence dosemeter (RPLD, GD-352M) to eye lens dose monitoring, by performing the calibration in accord with the ISO recommendations. The calibration was then verified through a series of experiments. For verification of the derived calibration factor (1.21  0.04,
0.04,  = 1) of the RPLD, we performed standard irradiations in the X-ray reference fields and the mockup measurements in the actual radiation fields in a hospital. The commercially available dosemeters, DOSIRIS was also put on the ISO cylinder phantom and the RANDO phantom together with the GD-352M in the verification experiments. The personal dose equivalents
= 1) of the RPLD, we performed standard irradiations in the X-ray reference fields and the mockup measurements in the actual radiation fields in a hospital. The commercially available dosemeters, DOSIRIS was also put on the ISO cylinder phantom and the RANDO phantom together with the GD-352M in the verification experiments. The personal dose equivalents 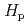 (3) obtained from the GD-352M and those obtained from the DOSIRIS were in good agreement with each other. Our results demonstrate the proper calibration of a commercially available RPLD that is applicable to the additional monitoring of the lens of the eyes for medical personnel.
(3) obtained from the GD-352M and those obtained from the DOSIRIS were in good agreement with each other. Our results demonstrate the proper calibration of a commercially available RPLD that is applicable to the additional monitoring of the lens of the eyes for medical personnel.
津田 修一; 斎藤 公明
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(17), p.1283 - 1291, 2022/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)環境中の線量率測定では、土壌または空気中に存在する放射性同位元素から放出されるガンマ線を検出するため、方向特性のよい球形または円筒形の測定器が通常使用される。われわれは、環境中において種々の測定器を用いた線量率相互比較実験を行い、方向特性に起因した線量率指示値のばらつきの程度を評価するとともに、ある直方体形状のCsI(Tl)結晶を有するシンチレーション検出器の線量率が、円筒形形状の測定器とほぼ同等になるデータに着目した。PHITSコードを用いて、様々な結晶形状のCsI(Tl)シンチレーション検出器のシミュレーションを実施した結果、方向依存性の小さいアスペクト比があることを明らかにした。この結果は、製作コスト面で有利な直方体形状のCsI(Tl)結晶を有するシンチレーション検出器を環境中の線量率測定に活用する可能性を示している。
辰野 宇大*; 脇 嘉理*; 角間 海七渡*; 二瓶 直登*; 和田 敏裕*; 吉村 和也; 中西 貴宏; 大手 信人*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(13-15), p.1052 - 1057, 2022/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:29.47(Environmental Sciences)Cesium-rich microparticles (CsMPs) with high cesium-137 ( Cs) concentrations were released and deposited in surface soil after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Radioactive materials on the soil surface layer enter rivers owing to soil erosion during rainfall. In this study, we investigated CsMPs runoff through the river via soil erosion during rainfall in the Takase River watershed in Namie Town, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. CsMPs were rarely detected in suspended solids (SS) in water samples collected during four rainfalls between February and July 2021. Furthermore, the proportion of
Cs) concentrations were released and deposited in surface soil after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Radioactive materials on the soil surface layer enter rivers owing to soil erosion during rainfall. In this study, we investigated CsMPs runoff through the river via soil erosion during rainfall in the Takase River watershed in Namie Town, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. CsMPs were rarely detected in suspended solids (SS) in water samples collected during four rainfalls between February and July 2021. Furthermore, the proportion of  Cs concentration derived from CsMPs to
Cs concentration derived from CsMPs to  Cs concentration in the form of SS (particulate
Cs concentration in the form of SS (particulate  Cs) in the water was
Cs) in the water was  6% on average, which suggests that
6% on average, which suggests that  Cs runoff in the form of CsMPs from the forest to the Takase River was not large.
Cs runoff in the form of CsMPs from the forest to the Takase River was not large.