Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tomita, Ryohei; Tomita, Jumpei; Suzuki, Daisuke; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/05
A new automated particle measurement (APM) combined with micromanipulation using large geometry secondary ion mass spectrometry instrument was proposed and demonstrated to remove the particle mixing effect, which indicated that the aggregation of uranium particles was detected as a single uranium particle, from APM results. The results showed that the new APM method was more effective than the traditional APM method in removing the particle mixing effect from the APM results and determining the existence of minor uranium isotopes in the samples.
 with
with  = 2.1 K revealed by
= 2.1 K revealed by  Te NMR
Te NMRMatsumura, Hiroki*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 13 of others*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Takuya; Shimojo, Hiroto; Kijima, Jun; Miura, Daiya; Onose, Yoshihiko*; Namba, Koji*; Uchida, Hiroaki*; Sakamoto, Kazuhiko*; Ono, Chika*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-019, 211 Pages, 2025/02
The uranium enrichment facilities at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) were constructed sequentially to develop uranium enrichment technology with centrifugal separation method. The developed technologies were transferred to Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited until 2001. And the original purpose has been achieved. Wastewater Treatment Facility, one of the uranium enrichment facilities, was constructed in 1976 to treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the facilities, and it finished the role in 2008. In accordance with the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities, interior equipment installed in this facility had been dismantled and removed since November 2021 to August 2023. This report summarizes the findings obtained through the work related to the contamination inspection methods cancellation the controlled area of Wastewater Treatment Facility from September 2023 to March 2024.
Owada, Mitsuhiro; Nakanishi, Yoshiki; Murokawa, Toshihiro; Togashi, Kota; Saito, Katsunori; Nonaka, Kazuharu; Sasaki, Yu; Omori, Koji; Chinone, Makoto; Yasu, Hideto; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-013, 221 Pages, 2025/02
The uranium enrichment facilities at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) were constructed sequentially to develop uranium enrichment technology with centrifugal separation method. The developed technologies were transferred to Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited until 2001. And the original purpose has been achieved. Wastewater Treatment Facility, one of the uranium enrichment facilities, was constructed in 1976 to treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the facilities, and it finished the role in 2008. In accordance with the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities, interior equipment installed in this facility had been dismantled and removed since November 2021 to August 2023. This report summarizes the findings obtained through the work related to dismantling and removal of interior equipment for decommissioning of Wastewater Treatment Facility.
 O
O , FeUO
, FeUO , and UO
, and UO -Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acid
-Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acidTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 605, p.155561_1 - 155561_9, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Yomogida, Takumi
Hoshako, 38(1), p.19 - 25, 2025/01
High-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near-edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy has enabled us to discuss the electronic structure of actinide compounds in more detail than with conventional XANES spectroscopy. We are conducting research with the aim of contributing to the prediction of the migration behavior of trace actinide elements in the environment by performing actinide speciation in various environmental samples. In this paper, we introduce the content of the discussion of the electronic state of U from the perspective of basic science, which is important for advancing application of HERFD-XANES spectroscopy to environmental science.
 and Fe-Zr melt
and Fe-Zr meltNakajima, Kunihisa; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(1), p.78 - 85, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)At TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, it is estimated that considerable amounts of cesium still remain in the reactors from the analysis results using the severe accident analysis codes and the reverse analysis from contaminated water. Since cesium is known to form stable compounds with uranium and zirconium, chemisorption experiments with uranium dioxide pellets and iron-zirconium melts for cesium hydroxide vapor were carried out. As the results, formations of cesium uranate, Cs UO
UO , and cesium zirconate, Cs
, and cesium zirconate, Cs ZrO
ZrO , were confirmed, indicating that cesium was chemisorbed on both of the uranium dioxide pellets and the iron-zirconium melts in an Ar-H
, were confirmed, indicating that cesium was chemisorbed on both of the uranium dioxide pellets and the iron-zirconium melts in an Ar-H -H
-H O flow and an Ar-H
O flow and an Ar-H flow, respectively. Therefore, it was considered that cesium released from fuel might be trapped by chemisorption with fuels and/or iron-zirconium melts during light water reactor severe accidents.
flow, respectively. Therefore, it was considered that cesium released from fuel might be trapped by chemisorption with fuels and/or iron-zirconium melts during light water reactor severe accidents.
Kato, Yuto*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Tonna, Ryutaro*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106196_1 - 106196_9, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.61(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Shimizu, Ryo
Dai-45-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/11
no abstracts in English
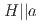 in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 11 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(12), p.123701_1 - 123701_5, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Oguri, Kaori; Hagura, Naoto*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Aoki, Katsumi; Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 556, p.165516_1 - 165516_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ningyo-toge is the uranium mine that has been operated in Japan. Various radioactive elements such as Uranium (U), and Radium (Ra) are still present in the mine ground water with very small amount, and behavior of those elements is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the composition of metal oxides and clay minerals in a soil of slag deposit at the mine, and systematics of adsorption structure of various ions were examined. Identifying the composition and chemical forms of minerals present in the soil of slag can provide useful information for the safety assessment and evaluation of influence on the surrounding environment.
Katsuoka, Nanako; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Sato, Nobuaki*
2023-Nendo "Busshitsu, Debaisu Ryoiki Kyodo Kenkyu Kyoten" Kenkyu Seika, Katsudo Hokokusho (Internet), 1 Pages, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Yoshiki; Matsumoto, Tetsuya*; Yamaguchi, Tomoki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3541 - 3551, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Guerinoni, E.*; Giusti, F.*; Dourdain, S.*; Dufr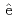 che, J.-F.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ueda, Yuki; Aoyagi, Noboru; Zemb, T.*; Pellet-Rostaing, S.*
che, J.-F.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ueda, Yuki; Aoyagi, Noboru; Zemb, T.*; Pellet-Rostaing, S.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 403, p.124820_1 - 124820_11, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Yomogida, Takumi; Ouchi, Kazuki; Morii, Shiori; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Koma, Yoshikazu; Konno, Katsuhiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.14945_1 - 14945_11, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Particles containing alpha ( ) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water in the Unit 3 reactor building of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS). We analyzed different concentrations of alpha nuclides samples collected at two sampling sites, torus room and Main steam isolation valve (MSIV) room. Most of the
) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water in the Unit 3 reactor building of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS). We analyzed different concentrations of alpha nuclides samples collected at two sampling sites, torus room and Main steam isolation valve (MSIV) room. Most of the  -nuclides in the stagnant water samples of the torus room and the MSIV room were present in particle fractions larger than 10
-nuclides in the stagnant water samples of the torus room and the MSIV room were present in particle fractions larger than 10  m. We detected uranium-bearing particles in
m. We detected uranium-bearing particles in  m-size by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-Ray (SEM-EDX) observation. Other short lived
m-size by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-Ray (SEM-EDX) observation. Other short lived  -nuclides were detected by alpha track detection. The
-nuclides were detected by alpha track detection. The  -nuclide-containing particles with several tens to several hundred
-nuclide-containing particles with several tens to several hundred  m in size were mainly comprised iron (Fe) by SEM-EDX analysis. This study clarifies that the morphologies of U and other
m in size were mainly comprised iron (Fe) by SEM-EDX analysis. This study clarifies that the morphologies of U and other  -nuclides in the sediment of stagnant water in the FDiNPS's Unit 3 reactor building.
-nuclides in the sediment of stagnant water in the FDiNPS's Unit 3 reactor building.
Kumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen (Internet), 49(1), p.15 - 17, 2024/03
Water radiolysis induces oxidative dissolution of uranium oxides. Understanding of this process is a chemical basis for safety assessment of the deep geological repository of spent fuel and would serve as knowledge for retrieval and storage of fuel debris after a severe accident of nuclear power reactors. In order to evaluate the release rate of radioactive elements from the UO matrix of spent nuclear fuel, several chemical kinetic models have been developed. However, the conventional reaction models were found out to be simplistic based on new insights obtained recent experimental studies. Therefore, the reaction mechanism of surface oxidation and dissolution of uranium is now a subject of revisit. Here, a few recent studies regarding the reaction mechanism are introduced.
matrix of spent nuclear fuel, several chemical kinetic models have been developed. However, the conventional reaction models were found out to be simplistic based on new insights obtained recent experimental studies. Therefore, the reaction mechanism of surface oxidation and dissolution of uranium is now a subject of revisit. Here, a few recent studies regarding the reaction mechanism are introduced.
Tonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 589, p.154862_1 - 154862_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dissolution behavior of FeUO compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO
compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U
with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO
as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO
compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U
dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U O
O ).
).

Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Aoki, Dai*; Knebel, G.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(22), p.226503_1 - 226503_7, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:85.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakatani, Takayoshi; Shimizu, Ryo; Tazaki, Makiko; Kimura, Takashi; Hori, Masato
Dai-44-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Saito, Tatsuo; Fumoto, Hiromichi*; Sugawara, Shinetsu*; Tsuchida, Shoji*; Kasai, Atsushi*; Furuta, Sadaaki*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(3), p.120 - 134, 2023/11
This paper is a summary of the activity report of the specialized study group of the Japan Health Physics Society on handling of naturally occurring radioactive wastes from humanities and social sciences perspective. To ensure the reliability of the long-term assessment, this special committee first reviews options for disposal of uranium waste depending on its concentration, especially those adopted or considered in Japan and overseas (U.S.A., U.K.) for uranium concentrations exceeding a sufficiently small amount of uranium (an average of 1 Bq/g of the sum of  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  U).
U).