Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
秋葉 宙*; 大政 義典*; 古府 麻衣子*; Zhang, M.*; 佐藤 駿*; 山室 修*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091010_1 - 091010_6, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)AGNES is a direct geometry chopper-type time-of-flight neutron spectrometer installed at the cold neutron guide (C3-1-1) of JRR-3 (Tokai, Japan). This instrument is well-suited for studies on low-energy excitations of powdered and amorphous samples, and quasi-elastic scattering with an energy resolution of 120  eV (standard mode) or 50
eV (standard mode) or 50  eV (high-resolution mode). During the long shutdown period of JRR-3 due to the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011, AGNES was significantly improved through the installation of supermirror-coated neutron guide tubes and collimator, installation of a new-type top-loading cryo-furnace, and renewal of data acquisition electronics and software. As a result, the neutron intensity has increased by 7.7 times in the standard mode and by 3.2 times in the high-resolution mode. These enhancements facilitate experiments with small amounts of samples, and under special environments, which have previously been challenging.
eV (high-resolution mode). During the long shutdown period of JRR-3 due to the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011, AGNES was significantly improved through the installation of supermirror-coated neutron guide tubes and collimator, installation of a new-type top-loading cryo-furnace, and renewal of data acquisition electronics and software. As a result, the neutron intensity has increased by 7.7 times in the standard mode and by 3.2 times in the high-resolution mode. These enhancements facilitate experiments with small amounts of samples, and under special environments, which have previously been challenging.
中島 一久; 中西 弘*; 小方 厚*; 原野 英樹*; 上田 徹*; 上坂 充*; 渡部 貴宏*; 吉井 康司*; 出羽 英紀; 細貝 知直; et al.
Proceedings of 6th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC98) (CD-ROM), p.809 - 811, 1998/01
光量子科学センターレーザー加速研究グループは高エネルギー加速器研究機構、東京大学原子力工学施設と共同でテーブルトップテラワットレーザーを用いたレーザー航跡場加速実験を実施し、17MeVの電子ライナックからのビームをピーク出力2TWパルス幅90fsのレーザーパルスによる航跡場において200MeV以上まで加速することに成功した。またこれを裏付ける航跡場の直接測定矢レーザーパルスの自己チャネリングの観測にも成功しており加速実験結果と良い一致を示している。さらにレーザー加速実験の高度化のためのフォトカソード電子銃を用いた高品質電子源の開発、高精度エネルギー測定のためのエマルジョン検出器を用いたスペクトロメーターの開発、高強度レーザーパルスの長距離伝播のためのキャピラリー放電プラズマ導波路の開発についても述べ、今後のレーザー加速実験計画について発表する。
 Re(n,2n)
Re(n,2n)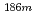 Re and
Re and 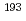 Ir(n,2n)
Ir(n,2n)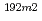 Ir at 14MeV energy region
Ir at 14MeV energy region池田 裕二郎; 春日井 好己*; 宇野 喜智; 今野 力; 前川 洋
Proc., Int. Conf. on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology,Vol. 2, 0, p.1078 - 1080, 1994/00
 Re(n,2n)
Re(n,2n)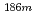 Re及び
Re及び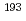 Ir(n,2n)
Ir(n,2n)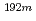 Ir反応は、「長寿命放射性核生成断面積」に関するIAEA-CRPでの対象であるが、生成放射能強度が微弱で、かつ、2~3年の冷却期間の後でも強い妨害放射能によるバックグランドが存在することから、測定が著しく困難である。特に、
Ir反応は、「長寿命放射性核生成断面積」に関するIAEA-CRPでの対象であるが、生成放射能強度が微弱で、かつ、2~3年の冷却期間の後でも強い妨害放射能によるバックグランドが存在することから、測定が著しく困難である。特に、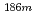 Re及び
Re及び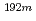 Irの放出
Irの放出 線エネルギーは、137keV及び155keVと低いことから、現状では、バックグランドの影響が高い。そこで、原研FNSではコンプトン抑止型
線エネルギーは、137keV及び155keVと低いことから、現状では、バックグランドの影響が高い。そこで、原研FNSではコンプトン抑止型 線スペクトロメーターを整備し、1989年に照射したRe及びIrサンプルの測定を行なった。その結果、バックグランドは、1/10程度に低減され、約1週間連続測定により、対応する
線スペクトロメーターを整備し、1989年に照射したRe及びIrサンプルの測定を行なった。その結果、バックグランドは、1/10程度に低減され、約1週間連続測定により、対応する 線を有意な統計精度で同定できた。求めた放射化率から14.9MeV中性子に対する断面積を世界で初めて導出し理論計算による予測値との比較を行ない、その妥当性を検討した。
線を有意な統計精度で同定できた。求めた放射化率から14.9MeV中性子に対する断面積を世界で初めて導出し理論計算による予測値との比較を行ない、その妥当性を検討した。
 -ray measurement due to air luminescence employing a liquid scintillation spectrometer
-ray measurement due to air luminescence employing a liquid scintillation spectrometer滝上 誠*; 石河 寛昭
Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 159(1), p.139 - 143, 1979/00
本研究は空気発光による新しい 線測定について提案したものである。
線測定について提案したものである。 線で空気中の窒素を刺激すると窒素分子の第1電子励起準位から蛍光放出が起こるので、この発光を液体シンチレーション・スペクトロメーターで効果的に測定することができた。本測定法は次のごとき利点を有する。1)空気自体が検出体なので他の検出器は一切不要である。2)
線で空気中の窒素を刺激すると窒素分子の第1電子励起準位から蛍光放出が起こるので、この発光を液体シンチレーション・スペクトロメーターで効果的に測定することができた。本測定法は次のごとき利点を有する。1)空気自体が検出体なので他の検出器は一切不要である。2) 線を高い計数効率(~70%)で測定できる。3)出力パルス波高は放射線の種類に依らず、空気中で失うエネルギーだけに比例するので、
線を高い計数効率(~70%)で測定できる。3)出力パルス波高は放射線の種類に依らず、空気中で失うエネルギーだけに比例するので、 線や
線や 線の空気発光は無視できるために
線の空気発光は無視できるために 線の弁別測定が可能である。4)窒素分子の発光スペクトル(3,000~4,500
線の弁別測定が可能である。4)窒素分子の発光スペクトル(3,000~4,500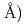 は光電子増倍管のspectral response とよく一致するので、希ガス・シンチレーターの場合のような波長変換体を必要としない。
は光電子増倍管のspectral response とよく一致するので、希ガス・シンチレーターの場合のような波長変換体を必要としない。
瑞穂 満
JAERI 1223, 49 Pages, 1972/08
ガスリコイル型中性子スペクトロメーターにおいて必要な粒子コリメーションに関して新しい方法うを開発し合計5つの方式の中性子スペクトロメーターを可能にした、主な内容は次のようである。(1)速いコインシデンスの可能な季孔コリメーター型スペクトろメーターの開発 (2)速いコインシテンスによるエレクトロニックコリメーション法の開発とその応用 (3)比例計数管におけるvライズタイム弁別型エレクトロニックコリメーションの開発とその応用 (4)方式(2)、(3)の併用によるスペクトルの改善法 (5)グリッドチェンバーにおけるライズタイム弁別型エレクトロニックコリメーションとその応用 (6)比例計数管、グリッドチェンバーにおける粒子弁別およびアスファルトスペクトル改善法
冠城 雅晃; 島添 健次*; 大鷹 豊*; 上ノ町 水紀*; 鎌田 圭*; Kim, J.*; 吉野 将生*; 庄司 育宏*; 吉川 彰*; 高橋 浩之*; et al.
no journal, ,
Nine years have been passed since the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), and the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris will be planned to start from 2021 fiscal year. But these retrieval samples will include not only nuclear fuel debris, but also the other materials. To accelerate the decommissioning, non-destructive assessments (NDA) for the nuclear fuel debris are required for the quick disposals. We are developing a high energy gamma-ray spectrometer under high dose-rate environments using CeBr scintillator. The goal of this research is to realize gamma-ray spectrometry at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. Then, we first developed a small cubic CeBr
scintillator. The goal of this research is to realize gamma-ray spectrometry at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. Then, we first developed a small cubic CeBr scintillator, and we studied the high dose-rate performance at dose rates of up to 790 mSv/h in a
scintillator, and we studied the high dose-rate performance at dose rates of up to 790 mSv/h in a  Co field. In this presentation, we will introduce the concept of Multi Cubic high energy gamma-ray spectrometer, and show the high dose-rate performance in a standard radiation field.
Co field. In this presentation, we will introduce the concept of Multi Cubic high energy gamma-ray spectrometer, and show the high dose-rate performance in a standard radiation field.