Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Ito, Yuma*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 8, p.60_1 - 60_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:83.04(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Radiation DNA damage is formed from direct and indirect effects. The direct effect is the interaction between DNA and a radiation, while the indirect effect is the chemical reaction between DNA and radiolytic chemical species. We believed that when the direct effect is induced, multiple lesions are formed within 10 base pairs (about 3.4 nm) of DNA. The damage reduces repair efficiency and induces biological effects. In this study, DNA damage induced by only indirect effects was quantitatively evaluated. Our results indicated that the multiple damage is formed when only 10s of eV energy is deposited to water in the vicinity of DNA, although its formation probability is less than 1%. In other words, the possibility of late biological effects cannot be excluded simply by imparting energy to water in the extreme vicinity of DNA without direct interaction between radiation and DNA. Our results are one of the most important findings for understanding low-dose radiation risk.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 209, p.110783_1 - 110783_7, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Since the compositions and properties of the fuel debris are uncertain, critical experiments are required to validate calculation codes and nuclear data used for the safety evaluation. For this purpose, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been modifying a critical assembly called "STACY." The first criticality of the modified STACY is scheduled for spring 2024. This paper reports the consideration results of the specifications of the basic core configurations of the modified STACY at the first criticality. We prepared two types of gird plates with different neutron moderation conditions (their intervals are 1.50 cm and 1.27 cm). However, there is a limitation on the number of available UO fuel rods. The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these experimental constraints were designed by computational analysis. A cylindrical core configuration with a 1.50 cm grid plate close to the optimum moderation condition needs 253 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered core configurations with 2.54 cm intervals by using doubled pitches of the grid plate. It will need 213 fuel rods for the criticality. In addition, we considered the experimental core configuration with steel/concrete simulant rods to simulate fuel debris conditions. This paper shows these core configurations and their evaluated specifications.
fuel rods. The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these experimental constraints were designed by computational analysis. A cylindrical core configuration with a 1.50 cm grid plate close to the optimum moderation condition needs 253 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered core configurations with 2.54 cm intervals by using doubled pitches of the grid plate. It will need 213 fuel rods for the criticality. In addition, we considered the experimental core configuration with steel/concrete simulant rods to simulate fuel debris conditions. This paper shows these core configurations and their evaluated specifications.
Ishikawa, Akihisa; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Hirai, Yuta*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Radiological Physics and Technology, 17(2), p.553 - 560, 2024/06
Kim, M.; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Malins, A.*; Abe, Tomohisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Machida, Masahiko; Saito, Kimiaki
Kankyo Hoshano Josen Gakkai-Shi, 12(2), p.39 - 53, 2024/04
More than ten years have passed since the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. But with the progress of decontamination, the evacuation order has been lifted and the return of residents is still ongoing. Under these circumstances, in order to quantitatively evaluate the effect of decontamination activities and cultivation on air dose rate reduction, a detailed environmental model was constructed using 3D-ADRES for a real area located in the Okuma town, Fukushima prefecture. Monte Carlo simulations were performed using the model to calculate realistic distributions of radioactive Cs based on measurement results and air dose rates reflecting changes over time. As a result, the distribution of air dose rates at 100 cm above ground level in the target area according to decontamination and cultivation activities was calculated. The calculated air dose rates reproduced the measured values well, and were confirmed to be appropriate as a method for evaluating the effects of decontamination and cultivation activities. This method is expected to serve as a reference for further decontamination management measures to reduce the air dose rate in the difficult-to-return zone, where entry is still restricted.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2024) (Internet), p.227 - 236, 2024/04
It is considered that a large amount of fuel debris was generated in the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. In particular, the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris, including concrete components, which are products of molten core-concrete interaction (MCCI), have not been well investigated. In this study, to plan physical simulation in critical experiments at the critical assembly using pseudo fuel debris samples including concrete, we evaluated the sensitivity to the effective multiplication factor of the Si and Ca cross sections in the concrete-simulant sample based on the results of elemental analysis of the prototype. These sensitivity calculations were carried out for each sample loading method and composition. We focused on the energy profile of the sensitivity of the  Ca capture reaction and confirmed that the shape of the sensitivity energy profile changed depending on the sample compositions and neutron moderation conditions. We could know the characteristics of each experimental method by clarifying the trends of sensitivity obtained in different experimental cases. It was found that increasing the amount of concrete in the samples and changing the neutron moderation conditions in the experimental core configurations produced similar changes in the shape of the sensitivity energy profile. This result shows the possibility of reproducing the characteristics of MCCI products through practical critical experiments using concrete materials that do not contain fissile materials.
Ca capture reaction and confirmed that the shape of the sensitivity energy profile changed depending on the sample compositions and neutron moderation conditions. We could know the characteristics of each experimental method by clarifying the trends of sensitivity obtained in different experimental cases. It was found that increasing the amount of concrete in the samples and changing the neutron moderation conditions in the experimental core configurations produced similar changes in the shape of the sensitivity energy profile. This result shows the possibility of reproducing the characteristics of MCCI products through practical critical experiments using concrete materials that do not contain fissile materials.
Abe, Shinichiro
CROSS T&T, (76), p.39 - 43, 2024/02
Non-destructive faults (the so-called soft errors) in microelectronics caused by cosmic rays have been recognized as a serious reliability problem. To guarantee the reliability of microelectronic devices, it is necessary to evaluate the soft error rate. We have developed some technics for the soft error simulation using PHITS code. We have also developed the terrestrial SER estimation methodology based on simulation coupled with one-time neutron irradiation testing. These results will be reported as the explanatory article in the journal of CROSS T&T published by the Comprehensive Research Organization for Science and Society (CROSS).
Yamamoto, Yojiro*; Hayakawa, Sho*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Computational Materials Science, 229, p.112389_1 - 112389_9, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)He bubbles are characteristic microstructures under fusion reactor conditions. They approach and coalesce through their own migration, which significantly impacts the microstructure and material properties. However, these processes, which involve multiple migrations of metal atoms, cannot be treated by molecular dynamics (MD) due to its timescale limitation. In this study, self-evolving atomistic kinetic Monte Carlo (SEAKMC) was used to expand the timescale and reproduce bubble coalescences in Fe. To enhance selections of events that led to the process by avoiding trivial events with an extremely low activation energy such as tiny vibrations of a He atom or short-range displacements of the Fe atom, we introduced two algorithms into SEAKMC, a two-step saddle point search for the former measure and setting a threshold for a displacement distance of the Fe atom for the latter. Furthermore, by adding another algorithm to set an upper bound for the activation energy to prevent selections of events with an impractically high activation energy, we succeeded to reproduce the change in the configuration from dumbbell to elliptical up to a simulated time of 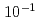 s, 8 orders longer than MD timescales. The developed method is effective for analyzing microstructures of metallic materials containing light elements and is the only method that can reach timescales comparable to those of experiments.
s, 8 orders longer than MD timescales. The developed method is effective for analyzing microstructures of metallic materials containing light elements and is the only method that can reach timescales comparable to those of experiments.
Gunji, Satoshi; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
Since the compositions and properties of the fuel debris are uncertain, critical experiments are required to validate calculation codes and nuclear data used for the safety evaluation. For this purpose, JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called "STACY". The first criticality of the new STACY is scheduled for spring 2024. This paper reports the consideration results of the core configurations of the new STACY at the first criticality. We prepared two sets of gird plates with different neutron moderation conditions (their intervals are 1.50 cm and 1.27 cm). However, there is a limitation on the number of available UO fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Fernex, F.*; Leclaire, N.*; Bardelay, A.*; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
Institut de radioprotection et de s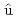 ret
ret nucl
nucl aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Arakaki, Yu; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called STACY from a solution system to a light-water moderated heterogeneous system to validate computation results of criticality characteristics of fuel debris generated in the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. To experimentally simulate the composition and characteristics of fuel debris, we will prepare several grid plates which make particular neutron moderation conditions and a number of rod-shaped concrete and stainless-steel materials. Experiments to evaluate fuel debris's criticality characteristics are scheduled using these devices and materials. This series of STACY experiments are planned to measure the reactivity of fuel debris-simulated samples, measure the critical mass of core configurations containing structural materials such as concrete and stainless steels, and the change in critical mass when their arrangement becomes non-uniform. Furthermore, two divided cores experiments are scheduled that statically simulate fuel debris falling, and also scheduled that subcriticality measurement experiments with partially different neutron moderation conditions. The experimental plans have been considered taking into account some experimental constraints. This paper shows the schedule of these experiments, as well as the computation results of the optimized core configurations and expected results for each experiment.
Furuta, Takuya
Isotope News, (787), p.20 - 23, 2023/06
Carbon ion radiotherapy has an advantage over conventional radiotherapy such that its superior dose concentration on the tumor helps to reduce unwanted dose to surrounding normal tissues. Nevertheless, a little dose to normal tissues, which is a potential risk of secondary cancer, is still unavoidable. In the current dose assessment, however, only assessment around target volume is performed for the tumor control and prevention of acute radiation injury of fatal organs. We therefore developed a system called RT-PHITS for CIRT to reproduce the carbon ion radiotherapy including the production and transport of secondary particles based on treatment planning data using PHITS. Using this system, whole-body dose assessment of patients in the past carbon ion radiotherapy can be performed. By comparing the dose assessment to the epidemiologic records of the patients, the relation between dose exposure of non-target organs and incidence of side effects such as secondary cancer will be elucidated.
Abe, Shinichiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(5), p.326 - 330, 2023/05
, 65(5), p.326 - 330, 2023/05
Non-destructive faults (the so-called soft errors) in microelectronics caused by environmental radiation such as neutrons and muons have been recognized as a serious reliability problem. The number of microelectronics requiring high reliability increases with the growth of the information society. Therefore, it is not realistic to evaluate the soft error rate (SER) of all microelectronics by measurement. Moreover, the evaluation of SER in the pre-manufacturing stage is sometimes required. As a result, the evaluation of SER by simulation become more important. We have developed the soft error simulation method with PHITS code. We have also simulated the neutron- and muon-induced soft errors. These results will be reported in the journal of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) as the explanatory article.
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 159, p.104630_1 - 104630_9, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this work, the methodology of Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) is applied to criticality tallies in Monte Carlo fission source cycles in order to evaluate the utility value of the distribution tail ends. Numerical results obtained under a sufficiently large number of particles per cycle show that the extreme value index (EVI) in GEV falls within the range of Weibull distribution including the EVI of Gumbel distribution as the role of a boundary value layer. GEV is also applied to a historically-challenging loosely-coupled system for demonstrating population diagnosis under an insufficient number of particles per cycle. It turns out that the transition from one equilibrium to other equilibrium makes the EVIs of upper and lower distribution tail ends depart from each other so that one of them falls in the range of Weibull distribution and the other in that of Frechet distribution.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(11), p.7076 - 7086, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:73.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Scientific insights of water radiolysis are widely used in the life sciences and so on, however, the formation mechanism of radicals, a product of water radiolysis, is still not well understood. We are challenging to develop a simulation code to solve this formation mechanism from the viewpoint of radiation physics. Our first-principles calculations have revealed that the behavior of secondary electrons in water is governed not only by collisional effects but also by polarization effects. Furthermore, from the predicted ratio of ionization to electronic excitation, based on the spatial distribution of secondary electrons, we successfully reproduce the initial yield of hydrated electrons predicted in terms of radiation chemistry. The code provides us a reasonable spatiotemporal connection from radiation physics to radiation chemistry. Our findings are expected to provide newly scientific insights for understanding the earliest stages of water radiolysis.
Furuta, Takuya; Koba, Yusuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Ishikawa, Akihisa*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 67(14), p.145002_1 - 145002_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:68.93(Engineering, Biomedical)Carbon ion radiotherapy has an advantage over conventional radiotherapy such that its superior dose concentration on the tumor helps to reduce unwanted dose to surrounding normal tissues. Nevertheless, a little dose to normal tissues, which is a potential risk of secondary cancer, is still unavoidable. The Monte Carlo simulation is a good candidate for the tool to assess secondary cancer risk, including the contributions of secondary particles produced by nuclear reactions. We therefore developed a new dose reconstruction system implementing PHITS as the engine. In this system, the PHITS input is automatically created from the DICOM data sets recorded in the treatment planning. The developed system was validated by comparing to experimental dose distribution in water and treatment plan on an anthropomorphic phantom. This system will be used for retrospective studies using the patient data in National Institute for Quantum and Science and Technology.
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 144, p.104099_1 - 104099_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Randomized Weierstrass function (RWF) has been under development for evaluating the uncertainty of random media criticality due to the material mixture under disorder. In this work, the modelling capability of RWF is refined so that the spectrum range can be controlled by specifying its lower and upper ends of the frequency domain variable. As a result, it becomes possible to make fair criticality comparison among replicas of random media under inverse power law power spectra. Technically, the infinite sum of trigonometric terms in RWF is extended to cover the arbitrarily low frequency domain and then truncated to finite terms for the sole purpose of spectrum range control. This means that the refinement is free of the convergence issue towards a fractal characteristic of Weierstrass function and thus termed Incomplete Randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF). As a demonstration, a three-dimensional version of IRWF is applied to the mixture of three fuels with different burnups in a water-moderated environment. Monte Carlo criticality calculations are carried out to evaluate the uncertainty of neutron effective multiplication factor due to the indeterminacy of the fuel mixture formation.
Chang, W.*; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(5), p.846 - 855, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.45(Biology)With the aim of developing a revaluation tool of treatment plan in carbon-ion radiotherapy using Monte Carlo (MC) simulation, we propose two methods; one is dedicated to identify realistic-tissue materials from a CT image with satisfying the well-calibrated relationship between CT numbers and stopping power ratio (SPR) provided by TPS, and the other is to estimate dose to water considering the particle- and energy-dependent SPR between realistic tissue materials and water. We validated these proposed methods by computing depth dose distribution in homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms composed of human tissue materials and water irradiated by a 400 MeV/u carbon beam with 8 cm SOBP using a MC simulation code PHITS and comparing with results of conventional treatment planning system (TPS). Our result suggested that use of water as a surrogate of real tissue materials, which is adopted in conventional TPS, is inadequate for dose estimation from secondary particles because their production rates cannot be scaled by SPR of the primary particle in water. We therefore concluded that the proposed methods can play important roles in the reevaluation of the treatment plans in carbon-ion radiotherapy.
Kobayashi, Keita; Nagai, Yuki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 155(3), p.034106_1 - 034106_9, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:67.66(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Zhao, C.*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nishitani, Shigeto*; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Materials Transactions, 62(7), p.929 - 934, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in measuring the diffusion coefficient of Cu in Fe in a low temperature range that had not been measured so far. Since the diffusion couple, which is a general method for measuring the diffusion coefficient, can be applied only at high temperature, atom probe tomography and Cu precipitation rate theory were used in this study. The estimated diffusion coefficient was found to be more reliable than that obtained in previous studies. Therefore, it is considered that the estimation by the atom probe provided higher accuracy. Furthermore, the kinetic Monte Carlo simulation revealed that the diffusion coefficient estimated by this method tends to be slightly overestimated as the temperature decreases.