Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ito, Akira; Kawakami, Susumu; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 2001-028, 38 Pages, 2002/01
In a repository for high-level radioactive waste, coupled thermo -hydro -mechanical and chemical (THMC) processes will ocurr, involving the interactive processes between radioactive decay heat from the vitrified waste, infiltration of groundwater, swelling pressure generation and chemical evolution of the buffer material and porewater chemistry. In this program, numerical experiment system for the coupled THMC processes will be developed in order to predict the long-term performance of the near-field (engineered barrier and host rock) for various geological environments. The simulation code development has been started in FY 2001 and three development steps are planned, because (1)development will be continued for some years, (2)feasibility of numerical experiment have to be confirmed by using existing tools. This report presents the following items of the simulation code development for the coupled THMC processes. (1)First step of the simulation code development (2)Mass transport passways in compacted bentonite (3)Parallelization of the simulation code
Makino, Hitoshi; ; Miyahara, Kaname
JNC TN8400 2000-033, 74 Pages, 2000/11
Natural phenomena is one of the potential factors perturbing the long-term stability of the geological environment, and for natural phenomena, it is necessary to consider uncertainties relevant to time, frequency and effect. Therefore it will be important to have information about the potential impacts of natural phenomena on the safety functions of geological disposal system in the future by assuming that natural phenomena perturbs the safety functions of the geological disposal system. In this report, we have considered 4 natural phenomena, 'uplift, subsidence and denudation', 'climatic and sea-level changes', 'earthquakes and fault movement' and 'volcanism', which had been extracted by investigation in foreign countries and by considering the characteristics of Japan as natural phenomena which may perturb the long-term stability of the geological environment. And we have considered mainly typical effects of naturaI phenomena on geological environment and investigated the typical impacts of those natural phenomena on the safety functions of the geological disposal system. On perturbation scenarios, the maximum of total doses have been less than regulatory guidelines in foreign countries in all situations except the cases assuming that a new fault, which causes significant pathway of groundwater flow and nuclide migration, intersects the waste packages. In the case, the maximum of total doses may reach the same level as regulatory guidelines in foreign countries or natural radiation exposure in Japan depending on fault generation time or grandwater flow rate through the fault. And, on isolation failure scenarios, it has been implied that nuclide mass/flux originated from geological disposal is comparable level with nuclide mass/flux in natural environment. These results could give useful information about the potential impacts of natural phenomena on the safety functions of geological disposal system, and also could show the potential importance of ...
Isogai, Takeshi*; Oda, Chie
JNC TN8400 2000-025, 48 Pages, 2000/09
Porewater chemistly in compacted bentonite would affect a performance of engineered barrier system in a high-level radioactive waste repository, whereas there are little information of the porewater based on experimental data. The previous study provided a new method of direct pH measurement for highly compacted bentonite system and demonstrated some tests for compacted bentonite samples (the dry densities: 1.6 [g/cm ] and 1.8 [g/cm
] and 1.8 [g/cm ]) both with the de-ionized water and with the NaCl solution. In this study, the solution equilibrated with low alkalinity cement were used in the direct pH measurement to see the effect of the composition of the external solutions, in which the bentonite column immersed. The result showed that the pH value of porewater in the cementitious condition was around 9 during the immersed time 1 to 3 months, while after 6 months became the porewater pH 10.6, which was equal to pH of the external solution.
]) both with the de-ionized water and with the NaCl solution. In this study, the solution equilibrated with low alkalinity cement were used in the direct pH measurement to see the effect of the composition of the external solutions, in which the bentonite column immersed. The result showed that the pH value of porewater in the cementitious condition was around 9 during the immersed time 1 to 3 months, while after 6 months became the porewater pH 10.6, which was equal to pH of the external solution.
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-010, 27 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of the radioactive wastes, gas generation by microorganism could be significant for the assessment of this system, because organic material included in groundwater, buffer material and wastes might serve as carbon sources for microorganisms. In this study, gas generation tests using microorganisms were carried out under anaerobic condition. The amount of methane and carbon dioxide that were generated by activity of Methane Producing Bacteria (MPB) were measured with humic acid, acetic acid and cellulose as carbon sources. The results showed that methane was not generated from humic acid by activity of MPB. However, in the case of using acetic acid and cellulose, methane was generated, but at high pH condition (pH=10), the amount of generated methane was lower than at low pH (pH=7). It was not clear whether the pH would affect the amount of generated carbon dioxide.
Mori, Koji*; Neyama, Atsushi*; Nakagawa, Koichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-064, 175 Pages, 2000/03
In this study, the following tasks have been performed in order to evaluate the stability of earthquake resistance for the engineered barrier system(EBS) of High Level Waste (HLW) geological isolation system. (1)validation studies for the liquefaction model. The function of single-phase analysis without interaction between soil and pore water in three-dimensional effective stress analysis code, which had been developed in this study, have been verified using by actual vibration test data. This fiscal year, some validation studies for the function of liquefaction analysis was conducted usig by actual measured data through the laboratory liquefaction test. (2)Supplemental Studies for JNC Second Progress Report. Through the JNC second progress report, it was considered that the stability of earthquake resistance of the engineered barrier system would be maintained under the major seismic event. At the same time we have recognized that several model parameters for joint-crack element, which takes into account for the response behavior of material discontinuous surface such as between overpack and buffer material, will become important in the response behavior of the whole EBS. This year, we have studied about several topics, which arise from technical discussion on JNC second progress report and we have discussed about total seismic stability of EBS. (3)Supplemental Studies for joint study with NRIDP. At this fiscal year, the joint study with National Research Institute for Disaster Prevention (NRIDP) will be final stage. UP to this day, incremental validation studies had been continued using by mesuared data obtained from vibration test. In this final stage, validation analysis has been conducted again using by current version new analysis code and maintained the validation data which will be contribute to the joint study mentioned above.
Tochiyama, Osamu*
JNC TJ8400 2000-044, 53 Pages, 2000/02
To estimate the polyelectrolyte effect and the effect of the heterogeneous composition of humic acids, the complex formation constants of Eu(III) and Ca(II) with Aldrich humic acid and polyacrylic acid were obtained, for Eu(10 to 10
to 10 M) by solvent extraction with TTA and TBP in xylene, for Ca (10
M) by solvent extraction with TTA and TBP in xylene, for Ca (10 M) with TTA and TOPO in cyclohexane and for Ca(10
M) with TTA and TOPO in cyclohexane and for Ca(10 M) by using ion-selective electrode. By defining the apparent formation as
M) by using ion-selective electrode. By defining the apparent formation as  = [MR
= [MR ]/([M][R]), where [R] denotes the concentration of dissociated functional group, [M] and [MR
]/([M][R]), where [R] denotes the concentration of dissociated functional group, [M] and [MR ] denote the concentration of free and bound metal ion and pcH is defined as-log[H], the values of log
] denote the concentration of free and bound metal ion and pcH is defined as-log[H], the values of log have been obtained at pcH 4.8 - 5.5 in 0.1 - 1.0M NaClO
have been obtained at pcH 4.8 - 5.5 in 0.1 - 1.0M NaClO and NaCl. Log
and NaCl. Log of Eu-humate varied from 5.0 to 9.3 and that of Ca-humate from 2.0 to 3.4..For both humate and polyacrylate, log
of Eu-humate varied from 5.0 to 9.3 and that of Ca-humate from 2.0 to 3.4..For both humate and polyacrylate, log increased with pcH or with the degree of dissociation. The increase in the ionic strength O.1 to 1.0 M decreased the log
increased with pcH or with the degree of dissociation. The increase in the ionic strength O.1 to 1.0 M decreased the log , the decrease in log
, the decrease in log of Eu(III)-humate is 1.6, that of Eu(III), polyacrylate 0.7, that of Ca(II)-humate 1.9 and that of Ca(II)-polyacrylate 1.2. While the increase in the metal ion produced no effect on log
of Eu(III)-humate is 1.6, that of Eu(III), polyacrylate 0.7, that of Ca(II)-humate 1.9 and that of Ca(II)-polyacrylate 1.2. While the increase in the metal ion produced no effect on log of polyacrylate, log
of polyacrylate, log of humate decreased. Depending on the concentration of Eu(III), the coexistence of Ca(II) reduced log
of humate decreased. Depending on the concentration of Eu(III), the coexistence of Ca(II) reduced log  of humate by 0 to 0.8. The dependence of log
of humate by 0 to 0.8. The dependence of log of humate on the metal ion concentration suggests the coexistence of strong and weak binding sites in the hmnic acid.
of humate on the metal ion concentration suggests the coexistence of strong and weak binding sites in the hmnic acid.
Shinohara, Yoshinori*; Tsujimoto, Keiichi*
JNC TJ1400 2000-002, 280 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Yoshinori*; Tsujimoto, Keiichi*
JNC TJ1400 2000-001, 137 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English

 and AnO
and AnO
 Species in Geologic Environments
Species in Geologic EnvironmentsChoppin, G. R.*; Bronikowski, M.*; Chen, J.*; Byegard, J.*; Rai, D.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-012, 155 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of pentavalent and hexavalent actinide species (AnO and AnO
and AnO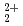 ) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO
) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO and AnO
and AnO
 , redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
, redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
Rai, D.*; Rao, L.*; Weger, H. T.*; GREGORY R.CHOPPI*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-010, 95 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of Pu(III), Am(III), and Cm(III) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. Where data for specific actinide(III) species are lacking, the data were selected based on chemical analogy to other trivalent actinides. In this study, the Pitzer ion-interaction model is mainly used to extrapolate thermodynamic constants to zero ionic strength at 25 C.
C.