Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ssbauer spectroscopy
ssbauer spectroscopy壬生 攻*; 三井 隆也; 田中 雅章*; 増田 亮*; 北尾 真司*; 小林 康浩*; 依田 芳卓*; 瀬戸 誠*
Journal of Applied Physics, 117(17), p.17E126_1 - 17E126_4, 2015/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:8.37(Physics, Applied)Measurement of the magnetic hyperfine fields in metallic thin wires under spin Hall conditions was attempted using the emerging technique synchrotron radiation M ssbauer spectroscopy. A M
ssbauer spectroscopy. A M ssbauer probe layer of
ssbauer probe layer of  Fe(0.2 nm),
Fe(0.2 nm),  Fe(0.6 nm), or
Fe(0.6 nm), or 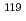 Sn(0.6 nm) was embedded as an electron spin detector near the surfaces of V, Au, Pt, and
Sn(0.6 nm) was embedded as an electron spin detector near the surfaces of V, Au, Pt, and  Fe wires. The magnitudes of the magnetic hyperfine fields at the
Fe wires. The magnitudes of the magnetic hyperfine fields at the  Fe and
Fe and 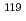 Sn nuclear sites that could be enhanced by nonequilibrium conduction electron spin polarization were measured both without and with the application of an electric current along the wire. Changes in the M
Sn nuclear sites that could be enhanced by nonequilibrium conduction electron spin polarization were measured both without and with the application of an electric current along the wire. Changes in the M ssbauer spectra were not clearly observed, indicating that the magnetic hyperfine field induced by nonequilibrium spin polarization is smaller than the detection limit at least for the measured systems and conditions.
ssbauer spectra were not clearly observed, indicating that the magnetic hyperfine field induced by nonequilibrium spin polarization is smaller than the detection limit at least for the measured systems and conditions.
 Fe polarization dependent synchrotron M
Fe polarization dependent synchrotron M ssbauer spectroscopy using a diamond phase plate and an iron borate nuclear Bragg monochromator
ssbauer spectroscopy using a diamond phase plate and an iron borate nuclear Bragg monochromator三井 隆也; 今井 康彦*; 増田 亮*; 瀬戸 誠*; 壬生 攻*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 22(2), p.427 - 435, 2015/03
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:50.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Energy domain  Fe polarization dependent synchrotron radiation M
Fe polarization dependent synchrotron radiation M ssbauer spectroscopy was developed by using a diamond X-ray phase plate and an iron borate nuclear Bragg monochromator. The former controls the polarization of the incident synchrotron radiation X-rays and the latter filters the
ssbauer spectroscopy was developed by using a diamond X-ray phase plate and an iron borate nuclear Bragg monochromator. The former controls the polarization of the incident synchrotron radiation X-rays and the latter filters the  Fe M
Fe M ssbauer radiation with a narrow bandwidth of 15 neV from the broadband synchrotron radiation. The developed nuclear diffraction optics allowed
ssbauer radiation with a narrow bandwidth of 15 neV from the broadband synchrotron radiation. The developed nuclear diffraction optics allowed  Fe M
Fe M ssbauer studies to beperformed with various polarization states. In this paper, the spectrometer system, beam characterization, performance test experiments and a grazing incidence M
ssbauer studies to beperformed with various polarization states. In this paper, the spectrometer system, beam characterization, performance test experiments and a grazing incidence M ssbauer measurement of an isotope enriched iron thin film are described.
ssbauer measurement of an isotope enriched iron thin film are described.
村上 元彦*; Goncharov, A. F.*; 平尾 直久*; 増田 亮*; 三井 隆也; Thomas, S. M.*; Bina, C. R.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.5428_1 - 5428_6, 2014/11
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:49.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The possible presence of dense magmas at Earth's core mantle boundary is expected to substantially affect the dynamics and thermal evolution of Earth's interior. However, the thermal transport properties of silicate melts under relevant high-pressure conditions are poorly understood. Here we report in situ high pressure optical absorption and synchrotron M ssbauer spectroscopic measurements of iron enriched dense silicate glasses, as laboratory analogues for dense magmas, up to pressures of 85 GPa. Our results reveal a significant increase in absorption coefficients, by almost one order of magnitude with increasing pressure to
ssbauer spectroscopic measurements of iron enriched dense silicate glasses, as laboratory analogues for dense magmas, up to pressures of 85 GPa. Our results reveal a significant increase in absorption coefficients, by almost one order of magnitude with increasing pressure to  50 GPa, most likely owing to gradual changes in electronic structure. This suggests that the radiative thermal conductivity of dense silicate melts may decrease with pressure and so may be significantly smaller than previously expected under core-mantle boundary conditions. Such dark magmas heterogeneously distributed in the lower mantle would result in significant lateral heterogeneity of heat flux through the core mantle boundary.
50 GPa, most likely owing to gradual changes in electronic structure. This suggests that the radiative thermal conductivity of dense silicate melts may decrease with pressure and so may be significantly smaller than previously expected under core-mantle boundary conditions. Such dark magmas heterogeneously distributed in the lower mantle would result in significant lateral heterogeneity of heat flux through the core mantle boundary.
 Te synchrotron-radiation-based M
Te synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy
ssbauer spectroscopy黒葛 真行*; 北尾 真司*; 小林 康浩*; 齋藤 真器名*; 増田 亮*; 三井 隆也; 依田 芳卓*; 瀬戸 誠*
Hyperfine Interactions, 226(1), p.687 - 691, 2014/04
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:68.16(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)The M ssbauer spectra of the 35.49 keV excited state of
ssbauer spectra of the 35.49 keV excited state of  Te were observed in the energy domain using synchrotron radiation for the first time. The obtained isomer shifts and Debye temperature agree with previous experiments. These results show that this method will be applicable to various compounds.
Te were observed in the energy domain using synchrotron radiation for the first time. The obtained isomer shifts and Debye temperature agree with previous experiments. These results show that this method will be applicable to various compounds.
 Te synchrotron-radiation-based M
Te synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of Fe
ssbauer spectroscopy of Fe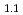 Te and FeTe
Te and FeTe Se
Se黒葛 真行*; 北尾 真司*; 小林 康浩*; 齋藤 真器名*; 増田 亮*; 三井 隆也; 依田 芳卓*; 瀬戸 誠*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(4), p.044708_1 - 044708_4, 2014/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:33.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The  Te M
Te M ssbauer spectra of Fe
ssbauer spectra of Fe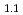 Te and FeTe
Te and FeTe Se
Se were measured using synchrotron-radiation-based M
were measured using synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy. The hyper fine field of Te in the antiferromagnetic phase of Fe
ssbauer spectroscopy. The hyper fine field of Te in the antiferromagnetic phase of Fe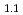 Te was evaluated to be 4(1) T at 20 K, and this hyper fine field is considered to be due to the transferred hyper fine field from Fe magnetic moments. The evaluated hyper fine field was comparatively large, suggesting the strong correlation with the magnetic moment of Fe that forms double stripe type magnetic structure. For the superconductor FeTe
Te was evaluated to be 4(1) T at 20 K, and this hyper fine field is considered to be due to the transferred hyper fine field from Fe magnetic moments. The evaluated hyper fine field was comparatively large, suggesting the strong correlation with the magnetic moment of Fe that forms double stripe type magnetic structure. For the superconductor FeTe Se
Se , no marked change in its M
, no marked change in its M ssbauer parameters was observed below or above the superconducting transition temperature, indicating that the change in the electronic state of Te was small.
ssbauer parameters was observed below or above the superconducting transition temperature, indicating that the change in the electronic state of Te was small.