Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
; Kano, Shigeki
PNC TN9410 98-049, 55 Pages, 1998/03
Low speed tribological properties of stainless steel, ceramics and hard metals were investigated in air at room temperature and in nitrogen atmosphere at high temperature for the consideration of sliding type support structure in intermediate heat exchanger of fast reactor. The following results are obtained. (1)In low speed friction measurements in air at room temperature, friction coefficients of ceramics and hard metals were smaller than that of stainless steel. Surface roughness of the specimens increased the friction force and silicon carbide showed the smallest friction coefficient among the specimens with mirror polished surface. (2)From the results of friction measurements at various sliding speeds in air at room temperature, friction coefficients of ceramics and hard metals were always stable and lower than that of stainless steel. Among ceramics, PSZ showed the smallest friction and silicon carbide showed the most stable friction at any sliding speeds. (3)Friction coefficients of silicon carbide and silicon nitride in nitrogen atmosphere at high temperature showed low values as measured at room temperature. On the contrary, friction coefficient of stainless steel measured in nitrogen atmosphere at high temperature were higher than that measured at room temperature, over 1. (4)In the reciprocal sliding tests in nitrogen atmosphere at high temperature, friction coefficient of stainless steel were over 1. On the contrary, the friction coefficients of ceramics were less than 1 instead of chipping during the slidings.
; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Kano, Shigeki; Yoshida, Eiichi
PNC TN9410 98-048, 56 Pages, 1998/03
Planar specimens of functionally gradient material (FGM) for thermal stress relaxation in fast reactor environment were formed and evaluated. FGMs of Al O
O -SUS316L system and Y
-SUS316L system and Y O
O -SUS316L system were deposited on SUS316L substrates by low pressure plasma spraying. The deposited coatings with 6 layers in which the ratio of ceramics/SUS316FR changes from 0 to 100% by 20% were successfully formed. Cross-sectional observation of the coatings showed no cracks and the hardness in the coating increased continuously from the substrate to the surface. From the results of X-ray diffraction, there were no changes in the structure of SUS316L and Y
-SUS316L system were deposited on SUS316L substrates by low pressure plasma spraying. The deposited coatings with 6 layers in which the ratio of ceramics/SUS316FR changes from 0 to 100% by 20% were successfully formed. Cross-sectional observation of the coatings showed no cracks and the hardness in the coating increased continuously from the substrate to the surface. From the results of X-ray diffraction, there were no changes in the structure of SUS316L and Y O
O between the powder and the coating. On the contrary, in the case of Al
between the powder and the coating. On the contrary, in the case of Al O
O ,
,  - Al
- Al O
O phase was detected in the coating formed from
phase was detected in the coating formed from 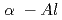 _
_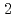
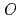 _
_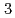 $ powder. The specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K or 923K for 3.6Ms(1000h). The coatings were damaged with many cracks in liquid sodium. It was revealed that the bonding strength between the sprayed particles were not sufficient. To improve the stability in liquid sodium, another specimens were formed with changing the chamber pressure during deposition. From the microstructural inspections of the specimens, the coating formed at higher chamber pressure showed less porosity.
$ powder. The specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K or 923K for 3.6Ms(1000h). The coatings were damaged with many cracks in liquid sodium. It was revealed that the bonding strength between the sprayed particles were not sufficient. To improve the stability in liquid sodium, another specimens were formed with changing the chamber pressure during deposition. From the microstructural inspections of the specimens, the coating formed at higher chamber pressure showed less porosity.
Morinaga, Masahiko*; *; *
PNC TJ9603 98-002, 48 Pages, 1998/03
[PURPOSE]Both the Nb-based and Mo-based alloys have been designed and developed in order to establish the frontier technique for super-heat-resisting materials used in the liquid alkali metal environment at high temperatures. In this study, mechanical properties of the designed Nb-1Hf alloy were experimentally evaluated. In addition, the brittleness of Nb-based alloys observed at 1073K were discussed. Moreover, characteristics of both the designed Nb-based and the Mo-based alloys were summarized in a consistent way. [EXPERIMENTAL METHODS] (1)Tensile test : The tensile test was performed at room temperature and 1473K in an Ar gas atmosphere for the designed Nb-1Hf alloy and also for commercial Nb-1Zr alloy. (2)High temperature creep test:The creep test of the designed Nb-1Hf alloy was carried out at 1473K in an Ar gas atmosphere under several applied stress levels. (3)TEM observation : The TEM observation was performed with the creep specimens tested at both 1073K and 1273K in order to get information for the 1073K brittleness of the Nb-1Zr alloy. [RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS] (1)Tensile test : The tensile stress and the proof stress of the designed Nb-1Hf alloy were slightly lower than those of commercial Nb-1Zr alloy at room tempetarure. But the alloy was superior in the elongation to the Nb-1Zr alloy. High temperature tensile properties were not able to be evaluated properly because of the large grain size of the specimens. (2)High temperature creep test : The Nb-1Hf alloy was superior in the ereep resistance to other solid solution hardened Nb-based alloys. (3)TEM observation : A modulated structure with about 1nm preiod was observed in the specimen which was brittle at 1073K. This was supposed to cause the 1073K brittleness of the Nb-1Zr alloy. [CONCLUSION] The tensile strength of the designed Nb-1Hf alloy was slightly lower at room temperature than that of the commercial Nb-1Zr alloy. But, the designed alloy was superior in high temperature creep properties to any
Saito, Junichi; Kano, Shigeki
PNC TN9410 97-073, 69 Pages, 1997/07
In order to understand the effect of implanted atom in ceramics and metals on the sodium corrosion, the electronic structures of un-implanted and implanted materials were calculated using DV-X cluster method which was one of molecular orbital calculations. The calculated materials were
cluster method which was one of molecular orbital calculations. The calculated materials were  -Si
-Si N
N ,
,  -SiC and
-SiC and  -SiC as ceramics, and f.c.c.Fe, b.c.c.Fe and b.c.c. Nb as metals. An Fe, Mo and Hf atom for ceramics, and N atom for metals were selected as implanted atoms. It is known that these metallic elements have exhibited the excellent corrosion resistance against liquid sodium in previous experiments. The summary of results is shown as follows. Energy levels of implanted atom appeared in or near energy band gap in ceramics. The change of ionicities of each element which showed amount of transferred charges and bond order which showed the covalent bond strength between atoms depended on substrates and implanted atoms. The strength of ionic bonding between atoms reduced in
-SiC as ceramics, and f.c.c.Fe, b.c.c.Fe and b.c.c. Nb as metals. An Fe, Mo and Hf atom for ceramics, and N atom for metals were selected as implanted atoms. It is known that these metallic elements have exhibited the excellent corrosion resistance against liquid sodium in previous experiments. The summary of results is shown as follows. Energy levels of implanted atom appeared in or near energy band gap in ceramics. The change of ionicities of each element which showed amount of transferred charges and bond order which showed the covalent bond strength between atoms depended on substrates and implanted atoms. The strength of ionic bonding between atoms reduced in  -Si
-Si N
N , as ionicities of constituent atom decreased by the implanted atom. The decreases of ionicity depended on implanted atoms and Hf implantation showed the largest decrease in implanted atoms. The bond order in
, as ionicities of constituent atom decreased by the implanted atom. The decreases of ionicity depended on implanted atoms and Hf implantation showed the largest decrease in implanted atoms. The bond order in  -Si
-Si N
N and
and  -SiC decreased by the implantation. When the implanted atom occupied at substitutional site in
-SiC decreased by the implantation. When the implanted atom occupied at substitutional site in  -SiC, the ionicities decreased but the bond order increased. Electron state densities of s and p components of implanted N atom appeared lower energy level than that of d component of constituent Fe (or Nb) atoms. The charge transfer took place to N atom from surrounding Fe (or Nb) atoms. Thus the ionicity of N atom was larger than mother metal. The bond order between mother elements reduced by N implantation. In particularly, there were significant decreases of bond order in b.c.c. Fe and b.c.c. Nb. Hence, the bond order in whole cluster decreased largely except for f.c.c. Fe. Consequently, it is ...
-SiC, the ionicities decreased but the bond order increased. Electron state densities of s and p components of implanted N atom appeared lower energy level than that of d component of constituent Fe (or Nb) atoms. The charge transfer took place to N atom from surrounding Fe (or Nb) atoms. Thus the ionicity of N atom was larger than mother metal. The bond order between mother elements reduced by N implantation. In particularly, there were significant decreases of bond order in b.c.c. Fe and b.c.c. Nb. Hence, the bond order in whole cluster decreased largely except for f.c.c. Fe. Consequently, it is ...
Morinaga, Masahiko*; *; *; *
PNC TJ9603 97-001, 95 Pages, 1997/03
[PURPOSE] Nb-based and Mo-basd alloys have been investigated in order to develop the frontiers of matelials technique which will be utililized in the environment of high-temperature liquid alkali metals. In this study, both mechanical properties and corrosion resistance to liquid Li were evaluated for two designed Mo-based alloys, Mo-15Re-0.1Zr and Mo-15Re-0.1Zr-0.1Ti. In addition, a series of corrosion test was performed with provisionally designed Nb-based alloys, Nb-(1-4)Hf. [EXPERIMENTAL METHODS] (1)High-temperature tensile test : A tensile test in the Ar atmosphere was carried out at 1473K for the designed Mo-based alloys. Commercial TZM alloy was also tested as a reference. (2)High-temperature creep test : A Creep test in the Ar atmosphere was performed at 1473K under the several applied stress levels for the designed Mo-based alloys. (3)Workability test : A three-point bend test was carried out at room temperature to evaluate the workability of the designed Mo-based alloys. (4)Corrosion resistance to liquid Li : Both the provisionally desingned Nb-based alloys and the designed Mo-based alloys were immersed in the liquid Li at 1473K. The weight change was measured as an indication of the corrosion resistance. Also, the Auger electron spectroscopy analysis was performed with several specimens to examine the surface state of them after corrosion tests. [RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS] (1)High-temperature tensile properties : The designed Mo-based alloys were superior in the tensile properties at 1473K to the commercial TZM alloy. In fact, both the tensile and yield strengths of them were about 1.5 and 2.3 times higher than the TZM alloy, respectively. (2)High-temperature creep properties : The creep rate of the designed Mo-based alloys at 1473K was lower, compared to other solid solution hardening Mo-based alloys, but higher than the precipitation hardening TZM alloy. (3)Workability : The workability of the designed Mo-based alloys was satisfactory regardless ...
Terai, Takayuki*
PNC TJ9602 97-002, 75 Pages, 1997/03
Nuclear materials are often utilized under severe conditions such as high temperature, thermal transient, irradiation, corrosion by liquid metal, particle implantation, electric field and magnetic field, and an investigation on the behavior of the materials is strongly required. However, the property change is so complicated by cooperative effects of these conditions that there have been few studies on it. This project aims to clarify degradation mechanism of ceramics under the complex conditions and to contribute to the development of new advanced ceramics and surface modification. For such purposes, (1)to clarify the change in microstructure, composition and crystal structure of ceramics, (2)to analyze the distribution and condition of radiation defects and implanted ions, (3)to measure physical properties such as electric conductivity and (4)to investigate chemical and mechanical property change due to corrosion are to be carried out. In FY 1996, compatibility of several kinds of ceramic coating materials with liquid metals such as molten lithium and lithium-lead alloy (Li17-Pb83) and electrical resistivity change of these materials in the presence of the liquid metals were investigated. As a result, most of the results were in good agreement with a thermodynamic prediction and most of the compounds maintained their high electrical resistivity even in the presence of liquid lithium and lithium-lead alloy. In addition, it was pointed out that in case of Y O
O , a complex compound (LiYO
, a complex compound (LiYO ) and a non-stoichiometric compound (Y
) and a non-stoichiometric compound (Y O
O ) were formed, which was out of the thermodynamic prediction.
) were formed, which was out of the thermodynamic prediction.
; ; ; ; ; ;
PNC TN9410 96-235, 258 Pages, 1996/03
The chemical decontamination technique has been developed in order to remove the crud adhering to the surface of the components constructing the primary coolant system, as a part of the measure to decrease the exposure in the annual inspection. The technique has been already applied to the prototype reactor "Fugen", in the core of which the fuel assemblies were not loaded. The chemical decontamination, for the core in which the fuel assemblies are loaded, has been planned for the purpose of improving the utilization factor. It is necessary to confirm, through the test before putting the plan into practice, that the decontamination reagent does not exert a bad influence upon the components constructing the fuel assembly. This report describes the test results which have been carried out so as to investigate the influence of the reagent on the components constructing the fuel assembly. The outline of the results is as follows: (1)The susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking of the chemical decontamination treatment and the residual decontamination reagent on the components constructing the fuel assembly is low enough. (2)The chemical decontamination treatment and the residual decontamination reagent do not exert a bad influence upon the integrity of the fuel assembly concerning the fuel rod holding function of the spacer and the characteristics of the fretting wear caused on the fuel claddings.
Morinaga, Masahiko*; Inoue, Satoshi*; Saito, Junichi*; *; *; Kano, Shigeki; Tachi, Yoshiaki
PNC TY9623 93-005, 134 Pages, 1993/03
None
*; Watanabe, Ryuzo*
PNC TJ9601 93-004, 68 Pages, 1993/03
Molybdenum/stainless steel functionally gradient material (FGM). which will be used as long life fuel cladding tubes in the fast breeder reactor, has been fabricated by slurry dipping and sintering process emphasizing the increase in unti-corrosion against liquid sodium and fission products. Slurries of different compositions were prepared by mixing the appropriate amount of molybdenum and stainless steel powders in the ethanol. Green compacts giving cylindrical shape, substrates. were formed by die pressing of stainless steel powders. The substrates were dipped in the slurry, dried in the air and CIP'ed stepwizely: they were encapsulated in Pyrex glass tubes and then HIP'ed 2h at 1573K at the pressure of 150MPa. The microstructural observation in the cross section of the sintered compacts revealed that the uniform dipped layer was formed and there was no defect such as large residual pores or small cracks. A defect free Mo/stainless steel FGM was successfully fabricated by the slurry dipping and sintering process, however, in the case of single phase coating of Mo layer on the stainless steel substrate, the serious delamination was observed. Some oxides and compounds were detected in the FGM layer by the use of SEM-EDX and EPMA analysis.