Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Research 2024-018, 16 Pages, 2025/03
The author aimed to contribute to the analysis of the accident behavior of coated cladding with improved oxidation resistance by chromium (Cr) coating on the outer surface of conventional zirconium alloy fuel cladding, and investigated dependence of the oxidation behavior of Cr on the steam flow rate and on temperature. Coated cladding is being developed as one of the Accident Tolerant Fuel (ATF) claddings, and it is important to analyze the behavior of coated cladding under accidental conditions with high accuracy in the purpose of safety evaluation, for which the oxidation kinetics of Cr in high temperature steam is necessary. In this study, based on the results of oxidation tests in high temperature steam using a thermobalance, an oxidation kinetics for Cr in the temperature range and steam flow rate that encompass the conditions of considerable accident was proposed. The results can be used for future analyses in analysis codes such as SAMPSON, thereby contributing to the development of coated cladding.
Shinotsuka, Hiroshi*; Nagata, Kenji*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Applied Surface Science, 685, p.162001_1 - 162001_11, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Silicon (Si) 2p photoelectron spectra of thermally oxidized Si(001) surfaces were analyzed using Bayesian estimation, a type of mathematical statistical processing, considering spin-orbit interactions. The accuracy of the estimation of fitting parameters and the model selection of the number of peaks were discussed. The spectral analysis was performed without any prior information on the positions of other Si peaks, except for the prominent bulk Si peak, and without using chemical-state assumptions. Our method completely verified previous findings on the surface species and the changes in peaks due to oxidation-induced strain as oxidation progressed.
 O
O , FeUO
, FeUO , and UO
, and UO -Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acid
-Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acidTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 605, p.155561_1 - 155561_9, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Satoshi; Ishii, Sho*; Kato, Hitoshi*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Hiruta, Kenta; Yoshida, Takuya; Uehara, Hiroyuki; Obata, Hiroki; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(1), p.56 - 64, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:57.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A dissolution method for analyzing the elemental composition of fuel debris using the sodium peroxide (Na O
O ) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O
) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na
and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na O
O in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al
in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al O
O , Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
, Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
Kikuchi, Shin; Koga, Nobuyoshi*
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 150(1), p.585 - 590, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kanzaki, Norie; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Nihon Onsen Kiko Butsuri Igakukai Zasshi, 16 Pages, 2024/11
Spa therapy in Misasa (Tottori Prefecture, Japan) is renowned worldwide for its radon therapy (particularly high-concentration radon hot-air bath therapy) along with mine therapy in Bad Gastein (Austria) and Montana (USA). Radon therapy is indicated for diseases related to the respiratory system, pain, digestive disorders, chronic degeneration, and aging caused by reactive oxygen species; however, most of these indications are based on empirical prescriptions. To address this, the authors have been conducting basic research to experimentally and mathematically identify significant radon and its progeny exposure pathways and their related behaviors in the body. The aim is to quantitatively evaluate the relationship between the biological reactions caused by radon inhalation and the absorbed doses in tissues and organs, and to elucidate new mechanisms related to these indications. Therefore, the mechanisms are being elucidated in terms of a series of moderate physiological stimuli caused by small amounts of oxidative stress induced by radon inhalation. Specifically, radon inhalation enhances antioxidant, immune regulation, and damage-repair functions; promotes anti-inflammation, hormone secretion, and circulatory metabolism; and induces apoptosis and heat shock proteins. New indications have been suggested, including inflammatory and neuropathic pain, inflammatory edema, gastric mucosal damage, ulcerative colitis, hyperuricemia, type 1 diabetes, liver and kidney damage, transient cerebral ischemia, and depression. Furthermore, combining radon therapy with antioxidants and therapeutic agents has been suggested to synergistically enhance the disease-suppressing effects of the therapy. Further clinical verification of the combined effects of radon therapy and conventional treatments is required to reduce the dosage of drugs that cause severe side effects.
Oguri, Kaori; Hagura, Naoto*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Aoki, Katsumi; Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 556, p.165516_1 - 165516_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ningyo-toge is the uranium mine that has been operated in Japan. Various radioactive elements such as Uranium (U), and Radium (Ra) are still present in the mine ground water with very small amount, and behavior of those elements is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the composition of metal oxides and clay minerals in a soil of slag deposit at the mine, and systematics of adsorption structure of various ions were examined. Identifying the composition and chemical forms of minerals present in the soil of slag can provide useful information for the safety assessment and evaluation of influence on the surrounding environment.
 Cl on Cu oxide Surfaces; Cu
Cl on Cu oxide Surfaces; Cu O(111) and bulk Cu
O(111) and bulk Cu O precursor "29"; Structure on Cu(111)
O precursor "29"; Structure on Cu(111)Hayashida, Koki*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Murase, Natsumi*; Yamada, Takashi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Di o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
Applied Surface Science, 669, p.160475_1 - 160475_6, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical) Am
Am O
O at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K
at 1473, 1573, and 1673 KWatanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Vauchy, R.; Kato, Masato; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Seki, Takayuki*; Hino, Tetsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155232_1 - 155232_5, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential data of U Am
Am O
O were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U
were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U An
An O
O , where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U
, where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U Am
Am O
O is higher than that of U
is higher than that of U Pu
Pu O
O . The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO
. The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO . At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am
. At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am , U
, U , and U
, and U (for charge compensation of Am
(for charge compensation of Am ). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
 7
7Kakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Anai, Ryota*; Saiki, Taiju*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(31), p.13052 - 13063, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)0xidation at the interface and the surface of Si(111) substrate with thin Hf films were studied using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy in conjunction with supersonic oxygen molecular beams (SOMB). An Hf/Si(111) with a coverage of 0.5 monolayer (ML) included HfSi and HfSi . Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf
. Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi
valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi could be oxidized into the Hf
could be oxidized into the Hf . Following the thermal O
. Following the thermal O exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO
exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO
via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO was generated on the surface.
was generated on the surface.
 C to 1000
C to 1000 C
CImagawa, Yuya; Hashidate, Ryuta; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Onizawa, Takashi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Kaito, Takeji; Onuma, Masato*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.762 - 777, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:62.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing 9Cr-oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel as a fuel cladding material for sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). Previous studies have formulated the creep rupture equation for 650 C to 850
C to 850 C. However, little data have been obtained above 850
C. However, little data have been obtained above 850 C, and no equation has been formulated. This study conducted creep tests to evaluate creep strength at 700
C, and no equation has been formulated. This study conducted creep tests to evaluate creep strength at 700 C to 1000
C to 1000 C. Two creep test methods, the internal pressure and ring creep tests under development, were used, and the validation of the ring creep test method was conducted. The results showed that 9Cr-ODS steel undergoes almost no strength change due to the matrix's phase transformation, and a single equation can express a creep rupture strength from 700
C. Two creep test methods, the internal pressure and ring creep tests under development, were used, and the validation of the ring creep test method was conducted. The results showed that 9Cr-ODS steel undergoes almost no strength change due to the matrix's phase transformation, and a single equation can express a creep rupture strength from 700 C to 1000
C to 1000 C. In validating the ring creep test method, analysis clarified the effect of stress concentration on the specimen. Plastic deformation occurs at high initial stress and may lead to early rupture. The results will be essential for future creep testing and evaluation of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS steel.
C. In validating the ring creep test method, analysis clarified the effect of stress concentration on the specimen. Plastic deformation occurs at high initial stress and may lead to early rupture. The results will be essential for future creep testing and evaluation of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS steel.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10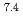 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
Hu, X.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Hori, Junichi*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(11), p.6057 - 6063, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Shunsuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.448 - 458, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 73(4), p.102 - 109, 2024/04
To evaluate the effects of dissolved oxygen concentration to water quality within SCC crack and the distribution of water quality in the depth direction under irradiation, immersion tests of stainless steel specimens given a gap and water radiolysis calculations for the water quality in the crevice gap were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that Fe O
O was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
Kumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen (Internet), 49(1), p.15 - 17, 2024/03
Water radiolysis induces oxidative dissolution of uranium oxides. Understanding of this process is a chemical basis for safety assessment of the deep geological repository of spent fuel and would serve as knowledge for retrieval and storage of fuel debris after a severe accident of nuclear power reactors. In order to evaluate the release rate of radioactive elements from the UO matrix of spent nuclear fuel, several chemical kinetic models have been developed. However, the conventional reaction models were found out to be simplistic based on new insights obtained recent experimental studies. Therefore, the reaction mechanism of surface oxidation and dissolution of uranium is now a subject of revisit. Here, a few recent studies regarding the reaction mechanism are introduced.
matrix of spent nuclear fuel, several chemical kinetic models have been developed. However, the conventional reaction models were found out to be simplistic based on new insights obtained recent experimental studies. Therefore, the reaction mechanism of surface oxidation and dissolution of uranium is now a subject of revisit. Here, a few recent studies regarding the reaction mechanism are introduced.
Tonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 589, p.154862_1 - 154862_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dissolution behavior of FeUO compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO
compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U
with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO
as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO
compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U
dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U O
O ).
).
Matsumura, Daiju; Kimura, Yusaku*; Tsuji, Takuya; Mizuki, Junichiro*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(5), p.296 - 299, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Arai, Taiki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Motohashi, Mitsuya*
Zairyo No Kagaku To Kogaku, 60(5), p.153 - 158, 2023/10
Si oxide films are currently widely used as insulating materials in electronic devices and biomaterials. The atomic bonding state of these films significantly influences the properties of each device, thus it is particularly necessary to understand and control the chemical bonding state between Si and O in the films. In this study, the Si oxide films formed by anodic oxidation on Si substrate surfaces in extremely low concentrations of HF solutions were analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy mainly focusing on Si2p and F1s spectra. Although the HF concentration is in the order of ppm, the films contain percent order of F atoms, suggesting the formation of Si-F and Si-O-F bonds in the films. It was also found that the different depth profiles for F and O atoms was observed, indicating that the surface reaction processes seem to be different depending on each element.
 -type layered manganese dioxide
-type layered manganese dioxideOkamoto, Norihiko*; Yoshisako, Hiroki*; Ichitsubo, Tetsu
Energy Storage Materials, 61, p.102912_1 - 102912_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:50.30(Chemistry, Physical)