Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Hironaka, Kota; Ito, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a method for non-destructive measurement of nuclear material by using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. For NRTA system to carry out the short-distance TOF measurements with high resolutions, a short-pulsed neutron source is required. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) is very suitable as such a neutron source because of its short pulse width. Moreover, the compactness of the laser system is also expected due to the remarkable development of laser technology in recent years. In the present study, we have developed a technology for applying LDNS to the NRTA system and conducted the demonstration experiment using the LFEX laser at Osaka University to investigate the feasibility of the system. In this experiment, we successfully observed the neutron resonance peaks of indium and silver samples.
 Pd and
Pd and  Tc
TcToh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Tsuneyama, Masayuki*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Ebihara, Mitsuru*
Analytical Chemistry, 93(28), p.9771 - 9777, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:37.70(Chemistry, Analytical)Terasaka, Yuta; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Uritani, Akira*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 996, p.165151_1 - 165151_8, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)For the measurement of radiation distribution inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) buildings, the evaluation of a small-diameter quartz optical fiber as a one-dimensional position-sensitive sensor was conducted. The sensor determines the incident position of radiation into the fiber using the time-of-flight information of emitted Cerenkov photons in the optical fiber. Compared with the conventional sensor using the plastic scintillating fiber, the quartz optical fiber has much higher position resolution, which may be the result of the improvement of timing characteristics caused by the prompt emission mechanism of the Cerenkov radiation. Additionally, the response of position-sensitive quartz optical fiber sensor under high radiation field was evaluated, and good count rate linearity was confirmed using the 10 m long quartz optical fiber with a diameter of 0.4 mm up to the dose rate at least 20 mSv/h, and the radiation tolerance property up to the accumulated dose of 1 kGy was evaluated.
Kirihara, Yoichi; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sanami, Toshiya*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Itoga, Toshiro*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Takemoto, Akinori*; Yamaguchi, Masashi*; Asano, Yoshihiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.444 - 456, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:62.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakao, Taro; Terada, Kazushi; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.03021_1 - 03021_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:95.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new data acquisition system (DAQ system) in J-PARC Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) ANNRI was developed. Increasing beam power of MLF in recent years allows beam line users to obtain high quantity experimental data yields. Compared to 2008, more than 20 times beam current is achieved in 2015. For the purpose to correspond strong beam power of MLF, a new DAQ system for the array of the Ge detectors in ANNRI is developed. The DAQ system is also going to be used for processing signals from a Li glass detector, which is under development at ANNRI for measurement of total neutron cross sections. Commissioning experiment of a new DAQ system at ANNRI was performed by using 0.1mmt Au sample with 500kW J-PARC proton beam power. An applicability of time-of-flight method for both neutron capture and total cross-sections measurements was checked. ADC and TDC nonlinearity, energy resolution, multi-channel coincidence and dead time performance for the array of the Ge detectors were also evaluated. The dead time value for Ge detectors was successfully decreased to 1/4 from the previous DAQ system with minor deterioration on energy resolution. The author would like to thank the accelerator and technical staff at J-PARC for operation of the accelerator and the neutron production target and for the other experimental supports. Present study includes the result of "Research and Development for accuracy improvement of neutron nuclear data on minor actinides" entrusted to the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
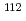 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARC
Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARCHayakawa, Takehito*; Toh, Yosuke; Huang, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Chiba, Satoshi*; Kajino, Toshitaka*
Physical Review C, 94(5), p.055803_1 - 055803_6, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.95(Physics, Nuclear)Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Takada, Masashi*; Ishibashi, Kenji*
AIP Conference Proceedings 769, p.1680 - 1683, 2005/05
Response function of liquid organic scintillators is essential to derive the accurate neutron spectrum. Experimental data above 100 MeV, however, are very scarce. The existing Monte Carlo codes, SCINFUL and CECIL, are often used for estimation of the response function instead of the experimental data. These codes are known to reproduce well the response function for incidences below 100 MeV. Unfortunately, the codes are not applicable to the calculation in the higher energy region. In order to determine the response functions above 100 MeV, a new Monte Carlo code, designated as SCINFUL-QMD, has been developed. In the comparison with the experimental data up to 800 MeV, the validation of SCINFUL-QMD was confirmed. The results of SCINFUL-QMD agreed with the experimental data better than those of other calculation codes.
Kobayashi, Katsuhei*
JNC TJ9400 2000-009, 63 Pages, 2000/02
The present status of nuclear data for technetium (Tc)-99, which is a well-known fission product (FP), has been reviewed and investigated. And making use of the Kyoto university Lead Slowing-down Spectrometer (KULS), the cross section of the  Tc (n,
Tc (n,  )
)  Tc reaction has been measured in the energy range from thermal to keV neutron energy with an Ar-gas proportinal counter. The neutron flux/spectrum has been monitored with a BF
Tc reaction has been measured in the energy range from thermal to keV neutron energy with an Ar-gas proportinal counter. The neutron flux/spectrum has been monitored with a BF proportional counter, and the relative measurement has been normalized to the well-known standard capture cross section value for the
proportional counter, and the relative measurement has been normalized to the well-known standard capture cross section value for the  Tc (n,
Tc (n,  )
)  Tc reaction at 0.0253 eV. Self-shielding corrections, especially near the resonance peaks, were made by the calculations with the MCNP code. Although the experimental data measured by Chou et al with a lead slowing-down spectrometer are higher in general, the energy dependency is similar to the present measurement. The evaluated data in ENDF/B-VI and JENDL-3.2 are higher near the resonances at 5.6 and 20 eV and above several 100 eV. A lead slowing-down spectrometer was installed coupled to a 46 MeV electron linac at the Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto university (KURRI). Characteristics of the Kyoto University Lead Slowing-down Spectrometer (KULS) were measured and (1)the relation between neutron slowing-down time t(
Tc reaction at 0.0253 eV. Self-shielding corrections, especially near the resonance peaks, were made by the calculations with the MCNP code. Although the experimental data measured by Chou et al with a lead slowing-down spectrometer are higher in general, the energy dependency is similar to the present measurement. The evaluated data in ENDF/B-VI and JENDL-3.2 are higher near the resonances at 5.6 and 20 eV and above several 100 eV. A lead slowing-down spectrometer was installed coupled to a 46 MeV electron linac at the Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto university (KURRI). Characteristics of the Kyoto University Lead Slowing-down Spectrometer (KULS) were measured and (1)the relation between neutron slowing-down time t( s) and energy E(keV) (E=190/t
s) and energy E(keV) (E=190/t in Bi hole and E=156/t
in Bi hole and E=156/t in Pb hole) and (2)the energy resolution (
in Pb hole) and (2)the energy resolution ( 40% in Bi and Pb holes) were experimentally investigated. (3)The neutron energy spectrum in the KULS was also measured by the neutron TOF method. The results obtained by the MCNP code were in general agreement with these experimental ones.
40% in Bi and Pb holes) were experimentally investigated. (3)The neutron energy spectrum in the KULS was also measured by the neutron TOF method. The results obtained by the MCNP code were in general agreement with these experimental ones.
JNC TJ9400 2000-008, 61 Pages, 2000/02
For studies on nuclear transmutation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs) in a fast reactor, detailed characteristics of reactor core such as transmutation performance have to be investigated, so accurate neutron cross section data of LLFPs become necessary. Therefore, the keV-neutron capture cross sections of Tc-99, which is one of important LLFPs, were measured in the present study to obtain the accurate data. The measurement was relative to the standard capture cross sections of Au-197. A neutron time-of-flight method was adopted with a ns-pulsed neutron source by a Pelletron accelerator and a large anti-Compton NaI(TI) gamma-ray detector. As a result, the capture cross sections of Tc-99 were obtained with the error of about 5 % in the incident neutlon energy region of 10 to 600 keV. The present data were compared with other experimental data and the evaluated values of JENDL-3.2, and it was found that the evaluations of JENDL-3.2 were 15-20 % smaller than the present measurements.
Shibata, Takemasa; Ogura, Koichi
JAERI-Research 99-008, 10 Pages, 1999/02
no abstracts in English
Kokooo*; Murata, Isao*; Nakano, D.*; Takahashi, Akito*; Maekawa, Fujio; Ikeda, Yujiro
Fusion Technology, 34(3), p.980 - 984, 1998/11
no abstracts in English
PNC TJ9601 98-002, 115 Pages, 1998/03
In fuel cycles with recycled actinide, core characteristics are largely influenced by minor actinide (MA: Np, Am), Accurate nuclear data of MA such as fission cross section are required to estimate the effect of MA with high accuracy. In this study, fast neutron induced fission cross section of MA was measured using Dynamitron Accelerator in Tohoku University. New or improved techniques and tools with high precision and fast timing capability were developed for this study. Those are as follows: (1)Development of a sealed fission chamber,(2)Intensification of Li neutron target, (3)Improvement of time-resolution of Time-of-Right (TOF) electronic circuit, (4)Introduction of MA (Np237, Am241 and Am243) samples with large sample mass and (5)Introduction of a U235 sample with high purity. Using these improved tools and samples, fission cross section of Np237 was measured between 10 to 100 keV. On the other hand, averaged fission cross section for Maxwell distribution spectrum with kt=25.3 keV was measured for Am241 and Am243.
PNC TJ9601 97-001, 51 Pages, 1997/03
In fuel cycles with recycled actinide, core characteristics are largely influenced by minor actinide (MA:Np, Am, Cm). Accurate nuclear data of MA such as fission cross section are required to estimate the effect of MA with high accuracy.In this study fast neutron induced fission cross section of MA is measured using Dynamitron Accelerator in Tohoku University. The experimental method and the samples, which were developed or introduced during the last year, were improved in this fiscal year: (1)Development of a sealed fission chamber, (2)Intensification of Li neutron target, (3)Improvement of time-resolution of Time-of-flight (TOF) electronic circuit, (4)Introduction of Np237 samples with large sample mass and (5)Introduction of a U235 sample with high purity. Using these improved tools and samples, the fission cross section ratio of NP237 relative to U235 was measured between 5 to 100keV, and the fission cross section of Np237 was deduced. On the other hand, samples of Am241 and Am243 were obtained from Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) after investigating fission cross section of two americium isotopes (Am241 and Am243) which are important for core physics calculation of fast reactors.
Ogiwara, Norio; Miyo, Yasuhiko;
Vacuum, 47(6-8), p.575 - 578, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; ; ; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takada, Hiroshi; Chiba, Satoshi; Numajiri, M.*; Nakamura, Takashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(9), p.827 - 833, 1995/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:92.17(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; ; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-M 94-056, 11 Pages, 1994/03
no abstracts in English
T.Elevant*; M.Hoek*; Nishitani, Takeo
JAERI-M 93-123, 20 Pages, 1993/06
no abstracts in English
Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-M 93-099, 12 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English
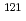 Sb,
Sb, 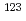 Sb,
Sb,  Ce and
Ce and 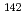 Ce in the resonance region
Ce in the resonance regionOkubo, Makio; Mizumoto, Motoharu; Nakajima, Yutaka
JAERI-M 93-012, 44 Pages, 1993/02
no abstracts in English