Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Yokota, Hiromi*; Fujimoto, Katsushige*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Bunseki Kagaku, 73(9), p.515 - 522, 2024/09
On-line isotope dilution-laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (on-line ID-LA-ICP-MS) is capable of quantification for each point ablated by laser, then the quantitative mapping of elements can be also conducted by reconstruction of the obtained each point data. The volume of data obtained as flow peaks in this system as a flow injection analysis, will be multiplied by each data such as number of m/z, scan time, time resolution and measurement position, and the total amount of data is enormous, resulting in a large human power and time consumption for data processing. In this paper, an original application software using Python to improve the efficiency of data processing in on-line ID-LA-ICP-MS was developed. To discriminate between the time-to-peak intensity and the background noise, an automatic peak detection using penalized asymmetric least squares was developed.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kawashima, Shigeto*; Kajino, Mizuo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.743 - 758, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)An accurate estimation of radionuclides released during the Fukushima accident is essential. Therefore, authors investigated Te release using the Unit emission-regression estimation method, in which the deposition distribution is weighted based on the hourly deposition obtained from mesoscale meteorological model calculations assuming Unit emissions. The previous study focused on confirming the applicability of this method. Subsequent examination revealed that if any part of the time when a release have occurred is missing from the estimated release period, the entire source term calculation will be distorted. Therefore, this study performed the recalculation by extending the estimation period to cover all major releases. Consequently, unspecified release events were clarified, and their correspondence to in-core events was confirmed. The 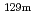 Te release caused by Zr cladding complete oxidation can explain the regional dependence of the
Te release caused by Zr cladding complete oxidation can explain the regional dependence of the 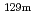 Te/
Te/ Cs ratio in the soil contamination map.
Cs ratio in the soil contamination map.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-004, 64 Pages, 2018/03
Experiment SB-SG-10 was conducted on November 17, 1992 using LSTF. Experiment simulated recovery actions from multiple steam generator (SG) tube rupture accident in PWR. Primary pressure was kept higher than broken SG secondary-side pressure due to coolant injection from high pressure injection (HPI) system into cold and hot legs even after start of full opening of intact SG relief valve (RV). Full opening of power-operated relief valve (PORV) in pressurizer (PZR) resulted in pressure equalization between primary and broken SG systems as well as PZR liquid level recovery. Broken SG RV opened once after start of intact SG RV full opening. Core was filled with saturated or subcooled liquid through experiment. Significant natural circulation prevailed in intact loop after start of intact SG RV full opening. Significant thermal stratification appeared in hot legs especially during time period of HPI coolant injection into hot legs.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-004, 59 Pages, 2016/07
The TR-LF-07 test simulated a loss-of-feedwater transient in a PWR. A SI signal was generated when steam generator (SG) secondary-side collapsed liquid level decreased to 3 m. Primary depressurization was initiated by fully opening a power-operated relief valve (PORV) of pressurizer (PZR) 30 min after the SI signal. High pressure injection (HPI) system was started in loop with PZR 12 s after the SI signal, while it was initiated in loop without PZR when the primary pressure decreased to 10.7 MPa. The primary and SG secondary pressures were kept almost constant because of cycle opening of the PZR PORV and SG relief valves. The PZR liquid level began to drop steeply following the PORV full opening, which caused liquid level formation at the hot leg. The primary pressure became lower than the SG secondary pressure, which resulted in the actuation of accumulator (ACC) system in both loops. The primary feed-and-bleed operation was effective to core cooling because of no core uncovery.
Takei, Hayanori; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(12), p.1032 - 1039, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)In high-intensity proton accelerator facilities, a failure of an electromagnet that steers beam pulses may result in thermal shock damage on the accelerator component by injecting an out-of-control pulse. It is important that a Machine Protection System (MPS) is appropriately designed to prevent this damage in the facilities such as Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). In this study, the simple evaluation method for the allowable injection time before the operation of the MPS was derived from the relation between the thermal stress and the yield stress of materials.The derived evaluation method was then applied to J-PARC. The allowable injection time for each component ranged from 0.1 to 70  s.
s.
Kuriyama, Masaaki; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Grisham, L. R.*; Honda, Atsushi; Ito, Takao; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Ohara, Yoshihiro; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.410 - 423, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:92.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kawai, Katsuo; Endo, Akira; Noguchi, Hiroshi
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-013, 66 Pages, 2002/05
Effective dose coefficients by inhalation and ingestion have been calculated for 334 nuclides, including (1) nuclides with half-lives 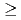 10min and their daughters that are not listed in ICRP Publications and (2) nuclides with half-lives
10min and their daughters that are not listed in ICRP Publications and (2) nuclides with half-lives  10min that are produced in a spallation target. Dose calculation was carried out using a nuclear decay database DECDC and a decay data library newly compiled from the ENSDF. The dose coefficients were calculated with the computer code DOCAP based on the respiratory tract model and biokinetic model of ICRP. The calculated results are presented as tables, which are the same forms as those in ICRP Publs.68 and 72. The complete listings of the dose coefficients are arranged on a CD-ROM, DoseCD, as indexed tables for inhalation of ten particle sizes, ingestion and injection into blood for workers and members of the public. The dose coefficients calculated in the present study are useful to calculate internal doses for a variety of radionuclides produced in high energy proton accelerator facilities.
10min that are produced in a spallation target. Dose calculation was carried out using a nuclear decay database DECDC and a decay data library newly compiled from the ENSDF. The dose coefficients were calculated with the computer code DOCAP based on the respiratory tract model and biokinetic model of ICRP. The calculated results are presented as tables, which are the same forms as those in ICRP Publs.68 and 72. The complete listings of the dose coefficients are arranged on a CD-ROM, DoseCD, as indexed tables for inhalation of ten particle sizes, ingestion and injection into blood for workers and members of the public. The dose coefficients calculated in the present study are useful to calculate internal doses for a variety of radionuclides produced in high energy proton accelerator facilities.
Gottdang, A.*; Klein, M.*; Mous, D. J. W.*; Kitamura, Toshikatsu; Mizutani, Yoshihiko*; Suzuki, Takashi; Aramaki, Takafumi; Togawa, Orihiko; Kabuto, Shoji*; Sudo, Kazuhiko*
AIP Conference Proceedings 576, p.403 - 406, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
JAERI-Research 97-057, 20 Pages, 1997/08
no abstracts in English
H.-S.Park*; Yamano, N.; Maruyama, Yu; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Kudo, Tamotsu; Sugimoto, Jun
JAERI-Review 96-018, 46 Pages, 1996/11
no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide; Soda, Kunihisa; Sugimoto, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(6), p.527 - 538, 1995/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:36.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; Murao, Yoshio
JAERI-M 83-044, 160 Pages, 1983/03
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 18(4), p.233 - 250, 1976/04
no abstracts in English