Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe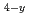 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Aoyama, Takahito; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Otani, Kyohei; Igarashi, Takahiro
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111229_1 - 111229_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So; Nakahara, Masaumi; Funakoshi, Tomomasa; Hoshino, Takanori; Takahatake, Yoko; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Aihara, Haruka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshida, Toshiki; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.168 - 174, 2025/05
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a project named "Systematic Treatment of RAdioactive liquid waste for Decommissioning (STRAD)" project since 2018 for fundamental and practical studies for treating radioactive liquid wastes with complicated compositions. Fundamental studies have been conducted using genuine liquid wastes accumulated in a hot laboratory of the JAEA called the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF), and treatment procedures for all liquid wastes in CPF were successfully designed on the results obtained. As the next phase of the project, new fundamental and practical studies on primarily organic liquid wastes accumulated in different facilities of JAEA are in progress. This paper reviews the representative achievements of the STRAD project and introduces an overview of ongoing studies.
Sato, Yuki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf046_1 - ncaf046_11, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hydridosilicates featuring SiH octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH
octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH
obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH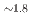 with H
with H fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH
fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH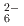 ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba
ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH
counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH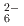 bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm
bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm , respectively. BaSiH
, respectively. BaSiH is thermally stable up to 95
is thermally stable up to 95 C above which decomposition into BaH
C above which decomposition into BaH and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH
and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (
consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (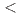 10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH
10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH
suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH .
.
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Ichiba, Yuta*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(4), p.389 - 400, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)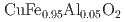
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Uchihara, Takeru*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Ishii, Yuta*; Nakao, Hironori*; Takehana, Kanji*; Imanaka, Yasutaka*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear Backend Technology Development
JAEA-Evaluation 2024-002, 86 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (hereinafter referred to as "JAEA") consulted the "Evaluation Committee on Research and Development Activities for Decommissioning" (hereinafter referred to as "Committee") about the in-advance evaluation of research themes which had started after FY2021 of R&D plan for the 4th medium- and long-term objectives period concerning "Decommissioning of nuclear facilities and development of technologies for the treatment of related radioactive waste" project in accordance with the "Guideline for evaluation of government R&D activities". In response, the Committee evaluated to the evaluation points of view made by JAEA.
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional van der Waals ferromagnet Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
(FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
Scaria, J.*; P drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 59(11), p.5747 - 5755, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Understanding and predicting the interaction mechanisms between chromium and magnetite is of particular interest to elucidate the biogeochemical behavior of Cr in the environment and to develop optimal soil remediation and water treatment strategies. However, while the elimination of the most toxic form of (Cr(VI)) by its reduction to Cr(III) has widely been documented, elucidating the exact mechanism involved in Cr(III) sorption to magnetite has attracted less attention. This study examined the interaction of Cr(III) solution with 10 nm-sized magnetites, whose stoichiometries were carefully defined and preserved in anaerobic conditions. This study reveals the joint effects of pH and magnetite stoichiometry on Cr(III) sorption mechanism, and that Cr(III)-(hydr)oxide precipitation is not necessarily the driving process of Cr(III) elimination from solutions. These results will help predict the fate and transport of chromium, as well as developing magnetite-based chromium remediation processes.
Sato, Yuki; Minemoto, Kojiro*; Nemoto, Makoto*
Proceedings of Waste Management Conference 2025 (WM2025) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2025/03

Chung, J.-H.*; Kwangwoo, S.*; Yokoo, Tetsuya R.; Ueta, Daichi*; Imai, Masaki; Kim, H.-S.; Kiem, D. H.; Han, M. J.*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 15, p.5978_1 - 5978_10, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Suetake, Koya*; Ogata, Sho*; Yasuhara, Hideaki*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Inui, Toru*; Kishida, Kiyoshi*
Dai-16-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.304 - 309, 2025/01
It is very important to predict the extent of EDZ (excavation disturbed zone) and the behavior of hydraulic conductivity after excavation of shafts and tunnels for geological disposal of radioactive waste. In this study, we attempted to reproduce the in-situ tunnel excavation test and the subsequent permeability test at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) using a three-dimensional tunnel excavation simulator. As a result, similar results to the in-situ tests were obtained for the extent of EDZ propagation by excavation and the results of permeability tests. The simulator is effective in predicting the mechanical effects of excavation, coupled phenomena such as deformation and seepage, and hydraulic conductivity in deep mudstones in Japan.
Maeda, Mizuho*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kimura, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(2), p.024707_1 - 024707_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Yuki; Kakuto, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Takayuki*; Shimano, Hiroyuki*
European Physical Journal; Special Topics, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Onoda, Yuichi; Uchita, Masato*; Tokizaki, Minako*; Okazaki, Hitoshi*
Nuclear Technology, 20 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Yuki; Minemoto, Kojiro*; Nemoto, Makoto*; Matsuura, Yasutaka*; Hayashi, Keisuke*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Decommissioning; Addressing the Past and Ensuring the Future 2023 (Internet), 4 Pages, 2025/00
The development of technology to visualize the distribution of radioactive substances at the decommissioning site of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) is important for reducing worker exposure and developing a detailed work plan. Sato, one of the authors, developed an integrated Radiation Imaging System (iRIS) that combines a Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) device, a Compton camera (a type of gamma-ray imager), and a survey meter, and have successfully produced a 3-D map of the working environment inside the FDNPS that visualizes the location of radioactive hot spots and the distribution of air dose rates. In addition, the authors are developing a system that enables users to experience the radiation environment of the FDNPS in virtual reality (VR) using the 3-D map visualizing such radiation information as input data. This VR system can use a commercially available portable VR head-mounted display, which not only displays the location of the radiation source in a virtual space, but also has the ability to calculate the exposure dose according to the working time. The development status of this VR system, which is expected to be effective in educating inexperienced workers and planning work, will be presented at the conference.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2024-016, 61 Pages, 2024/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust and high-dose rate monitor" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to develop a high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust and a high-dose rate monitor. To realize the high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust, we have developed novel scintillation materials with emission bands of 500-800 nm. Moreover, we have prepared several materials for the camera and software. We have also developed novel scintillation materials with emission bands of 650-1,000 nm, and simulation studies have been conducted for the high-dose-rate monitor system consisting of optical fiber.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-014, 76 Pages, 2024/12
An experiment denoted as SB-PV-03 was conducted on November 19, 2002 using the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) in the Rig of Safety Assessment-V (ROSA-V) Program. The ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-PV-03 simulated a 0.2% pressure vessel bottom small-break loss-of-coolant accident in a pressurized water reactor (PWR). The test assumptions included total failure of high pressure injection system of emergency core cooling system (ECCS) and noncondensable gas (nitrogen gas) inflow to the primary system from accumulator (ACC) tanks of ECCS. Secondary-side depressurization of both steam generators (SGs) as an accident management (AM) action to achieve the depressurization rate of 55 K/h in the primary system was initiated 10 min after the generation of a safety injection signal, and continued afterwards. Auxiliary feedwater injection into the secondary-side of both SGs was started for 30 min with some delay after the onset of the AM action. The AM action was effective on the primary depressurization until the ACC tanks began to discharge nitrogen gas into the primary system. The core liquid level recovered in oscillative manner because of intermittent coolant injection from the ACC system into both cold legs. Therefore, the core liquid level remained at a small drop. The pressure difference between the primary and SG secondary sides became larger after nitrogen gas ingress. Core uncovery occurred by core boil-off during reflux condensation in the SG U-tubes under nitrogen gas influx. When the maximum cladding surface temperature of simulated fuel rods exceeded the pre-determined value of 908 K, the core power was automatically reduced to protect the LSTF core. After the automatic core power reduction, coolant injection from low pressure injection (LPI) system of ECCS into both cold legs led to the whole core quench. After the continuous core cooling was confirmed through the actuation of the LPI system, the experiment was terminated.
Wakui, Takashi; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Jikken Rikigaku, 24(4), p.212 - 218, 2024/12
Irradiation damage is one of the main factors determining the lifetime of the mercury target vessel for spallation neutron source in J-PARC. To understand material degradation of the used vessels, it is planned to conduct an evaluation using inverse analyses with indentation tests on the structural materials of the used vessels and numerical experiments. This evaluation technique was applied to two kinds of ion-irradiated materials with different displacement damage doses, in which the irradiation condition was simulated. It could be confirmed that the ultimate strength increased, and the total elongation decreased with increasing irradiation. These trends are like the material degradation behaviors which have been reported by using small specimen's tensile tests.