Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukushima, Masahiro; Ando, Masaki; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 199(6), p.1029 - 1043, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Abe, Takumi; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.299 - 304, 2025/05
Currently, much research continues on stable energy sources that do not emit CO in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 16 Pages, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigated the impact of nuclear data updates from JENDL-4.0 (J4) to JENDL-5 (J5) on the light-water reactor fuel burnup calculations. Burnup calculations were conducted with J4 and J5 for PWR pin-cell and BWR fuel assembly geometries. The calculation results revealed significant burnup-dependent differences in the neutron multiplication factor (k ). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k
). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of
values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H
Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H O notably impacted the k
O notably impacted the k differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k
differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the
differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the  U,
U,  Gd, and
Gd, and  Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H
Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k
O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
Fuyushima, Takumi; Sayato, Natsuki; Otsuka, Kaoru; Endo, Yasuichi; Tobita, Masahiro*; Takemoto, Noriyuki
JAEA-Testing 2024-008, 38 Pages, 2025/03
In Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), irradiation tests had been conducted by loading specimens into capsules for irradiating fuels and materials. The thermal design calculation of capsules is significant to irradiate various types of specimens at the target temperature. The decommissioning plan of JMTR was approved in March 2021, and the Department of Waste Management and Decommissioning Technology Development is currently working on irradiation plans by foreign testing reactors as an alternative for JMTR. A one-dimensional thermal calculation code "GENGTC", which was developed at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in U.S., is used for capsule design and irradiation tests. GENGTC has been repeatedly improved as improvements of computer performance, but there were some defects in calculation function. Therefore, we investigated the cause of the problem and changed the program from the currently used FORTRAN77 language program to a Visual Basic language program that uses the macro calculation function of Excel. In addition, the program was improved to make it easier to use the calculation code.
Tomioka, Dai; Kochiyama, Mami; Ozone, Kenji; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2024-023, 38 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an implementing organization of near-surface disposal for low-level radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial and medical facilities in Japan. Information on the radioactivity concentration of these radioactive wastes is dispensable for the design and conformity assessment of the waste disposal facilities for the licensing application of the disposal project and its safety review. Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center has been improving the radioactivity evaluation procedure for the dismantling waste generated from the research reactors based on the activation calculation. In order to investigate the applicability of the ORIGEN code (included in SCALE6.2.4), which enables more accurate activation calculations using multigroup neutron spectra, we performed activation calculations with the ORIGEN-code and the ORIGEN-S code (included in SCALE6.0), which has been widely used in the past, for the dismantled wastes from the Rikkyo University Research Reactor, where radioactivity analysis data for the structural materials around the reactor core were compiled. As a result, the calculation time difference between ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S was small and the evaluated radioactivity concentrations of the former were in the range of 0.8-1.0 times those of the latter, which was in good agreement with those of radiochemical analysis in the range of 0.5-3.0 times. The applicability of ORIGEN was confirmed. In addition, activation calculations assuming trace elements in structural materials of nuclear reactor were performed with ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S and the results were compared. The causes of the large differences among 170 nuclides that are important for dose assessment in near-surface disposal were assessed each nuclide.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Ando, Masaki; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 199(1), p.18 - 41, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of integral experiments were conducted at FCA of JAEA, simulating LWR cores with a tight lattice cell of highly enriched MOX fuel containing more than 15% fissile plutonium. The three experimental configurations were constructed using foamed polystyrene with different void fractions to clarify the prediction accuracy of neutronic calculation codes and nuclear data among various neutron spectra. The nuclear characteristics measured in the experiments were criticality, moderator void reactivity worths, and sample reactivity worths. The preliminary analyses on experiments were conducted using a deterministic calculation code conventionally used for fast reactors with JENDL-4.0. Most reactivity worth calculations correlated well with the experimental values. Specifically for the softer neutron spectra configurations, the treatment of ultrafine energy groups obviously improved the prediction accuracy of the deterministic calculations. Furthermore, reference calculations were performed with MVP3 code by modeling the experimental setup in detail, confirming the validity of the deterministic calculations.
Sakamoto, Masahiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Kanno, Ikuo; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kaneko, Junichi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Yuki
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 212, p.111421_1 - 111421_8, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Maruyama, Shuhei; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 205, p.110591_1 - 110591_13, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Nagasumi, Satoru; Hasegawa, Toshinari; Kawai, Hiromi*; Wakisaka, Shinji*; Nagase, Sota*; Nakamura, Kento*; Yaguchi, Hiroki*; Ishii, Toshiaki; Nakano, Yumi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-008, 23 Pages, 2024/07
Five people from three universities participated in the 2023 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the analysis of HTTR core, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, the analysis of Iodine deposition behavior in primary cooling system and the feasibility study of energy storage system for HTGRs. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience and some students found it useful for their own research. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Riyana, E. S.; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Kanno, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.269 - 276, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Physical Review B, 108(22), p.224301_1 - 224301_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:62.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1386 - 1396, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The burnup calculations for estimating the nuclide composition of the spent fuel are highly dependent on nuclear data. Many nuclides in the latest version of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 were modified from JENDL-4.0 and the modification affects the burnup calculations. This study confirmed the validity of JENDL-5 in the burnup calculations. The PIE data of Takahama-3 was used for the validation. The effect of modifications of the parameters, e.g., cross sections and fission yields, from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5 on the nuclide compositions was quantitatively investigated. The calculation results showed that JENDL-5 has a similar performance to JENDL-4.0. The calculation results also revealed that the modifications of the cross sections of actinide nuclides, fission yields, and thermal scattering low data of hydrogen in H O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
 inferred from muon study
inferred from muon studyKadono, Ryosuke*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Koda, Akihiro*; Ito, Takashi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285503_1 - 285503_13, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.32(Physics, Condensed Matter)Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ho, H. Q.; Kitagawa, Kanta*; Fukuda, Takahito*; Ito, Ryo*; Nemoto, Masaya*; Kusunoki, Hayato*; Nomura, Takuro*; Nagase, Sota*; Hashimoto, Haruki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-013, 19 Pages, 2023/06
Eight people from five universities participated in the 2022 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the feasibility study for nuclear battery, the burn-up analysis of HTTR core, the feasibility study for  Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Kido, Kentaro; Kaneko, Masashi
Journal of Computational Chemistry, 44(4), p.546 - 558, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.83(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Katano, Ryota; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 196(10), p.1194 - 1208, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, we propose the ROM-Lasso method that enables efficient evaluation of sensitivity coefficients of neutronics parameters to cross-sections. In the proposed method, a vector of sensitivity coefficients is expanded by subspace bases, so-called Active Subspace (AS) based on the idea of Reduced Order Modeling (ROM). Then, the expansion coefficients are evaluated by the Lasso linear regression between cross-sections and neutronics parameters obtained by the random sampling. The proposed method can be applied in the case where the adjoint method is difficult to be applied since the proposed method uses only forward calculations. In addition, AS is an effective subspace that can expand the vector of sensitivity coefficients with the lower number of dimension. Thus, the number of unknows is reduced from the original number of input parameters and the calculation cost is dramatically improved compared to the Lasso regression without AS. In this paper, we conducted ADS burnup calculations as a verification. We have shown how AS bases are obtained and the applicability of the proposed method.
Suzuki, Kenta; Yashiro, Hiroshi*; Kawabata, Kuniaki
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
Isogawa, Hiroki*; Naoi, Motomasa*; Yamasaki, Seiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Katayama, Kazunari*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2022-015, 18 Pages, 2022/07
As a summer holiday practical training 2021, the impact of 10 years long-term shutdown on critical control rod position of the HTTR and the delayed neutron fraction (
 ) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0
) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0 0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as
0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am, 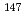 Pm,
Pm, 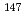 Sm,
Sm,  Gd. Regarding the
Gd. Regarding the 
 calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the
calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the 
 value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.
value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.