Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Kazuo; Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2024-007, 24 Pages, 2024/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. It has been observed experimentally that volatility of RuO is suppressed by HNO
is suppressed by HNO generated by HNO
generated by HNO radiolysis. The analysis of chemical reactions of NO
radiolysis. The analysis of chemical reactions of NO including HNO
including HNO and HNO
and HNO in the waste tank is essential to simulate of these phenomena. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been attempted to couple dynamically two computer codes SHAWED and SCHERN. The simulation of boiling behavior in the tank is conducted with SHAWED. SCHERN simulates chemical behaviors of HNO
in the waste tank is essential to simulate of these phenomena. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been attempted to couple dynamically two computer codes SHAWED and SCHERN. The simulation of boiling behavior in the tank is conducted with SHAWED. SCHERN simulates chemical behaviors of HNO , HNO
, HNO and NO
and NO in the tank. A programmatic coupling algorithm and a trial simulation of the accident are presented in this report.
in the tank. A programmatic coupling algorithm and a trial simulation of the accident are presented in this report.
Zablackaite, G.; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Kido, Kentaro; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 56(2), p.536 - 545, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Thwe Thwe, A.; Kadowaki, Satoshi; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.731 - 742, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, we performed numerical calculations of unsteady reaction flow considering detailed chemical reactions, investigated the unstable behavior of hydrogen-air dilute premixed flame due to intrinsic instability, and clarified the effects of unburned gas temperature and pressure. I made it. The unstable behavior of the flame in a wide space was simulated, and the burning rate of the cellular flame was obtained. Then, the effects of heat loss and flame scale on flame unstable behavior were investigated. The burning velocity of a planar flame increases as the unburned-gas temperature increases and it decreases as the unburned-gas pressure and heat loss increase. The normalized burning velocity increases when the pressure increases and heat loss becomes large, and it decreases when the temperature increases. This is because the high unburned-gas pressure and heat loss promote the unstable behavior and instability of flame.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2023-001, 26 Pages, 2023/05
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been developed using computer simulation programs to assess the radioactive source term from those facilities. The proposed approach consists analyses with three computer programs. At first, the simulation of boiling behavior in the HLLW tank is conducted with SHAWED code. Next step, the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code based on the results at the first step simulation such as flowed out mixed steam flow rate, temperature and volatilized Ru from the tank. The final analysis step is carried out for estimating amount of released radioactive materials with SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitric acid, nitrogen oxide and Ru based on the condition also simulated MELCOR. Series of sample simulations of the accident at a hypothetical typical facility are presented with the data transfer between those codes in this report.
Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Kato, Atsushi; Hayakawa, Masato; Shimoyama, Kazuhito; Ara, Kuniaki; Hatakeyama, Nozomu*; Yamauchi, Kanau*; Eda, Yuhei*; Yui, Masahiro*
Proceedings of 2023 International Congress on Advanced in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/04
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-013, 20 Pages, 2022/01
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. An idea has been proposed to implement a steam condenser as an accident countermeasure. This measure is expected to prevent nitric acid steam diffusing in facility building and to increase gaseous Ru trapping ratio into condensed water. A simulation study has been carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building to analyze the efficiency of steam condenser. In this study, SCHERN computer code simulates chemical behaviors of Ru in nitrogen oxide, nitric acid and water mixed vapor based on the conditions obtained from simulation with thermal-hydraulic computer code MELCOR. The effectiveness of steam condenser has been analyzed quantitively in preventing mixed vapor diffusion and gaseous Ru trapping effect. Some issues to be solved in analytical model has been also clarified in this study.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-005, 25 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an empirical correlation equation of Ru mass transfer coefficient across the vapor-liquid surface, which can be useful for quantitative simulation of Ru mitigating behavior, has been obtained from data analyses of small-scale experiments conducted to clarify gaseous Ru migrating behavior under steam-condensing condition. A simulation study has been also carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building successfully to demonstrate the feasibility of quantitative estimation of amount of Ru migrating in the facility using the obtained correlation equation implemented in SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitrogen oxide based on the condition also simulated thermal-hydraulic computer code.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-008, 35 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides (NO ) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO
) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Gou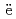 llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1287 - 1296, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:65.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to clarify the cesium iodide (CsI) transport behavior with a focus on the mechanisms of gaseous iodine formation in the reactor coolant system of LWR under a severe accident condition, a reproductive experiment of CsI transport behavior was conducted using a facility equipped with a thermal gradient tube. Various analyses on deposits and airborne materials during transportation could elucidate two mechanisms for the gaseous iodine formation. One was the gaseous phase chemical reaction in Cs-I-O-H system at relatively high-temperature region, which led to gaseous iodine transport to the lower temperature region without any further changes in gas species due to the kinetics limitation effects. The other one was the chemical reactions related to condensed phase of CsI, namely those of CsI deposits on walls with surface of stainless steel to form Cs CrO
CrO compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Naoki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(2), p.69 - 80, 2019/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that nitrogen oxide affects strongly to the transport behavior of Ru. Chemical reactions of nitrogen oxide with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. An analysis method has been developed with coupling two types of computer codes to simulate not only thermo-hydraulic behavior but also chemical reactions in the flow paths of carrier gases. A simulation study has been also carried out with a typical facility building.
Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(2), p.228 - 240, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:63.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to improve LWR source term under severe accident conditions, the first version of a fission product (FP) chemistry database named "ECUME" was developed. The ECUME is intended to include major chemical reactions and their effective kinetic constants for representative SA sequences. It is expected that the ECUME can serve as a fundamental basis from which FP chemical models in the SA analysis codes can be elaborated. The implemented chemical reactions in the first version were those for representative gas species in Cs-I-B-Mo-O-H system. The chemical reaction kinetic constants were evaluated from either literature data or calculated values using ab-initio calculations. The sample chemical reaction calculation using the presently constructed dataset showed meaningful kinetics effects at 1000 K. Comparison of the chemical equilibrium compositions by using the dataset with those by chemical equilibrium calculations has shown rather good consistency for the representative Cs-I-B-Mo-O-H species. From these results, it was concluded that the present dataset should be useful to evaluate FP chemistry in Cs-I-B-Mo-O-H system under LWA SA conditions.
Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Proceedings of 2017 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2017/09
This paper presents the development of a reproductive experimental setup for FP release and transport and an analysis tool considering chemical reaction kinetics for the construction of the FP chemistry database. The performance test of the reproductive experimental setup TeRRa using CsI compounds show that TeRRa can reproduce well a FP chemistry-related behavior such as aerosol formation, growth and deposition behavior. An analytical tool has been developed based on the commercial ANSYS-FLUENT code. Some additional models was added to evaluate detailed FP chemistry during release and transport in this study. A test analysis simulating the CsI heating test in steam atmosphere was carried out to demonstrate the performance of the improved code. The result shows the appropriateness of the additional models.
 Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrier
Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrierG tz, M.*; G
tz, M.*; G tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D
tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th
llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch
rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 961, p.1 - 21, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.59(Physics, Nuclear)The kinematics of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Iwatsuki, Jin; Aita, Hideki; Kasahara, Seiji; Kubo, Shinji
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2016) (CD-ROM), p.1022 - 1028, 2016/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has manufactured 100 NL/h-H -scale hydrogen test apparatus. In advance to conduct the continuous operation, we investigated performance of the components in each section of the IS process. In this paper, the results of test of Bunsen and HI concentration sections was shown. In Bunsen reaction, section, we confirmed that outlet gas flow rate included no SO
-scale hydrogen test apparatus. In advance to conduct the continuous operation, we investigated performance of the components in each section of the IS process. In this paper, the results of test of Bunsen and HI concentration sections was shown. In Bunsen reaction, section, we confirmed that outlet gas flow rate included no SO gas, indicating that all the feed SO
gas, indicating that all the feed SO gas was absorbed to the solution in the Bunsen reactor for the Bunsen reaction. On the basis of these results, we evaluated that Bunsen reactor was workable. In HI concentration section, HI concentration was conducted by EED stack. As a result, it can concentrate HI in HIx solution as theoretically predicted on the basis of the previous paper. Based on the results added to that shown in Series II, we have conducted a trial continuous operation and succeeded it for 8 hours.
gas was absorbed to the solution in the Bunsen reactor for the Bunsen reaction. On the basis of these results, we evaluated that Bunsen reactor was workable. In HI concentration section, HI concentration was conducted by EED stack. As a result, it can concentrate HI in HIx solution as theoretically predicted on the basis of the previous paper. Based on the results added to that shown in Series II, we have conducted a trial continuous operation and succeeded it for 8 hours.
Kido, Kentaro; Hata, Kuniki; Maruyama, Yu; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Hoshi, Harutaka*
NEA/CSNI/R(2016)5 (Internet), p.204 - 212, 2016/05
Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Wakai, Eiichi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.2138 - 2141, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), a back plate of the target assembly will be exchanged during the in-service period. During the works, the lithium components will react chemically with the surrounding atmosphere. In this research, the chemical reaction of lithium in air, oxygen and nitrogen containing variable humidity at room temperature has been investigated to estimate the chemical reaction during the exchange works.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
CONTAIN-LMR code is an integrated analysis tool to predict the consequence of severe accident in a liquid metal fast reactor. A sodium-concrete reaction is one of the most important phenomena, and Sodium-Limestone Concrete Ablation Model (SLAM) has been installed into the original CONTAIN code. The SLAM treats chemical reaction kinetics between the sodium and the concrete compositions mechanistically, the application is limited to the limestone concrete. In order to apply SLAM to the siliceous concrete which is an ordinary structural concrete in Japan, the chemical reaction kinetics model has been improved. The improved model was validated to analyze a series of sodium-concrete experiments which were conducted in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. It has been found that relatively good agreement between calculation and experimental results is obtained and the CONTAIN-LMR code has been validated with regard to the sodium-concrete reaction phenomena.
Arai, Yasuo; Minato, Kazuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 344(1-3), p.180 - 185, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Minato, Kazuo; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Mizuguchi, Koji*; Sato, Takeyuki*; Amano, Osamu*; Miyamoto, Satoshi*
Proceedings of GLOBAL2003 Atoms for Prosperity; Updating Eisenhower's Global Vision for Nuclear Energy (CD-ROM), p.778 - 781, 2003/11
The simulation technology for the pyrochemical reprocessing of oxide fuels was developed to analyze experimental data, to predict experimental results, and to propose adequate conditions and processes. The simulation method was based on calculations of chemical equilibrium and electrochemical reactions. Some model calculations to simulate the experimental results were made on the process of electro-codeposition of UO and PuO
and PuO . Although it was difficult to trace the experiments and compare the calculated results with the experimental results quantitatively due to the limitation of available data on the experimental conditions, the calculated results were consistent with the experimental results. The phenomena of the repeated oxidation-reduction reactions between Pu
. Although it was difficult to trace the experiments and compare the calculated results with the experimental results quantitatively due to the limitation of available data on the experimental conditions, the calculated results were consistent with the experimental results. The phenomena of the repeated oxidation-reduction reactions between Pu and Pu
and Pu ions and those between Fe
ions and those between Fe and Fe
and Fe ions were theoretically analyzed,which caused the low current efficiency in the electro-codeposition process.
ions were theoretically analyzed,which caused the low current efficiency in the electro-codeposition process.
 Ce by the
Ce by the  La(p,n)
La(p,n) Ce reaction
Ce reactionIshioka, Noriko; Izumo, Mishiroku; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Sekine, Toshiaki
JAERI-Tech 2001-095, 23 Pages, 2002/01
no abstracts in English