Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Reeb, C.*; Davy, C. A.*; Pierlot, C.*; Bertin, M.*; Cantarel, V.; Lambertin, D.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 162, p.106963_1 - 106963_16, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.32(Construction & Building Technology)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Osaka University*
JAEA-Review 2019-029, 36 Pages, 2020/02
JAEA/CLADS, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Gel Filler that Facilitates Fuel Debris Retrieval". When gel materials such as polymer, silicate and clay minerals with adjusted viscosity are used in the process of debris retrieval, the gel would not leak down from the damaged parts, resulting in the reduction of surrounding air dose rate. In addition, gel materials can reduce the diffusion and scattering of dust that is produced by cutting. For these reasons, we propose a method where inside of a containment vessel is filled by gel materials in order to simplify the debris retrieval.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kurata, Masaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Nozawa, Takashi*; Sato, Daiki*; Murakami, Nozomu*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.206 - 216, 2019/09
After the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant, research and development (R&D) program for establishing technical basis of accident-tolerant fuel (ATF) started from 2015 in Japan. Since then, both experimental and analytical studies necessary for designing a new light water reactor (LWR) core with ATF candidate materials are being conducted within the Japanese ATF R&D Consortium for implementing ATF to the existing LWRs, accompanying with various technological developments required. Until now, we have accumulated experimental data of the candidate materials by out-of-pile tests, developed fuel evaluation codes to apply to the ATF candidate materials, and evaluated fuel behavior simulating operational and accidental conditions by the developed codes. In this paper, the R&D progresses of the ATF candidate materials considered in Japan are reviewed based on the information available such as proceedings of international conference and academic papers, providing an overview of ATF program in Japan.
Lambertin, D.*; Davy, C. A.*; Hauss, G.*; Planel, B.*; Marchand, B.*; Cantarel, V.
Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Innovation in Low-Carbon Cement and Concrete Technology (ILCCC 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2019/06
Composite materials made of geopolymer (GP) cement and organic liquids are useful to synthetize porosity-controlled media, for the management of radioactive organic liquid waste, or as phase change materials (PCM). Indeed, GP cements are able to integrate huge amounts of organic oils by direct emulsion in the fresh paste. The emulsion (GEOIL) remains stable during GP hardening. In this contribution, by using 3D X Ray micro Computed Tomography (micro CT) with a voxel size of 1 micron , we investigate the effect of formulation parameters (oil proportion, Si/Al molar ratio, surfactant) on the 3D oil droplet structure of GEOIL pastes. Samples are emulsified in the fresh state, and imaged in the hardened state. Porosity, oil droplet size distribution and mean distance between droplets are all determined quantitatively. It is observed that the presence of surfactant provides significantly smaller oil droplets. The increase in Si/Al ratio also decreases the oil droplet sizes, but to a lesser extent.
, we investigate the effect of formulation parameters (oil proportion, Si/Al molar ratio, surfactant) on the 3D oil droplet structure of GEOIL pastes. Samples are emulsified in the fresh state, and imaged in the hardened state. Porosity, oil droplet size distribution and mean distance between droplets are all determined quantitatively. It is observed that the presence of surfactant provides significantly smaller oil droplets. The increase in Si/Al ratio also decreases the oil droplet sizes, but to a lesser extent.
Fukushima, Yoshiaki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Tamura, Kenji*; Shibata, Kaoru
Applied Clay Science, 155, p.15 - 19, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.93(Chemistry, Physical)Dynamics of a fluoromica (ME100) cation exchanged for dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium ion (DODA )/ polypropylene composite was analyzed by quasi elastic neutron scattering (QENS), besides XRD and DSC. The QENS spectra for the DODA-ME100 at low Q=2.75 nm
)/ polypropylene composite was analyzed by quasi elastic neutron scattering (QENS), besides XRD and DSC. The QENS spectra for the DODA-ME100 at low Q=2.75 nm were not changed even at temperature higher than 445 K, the melting point of DODA
were not changed even at temperature higher than 445 K, the melting point of DODA . The results suggested the long range (
. The results suggested the long range ( 2 nm) molecular motions in interlayer space are restricted due to the rigid silicate layers and the strong electrostatic interaction between DODA
2 nm) molecular motions in interlayer space are restricted due to the rigid silicate layers and the strong electrostatic interaction between DODA and the ME100. Elastic intensity scan results suggested that a little amount of motion of the polymer chains in the composite was also restricted in the molten state at 445 K. The QENS is expected to be one of the useful tools for studying the composite materials.
and the ME100. Elastic intensity scan results suggested that a little amount of motion of the polymer chains in the composite was also restricted in the molten state at 445 K. The QENS is expected to be one of the useful tools for studying the composite materials.
Sano, Yuichi; Ashida, Takashi
JAEA-Review 2017-021, 180 Pages, 2017/11
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) is responsible to promote international cooperation in the R&D activities on the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and to develop the necessary human resources. CLADS held the Research Conference on Cementitious Composites in Decommissioning and Waste Management (RCWM2017) on 20th and 21st June, 2017. This report compiles the abstracts and the presentation materials in the above conference.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Nagase, Fumihisa; Kurata, Masaki; Nozawa, Takashi; Watanabe, Seiichi*; Kirimura, Kazuki*; Kakiuchi, Kazuo*; Kondo, Takao*; Sakamoto, Kan*; Kusagaya, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2017 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/09
In Japan, the research and development (R&D) project on accident tolerant fuel and other components (ATFs) of light water reactors (LWRs) has been initiated in 2015 for establishing technical basis of ATFs. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has coordinated and carried out this ATF R&D project in cooperation with power plant providers, fuel venders and universities for making the best use of the experiences, knowledges in commercial uses of zirconium-base alloys (Zircaloy) in LWRs. ATF candidate materials under consideration in the project are FeCrAl steel strengthened by dispersion of fine oxide particles(FeCrAl-ODS) and silicon carbide (SiC) composite, and are expecting to endure severe accident conditions in the reactor core for a longer period of time than the Zircaloy while maintaining or improving fuel performance during normal operations. In this paper, the progresses of the R&D project are reported.
Ung r, T.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tomota, Yo*; Rib
r, T.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tomota, Yo*; Rib rik, G.*; Shi, Z.*
rik, G.*; Shi, Z.*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 48(1), p.159 - 167, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:91.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Awual, M. R.; Eldesoky, G. E.*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Naushad, M.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Alothman, Z. A.*; Suzuki, Shinichi
Chemical Engineering Journal, 279, p.639 - 647, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:260 Percentile:99.17(Engineering, Environmental) from synthetic, pharmaceutical and alloy samples
from synthetic, pharmaceutical and alloy samplesNaushad, M.*; Alothman, Z. A.*; Alam, M. M.*; Awual, M. R.; Eldesoky, G. E.*; Islam, M.*
Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 12(9), p.1677 - 1686, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:82.95(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Awual, M. R.; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Shinichi; Shiwaku, Hideaki
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 291, p.111 - 119, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:261 Percentile:98.84(Engineering, Environmental)Awual, M. R.; Hasan, M. M.*; Shahat, A.*; Naushad, M.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Chemical Engineering Journal, 265, p.210 - 218, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:296 Percentile:99.37(Engineering, Environmental)Awual, M. R.
Chemical Engineering Journal, 266, p.368 - 375, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:709 Percentile:99.93(Engineering, Environmental)Awual, M. R.; Hasan, M. M.*
Sensors and Actuators B; Chemical, 206, p.692 - 700, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:235 Percentile:99.64(Chemistry, Analytical)Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Shimura, Kenichiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.469 - 472, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.66(Instruments & Instrumentation)SiC/SiC composites are one of the candidate materials for first wall in a fusion reactor because of their high strength at high temperature and low residual radioactivity after irradiation. In the fusion reactor, these materials are required to have high thermal diffusivity for heat exchange and reducing the thermal shock. Under fusion conditions, helium (He) and hydrogen (H) are produced in SiC. In this study, the effect of He ions implantation on the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composite were investigated. In the results, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites decreased after He ions implantation. However, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites hardly reduced in the operation temperature of fusion reactor. The thermal diffusivities of He implanted specimens were partly recovered by annealing. The defect concentration induced by He implantation, X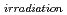 , in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X
, in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X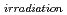 rapidly decreased around 500
rapidly decreased around 500  C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500
C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500  C.
C.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Key Engineering Materials, 297-300, p.143 - 147, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Ishihara, Masahiro; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Baba, Shinichi; Hanawa, Satoshi
Key Engineering Materials, 297-300, p.201 - 206, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Baba, Shinichi; Nemoto, Makoto*; Sozawa, Shizuo; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAERI-Tech 2005-055, 157 Pages, 2005/09
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) has been carrying out the research on radiation damage mechanism of heat-resistant ceramics composite materials, as one of the subjects of the innovative basic research on high temperature engineering using the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). A series of preliminary irradiation tests is being made using the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). The present report describes results of post-irradiation examinations so far on specimens irradiated in the second and third capsule, designated 98M-41A and 99M-30A, to fast neutron fluences of 1.0 10
10 m
m (E
(E 1MeV) at temperatures of 973K-1173K and 1273K-1473K. The PIE were conducted as the fundamental statistics index of the diametral dimensions for irradiated specimen, irradiation induced dimensional change rate and thermal expansion rate.
1MeV) at temperatures of 973K-1173K and 1273K-1473K. The PIE were conducted as the fundamental statistics index of the diametral dimensions for irradiated specimen, irradiation induced dimensional change rate and thermal expansion rate.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Transactions of 18th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-18), p.600 - 605, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Vacik, J.*; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Kitazawa, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Juha, L.*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 66(2-4), p.581 - 584, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.10(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English