Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Kaho; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Kakuta, Masakatsu*; Hayasaka, Toshiro*
JAEA-Testing 2025-003, 52 Pages, 2025/11
There is an emergency response team against nuclear facilities accidents of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The team is managed by the Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment. One of the important tasks of the team is purchasing remote-control robots, the quadrupedal robots (called Spot), were purchased in 2022 and 2023 to prepare for the nuclear disaster in JAEA. This report shows the remote-control manual for the quadrupedal robots (Spot), and it is focused on the necessary operations for the team.
Watanabe, Kaho; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Imahashi, Masaki; Taguchi, Yuji; Iitsuka, Yoshinobu; Ouchi, Takuya; Inoue, Shuichi; Kozawa, Takayuki; Nemoto, Takahiro; Sugaya, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Testing 2025-001, 56 Pages, 2025/11
There is an emergency response team against 7 nuclear facilities (JRR-3 in Nuclear Science Research Institute, Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) in Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, JMTR, HTTR and Joyo in Oarai Research and Development Institute, Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor Monju, Fugen Decommissioning Engineering Center) accidents of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The team is in Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development (NARREC). On site surveys which are about the situations and the access entering route of the 7 site emergencies were conducted by the team in 2021. And the results of the surveys made the team get two Spot (quadrupedal robots) in 2022. This is because the team thought using Spot gave operators the less exposure than using crawler robots which had been belonged to the team. After that it was confirmed that the Spot have the ability to respond to the emergency on the route of each facility in 2023. This report shows the results of the Spot's run function (= shooting videos, running oversteps, running up and down stairs, and so on) confirmation about 6 facilities (JRR-3, JMTR, HTTR, Joyo, Monju and Fugen).
Li, X.; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Sato, Ikken*; Yamashita, Takuya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111217_1 - 111217_13, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Motome, Yuiko; Agake, Toshiki; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2024-015, 30 Pages, 2025/01
The tables for calibration of control rods were verified, which is used positive period method and improved rod drop method of periodic inspection at Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). Those tables are "DOUBLING TIME-REACTIVITY" and "DECAY OF NEUTRON FLUX AFTER INSTANTANEOUS REDUCTION OF REACTIVITY". They are prepared around 1975. Since those tables do not clearly express source of values and records of data used in calculations, the authors verified those tables again. For the verification, the tables were reproduced as follows. For the positive period method, the relationship between the period and reactivity was analytically evaluated by using the inhour equation with NSRR's parameters. For the improved rod drop method, the ratios of neutron flux after the rod drop with parameters of negative reactivities was calculated using the EUREKA- 2 code. As a result, the values described in the tables well agree with those by the present evaluation because it is confirmed that standard deviations of the differences in the value by between the present evaluation and the tables are less than 0.035%. For this reason, it is verified that these tables are valid in the practical use for NSRR operations.
Fujita, Tatsuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.470 - 479, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study confirmed the efficiency of a combined approach of the control variates (CV) and the Latin hypercube sampling (LHS), which enhanced the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification due to cross-section (XS) covariance data, by considering the effect of statistical variation and also performed the sensitivity analyses on the influence due to the selection of alternative parameter to apply CV. The convergence performance for the uncertainty of infinite multiplication factor (k-infinity) during the random sampling was compared between several efficient sampling techniques such as the antithetic sampling (AS), LHS, CV, and the combined approaches of them in the PWR-UO fuel assembly geometry. The k-infinity uncertainty was evaluated by statistically processing several times Serpent2 calculations using perturbed ACE-formatted XS files based on ENDF/B-VIII.0. CV+LHS was more efficient than AS, LHS, and CV+AS. In addition, sensitivity analyses were performed to select alternative parameters used in CV. The 3
fuel assembly geometry. The k-infinity uncertainty was evaluated by statistically processing several times Serpent2 calculations using perturbed ACE-formatted XS files based on ENDF/B-VIII.0. CV+LHS was more efficient than AS, LHS, and CV+AS. In addition, sensitivity analyses were performed to select alternative parameters used in CV. The 3 3 mini fuel lattice calculation can improve the efficiency of CV+LHS. The reason was qualitatively considered that this calculation can capture the influence of XS covariance data for Gd isotopes. Consequently, the applicability of CV+LHS for the improvement of convergence performance to evaluate the k-infinity uncertainty during the random sampling was confirmed.
3 mini fuel lattice calculation can improve the efficiency of CV+LHS. The reason was qualitatively considered that this calculation can capture the influence of XS covariance data for Gd isotopes. Consequently, the applicability of CV+LHS for the improvement of convergence performance to evaluate the k-infinity uncertainty during the random sampling was confirmed.
Fujita, Tatsuya
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2024) (Internet), p.718 - 727, 2024/04
The convergence process of the k-infinity uncertainty during random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification was compared between several efficient sampling techniques. The k-infinity uncertainty was evaluated by statistically processing several times of SERPENT 2.2.1 calculations using perturbed ACE files based on JENDL-5 cross-section covariance data. The antithetic sampling (AS), the Latin hypercube sampling (LHS), the control variates (CV), and the combination approaches of them were focused on in the present paper. In PWR-UO fuel assembly geometry without the nuclide depletion, as discussed in past studies, AS and LHS showed higher efficient convergence than nominal sampling without any efficient sampling techniques. In terms of CV, though a stand-alone application did not have a large impact on the k-infinity uncertainty convergence, its performance was improved in combination with AS, as discussed in the past study. In addition, a new combined approach of LHS and CV (CV+LHS) was proposed in the present paper. CV+LHS improved the k-infinity uncertainty convergence and was more efficient than CV+AS. The main reason for this improvement was that the convergence for the mean value of alternative parameters in CV was enhanced by applying LHS. Consequently, this study proposed the new combined approach of CV+LHS and confirmed its efficiency performance for the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification in the PWR-UO
fuel assembly geometry without the nuclide depletion, as discussed in past studies, AS and LHS showed higher efficient convergence than nominal sampling without any efficient sampling techniques. In terms of CV, though a stand-alone application did not have a large impact on the k-infinity uncertainty convergence, its performance was improved in combination with AS, as discussed in the past study. In addition, a new combined approach of LHS and CV (CV+LHS) was proposed in the present paper. CV+LHS improved the k-infinity uncertainty convergence and was more efficient than CV+AS. The main reason for this improvement was that the convergence for the mean value of alternative parameters in CV was enhanced by applying LHS. Consequently, this study proposed the new combined approach of CV+LHS and confirmed its efficiency performance for the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification in the PWR-UO fuel assembly geometry. The applicability of CV+LHS for the nuclide-depletion calculations will be confirmed in future studies.
fuel assembly geometry. The applicability of CV+LHS for the nuclide-depletion calculations will be confirmed in future studies.
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ono, Takahiro; Kakutani, Satomi; Yoshida, Moeka; Suzuki, Soichiro
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 36(1), p.125 - 133, 2024/02
The Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development was established for the purpose of developing and verifying remote control equipment for promoting the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and the external use of this center was started in 2016. The mission of this center is to contribute to the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and for the reconstruction of Fukushima Prefecture. In this review, we describe the equipment related to the full-scale mock-up test, the component test for a remote-control device and the virtual reality system in this center. In addition, the case examples for usage of these equipment are introduced.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
The benchmark analyses on the TRIGA reactor of the IEU-COMP-THERM-013 (ICT-013) in the ICSBEP handbook using the MVP version 3 code were carried out with the Japanese, US and European nuclear data libraries, including JENDL-5. The analyses on effective neutron multiplication factors (k 's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k
's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k 's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k
's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k 's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k
's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k 's. Most of the errors involved in k
's. Most of the errors involved in k 's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k
's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k 's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
Yamada, Taichi; Watanabe, Kaho; Suzuki, Soichiro; Kawabata, Kuniaki
Automation Systems, 39(464), p.88 - 92, 2023/09
In Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) emergency response and decommissioning, high radiation or unknown environments significantly restrict human workers' activity. Thus, a remotely controlled robot is essential to operate in such an environment instead of human workers. However, remote robot operation is not easy, and it is required to understand the robot's capability, that is, what/how the robot can do on the site. Therefore, robot evaluation method development is important for remote robot operation in disaster sites. We survey the required capabilities for a remotely controlled robot from the remote operation cases in FDNPS and develop test methods to evaluate the capabilities. This paper introduces the survey of FDNPS remote operation cases and the test method development.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Hazama, Taira; Katagiri, Hiroki; Takegoshi, Atsushi*
Nuclear Technology, 209(8), p.1197 - 1214, 2023/08
Yamada, Taichi; Watanabe, Kaho; Suzuki, Soichiro; Kawabata, Kuniaki
Keisoku To Seigyo, 62(5), p.268 - 271, 2023/05
In Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) emergency response and decommissioning, high radiation or unknown environments significantly restrict human workers' activity. Thus, a remotely controlled robot is essential to operate in such an environment instead of human workers. However, remote robot operation is not easy, and it is required to understand the robot's capability, that is, what/how the robot can do on the site. Therefore, robot evaluation method development is important for remote robot operation in disaster sites. We survey the required capabilities for a remotely controlled robot from the remote operation cases in FDNPS and develop test methods to evaluate the capabilities. This paper introduces the survey of FDNPS remote operation cases and the test method development.
Takabe, Yugo; Otsuka, Noriaki; Fuyushima, Takumi; Sayato, Natsuki; Inoue, Shuichi; Morita, Hisashi; Jaroszewicz, J.*; Migdal, M.*; Onuma, Yuichi; Tobita, Masahiro*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-040, 45 Pages, 2023/03
Because of the decommission of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), the domestic neutron irradiation facility, which had played a central role in the development of innovative nuclear reactors and the development of technologies to further improve the safety, reliability, and efficiency of light water reactors, was lost. Therefore, it has become difficult to pass on the operation techniques of the irradiation test reactors and irradiation technologies, and to train human resources. In order to cope with these issues, we conducted a study on the implementation of irradiation tests using overseas reactors as neutron irradiation sites as an alternative method. Based on the "Arrangement between the National Centre for Nuclear Research and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency for Cooperation in Research and Development on Testing Reactor," the feasibility of conducting an irradiation test at the MARIA reactor (30 MW) owned by the National Centre for Nuclear Research (NCBJ) using the temperature control system, which is one of the JMTR irradiation technologies, was examined. As a result, it was found that the irradiation test was possible by modifying the ready-made capsule manufactured in accordance with the design and manufacturing standards of the JMTR. After the modification, a penetration test, an insulation continuity test, and an operation test in the range of room temperature to 300 C, which is the operating temperature of the capsule, were conducted and favorable results were obtained. We have completed the preparations prior to transport to the MARIA reactor.
C, which is the operating temperature of the capsule, were conducted and favorable results were obtained. We have completed the preparations prior to transport to the MARIA reactor.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
Kawamura, Sho; Kikuchi, Masanobu; Hosoya, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2021-041, 103 Pages, 2023/02
In response to new regulatory standard for research and test reactor which is enforced December 2013, JRR-3 got license in November 2018 by formulate new design basis ground motion. After that we evaluated for insertion property of control rod using that new design basis ground motion, and that evaluation results were accepted as approval of the design and construction method by Nuclear Regulation Authority. Now, we re-evaluated to insertion property of control rod about neutron absorber and follower fuel element by time history response analysis method. In this report, it shows that new results have sufficiency of margin compared with the past results that are accepted as approval of the design and construction method.
 -ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a
-ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a  -ray field
-ray fieldKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Terasaka, Yuta; Tomita, Hideki*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Uritani, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167636_1 - 167636_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:83.11(Instruments & Instrumentation)We focus on the thickness and property controls of inorganic scintillators used for thermal neutron detection in intense  -ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20
-ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20 (a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF
(a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF :Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a
:Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron detection for GS20
-ray field, the neutron detection for GS20 with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a
with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron/
-ray field, the neutron/ -ray discrimination of GS20
-ray discrimination of GS20 was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
Kato, Shinya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Akaev, A.*; Vurim, A.*; Baklanov, V.*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-13) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/09
The In-Vessel Retention (IVR) of molten-core in Core Disruptive Accidents (CDAs) is of prime importance in enhancing the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors. One of the main subjects in ensuring IVR is to design the Control Rod Guide Tube (CRGT) which allows effective discharge of molten core materials from the core region. The effectiveness of the CRGT design is assessed through CDA analyses, and it is reasonable for these analyses to develop a computer code collaborated with experimental researches. Thus, experiments addressing the discharge behavior of the molten-core materials through the CRGT have proceeded as one of the subjects in the collaboration research named the EAGLE-3 project, and the obtained experimental results are reflected in the development of the SIMMER code. In this project, a series of out-of-pile tests using molten-alumina as the fuel simulant was conducted to understand the discharge behavior of molten-core materials through the CRGT. In this study, in order to investigate the effect of an internal structure in the CRGT on the discharge behavior of the molten-core materials, the data of an out-of-pile test in which the molten-alumina penetrated to a duct with the internal structure were analyzed. In addition, the post-test analysis using the SIMMER code was conducted and the results were compared with the test results.
Isogawa, Hiroki*; Naoi, Motomasa*; Yamasaki, Seiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Katayama, Kazunari*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2022-015, 18 Pages, 2022/07
As a summer holiday practical training 2021, the impact of 10 years long-term shutdown on critical control rod position of the HTTR and the delayed neutron fraction (
 ) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0
) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0 0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as
0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am, 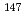 Pm,
Pm, 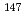 Sm,
Sm,  Gd. Regarding the
Gd. Regarding the 
 calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the
calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the 
 value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.
value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.
Kasahara, Naoto*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Nakamura, Izumi*; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Sato, Takuya*; Ichimiya, Masakazu*
Transactions of the 26th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/07
Utilizing fracture control, we are developing a technology to suppress the expansion of damage caused by an event that exceeds the design assumption. We made a plan to develop three issues; (1) Technology for mitigating failure consequence at extremely high temperatures, (2) Technology for mitigating failure consequence against excessive earthquakes, and (3) Methodology for improving reactor structure resilience.
Kamiyama, Kenji; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kato, Shinya; Imaizumi, Yuya; Mukhamedov, N.*; Akayev, A.*; Pakhnits, A.*; Vurim, A.*; Baklanov, V.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/04
Nagase, Fumihisa; Otomo, Takashi; Uetsuka, Hiroshi*
Nuclear Technology, 208(3), p.484 - 493, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)An Ag-In-Cd control rod alloy was heated in argon or oxygen at 1073-1673 K for 60-3600 s and the release behavior of the elements was examined. Complete liquefaction of the alloy occurred between 1123 and 1173 K, and elemental release was quite limited below the liquefaction temperature. In argon, almost all of the Cd content was released within 3600 s at  1173 K and within 60 s at
1173 K and within 60 s at  1573 K, while the released fractions of Ag and In were
1573 K, while the released fractions of Ag and In were  3% and
3% and  8%, respectively. In oxygen, the release of Cd, which was quite small at temperatures up to 1573 K, drastically increased to
8%, respectively. In oxygen, the release of Cd, which was quite small at temperatures up to 1573 K, drastically increased to  30-50% at 1673 K for short periods. Releases of Ag and In were also small in oxygen under the examined conditions. Comparison with the experimental data suggests that conventional empirical release models may underestimate the Cd release at lower temperatures just after control rod failure in severe accidents.
30-50% at 1673 K for short periods. Releases of Ag and In were also small in oxygen under the examined conditions. Comparison with the experimental data suggests that conventional empirical release models may underestimate the Cd release at lower temperatures just after control rod failure in severe accidents.