Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Ando, Masaki; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 199(6), p.1029 - 1043, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Katano, Ryota; Abe, Takumi; Cibert, H.*
JAEA-Research 2024-019, 22 Pages, 2025/05
An accelerator-driven system (ADS) dedicated to transmutation of minor actinides (MAs) is driven in subcritical states. It is important for establishment of the subcriticality control of ADS to predict the burnup reactivity. To validate the prediction accuracy, the burnup reactivity, especially at the first cycle, must be measured with sufficient accuracy. In this study, we focus on Current-To-Flux (CTF) method. We have simulated the burnup reactivity monitoring during the ADS normal operation with the CTF method by performing fixed-source-burnup calculations using a continuous energy Monte Carlo code SERPENT2 with some tallies that models in-core fission chambers and have estimated its measurement uncertainty. We have clarified that the 10% biases of measure burnup reactivities appear independently of the burnup duration and their detector position dependence is particularly small in the outer region of the system.
Abe, Takumi; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.299 - 304, 2025/05
Currently, much research continues on stable energy sources that do not emit CO in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 16 Pages, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigated the impact of nuclear data updates from JENDL-4.0 (J4) to JENDL-5 (J5) on the light-water reactor fuel burnup calculations. Burnup calculations were conducted with J4 and J5 for PWR pin-cell and BWR fuel assembly geometries. The calculation results revealed significant burnup-dependent differences in the neutron multiplication factor (k ). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k
). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of
values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H
Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H O notably impacted the k
O notably impacted the k differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k
differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the
differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the  U,
U,  Gd, and
Gd, and  Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H
Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k
O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
Fuyushima, Takumi; Sayato, Natsuki; Otsuka, Kaoru; Endo, Yasuichi; Tobita, Masahiro*; Takemoto, Noriyuki
JAEA-Testing 2024-008, 38 Pages, 2025/03
In Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), irradiation tests had been conducted by loading specimens into capsules for irradiating fuels and materials. The thermal design calculation of capsules is significant to irradiate various types of specimens at the target temperature. The decommissioning plan of JMTR was approved in March 2021, and the Department of Waste Management and Decommissioning Technology Development is currently working on irradiation plans by foreign testing reactors as an alternative for JMTR. A one-dimensional thermal calculation code "GENGTC", which was developed at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in U.S., is used for capsule design and irradiation tests. GENGTC has been repeatedly improved as improvements of computer performance, but there were some defects in calculation function. Therefore, we investigated the cause of the problem and changed the program from the currently used FORTRAN77 language program to a Visual Basic language program that uses the macro calculation function of Excel. In addition, the program was improved to make it easier to use the calculation code.
Tomioka, Dai; Kochiyama, Mami; Ozone, Kenji; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2024-023, 38 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an implementing organization of near-surface disposal for low-level radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial and medical facilities in Japan. Information on the radioactivity concentration of these radioactive wastes is dispensable for the design and conformity assessment of the waste disposal facilities for the licensing application of the disposal project and its safety review. Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center has been improving the radioactivity evaluation procedure for the dismantling waste generated from the research reactors based on the activation calculation. In order to investigate the applicability of the ORIGEN code (included in SCALE6.2.4), which enables more accurate activation calculations using multigroup neutron spectra, we performed activation calculations with the ORIGEN-code and the ORIGEN-S code (included in SCALE6.0), which has been widely used in the past, for the dismantled wastes from the Rikkyo University Research Reactor, where radioactivity analysis data for the structural materials around the reactor core were compiled. As a result, the calculation time difference between ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S was small and the evaluated radioactivity concentrations of the former were in the range of 0.8-1.0 times those of the latter, which was in good agreement with those of radiochemical analysis in the range of 0.5-3.0 times. The applicability of ORIGEN was confirmed. In addition, activation calculations assuming trace elements in structural materials of nuclear reactor were performed with ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S and the results were compared. The causes of the large differences among 170 nuclides that are important for dose assessment in near-surface disposal were assessed each nuclide.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2024-017, 208 Pages, 2025/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2023. Car-borne surveys, a measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the temporal changes in the score were analyzed. A system to report the tritium concentration level in seawater to the Nuclear Regulation Authority was operated, and the variation of tritium concentration before and after the discharge of ALPS treated water to the ocean was analyzed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan until FY2023 was analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys. Representative life patterns that can be expected after the return to the evacuation-designated restricted area were set, and the cumulative exposure doses were evaluated for the local governments and residents in the area. The measurement results for FY2023 were published on the Web site and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Taniguchi, Takumi; Matsumoto, Saori; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Fujita, Hideki*; Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Osugi, Takeshi
JAEA-Review 2024-059, 20 Pages, 2025/03
The basic performance required for solidifying waste into cement, such as fluidity before curing and strength after curing, is expected to be affected by the chemical effects of substances and components contained in the waste. The fluidity before curing and the strength properties after curing are greatly influenced by the curing speed of the cement. We investigated existing knowledge with a focus on chemical substances that affect the curing speed of cement. In this report, chemical substances that affect fluidity are broadly classified into inorganic substances such as (1) anion species, (2) metal elements such as heavy metals, (3) inorganic compounds as cement admixtures, and (4) organic compounds as cement admixtures. Based on the investigation, we actually added chemicals and measured the setting time. As a result, it was found that there are multiple mechanisms contributing to accelerated hardening. We investigated chemical substances that inhibit the curing reaction of cement, and were able to compile information to consider ingredients that are contraindicated in cement curing.
Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 35(1), p.4 - 11, 2025/03
Iron reacts with hydrogen to form solid solutions with body-centered cubic, face-centered cubic, hexagonal close packed, and double hexagonal close packed structures at high temperatures and high pressures. Neutron diffraction is the most powerful tool for determining the occupation sites and occupancies of hydrogen atoms dissolved in a metal lattice. Structural parameters, including hydrogen occupation sites and occupancies, are refined via Rietveld analysis for neutron diffraction data. We present our expertise in Rietveld refinement of iron hydrides accumulated over 10 years.
Tanabe, Kosuke*; Komeda, Masao; Toh, Yosuke; Kitamura, Yasunori*; Misawa, Tsuyoshi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(3), p.198 - 202, 2025/03
, 67(3), p.198 - 202, 2025/03
no abstracts in English
Hizukuri, Kyoko*; Fujibuchi, Toshio*; Han, D.*; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; Furuta, Takuya
Radiological Physics and Technology, 18(1), p.196 - 208, 2025/03
One of the radiation protection measures for medical personnel engaged in X-ray fluoroscopy is the use of radiation-protective plates and a simulation tool to evaluate effect of the plates is desired. Monte Carlo simulation has an advantage of being able to accurately calculate the interaction between radiations and various objects present in the X-ray room. However, Monte Carlo simulation has a disadvantage of being computationally time-consuming. Therefore, we developed a new simplified method to calculate the dose distribution in a short time with the presence of protective plates using pre-computed directional vectors (SCV). Using the Monte Carlo code PHITS, we simulated the ambient dose equivalent distribution the X-ray fluoroscopy room without the presence of protective plates. Assuming the dose at each voxel was all contributed from radiations in the direction indicated by the directional vector, the shielding effect of the protective plates for the dose at the voxel was determined whether the line toward backtrace of the directional vector has a intersect with the protective plate or not. With SCV, the computational time for the whole dose distribution with the presence of a protective plate was reduced approximately 1/6000 of the full PHITS simulation keeping the good accuracy to evaluate the effect of the plate.
Fujita, Tatsuya; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(2), p.179 - 196, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study newly established a direct coupling code system consisting of the nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 2, and the three-dimensional heterogeneous transport code GENESIS (FRENDY-V2/GENESIS) for easy implementation of the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification considering the implicit effect due to nuclear cross-section (XS) perturbations. The multi-group macroscopic XSs prepared for GENESIS were generated by FRENDY version 2, where the Dancoff factor was calculated by the neutron current method. Then the background XSs were evaluated based on the Carlvik two-term rational approximation. The infinite multiplication factor (k-infinity) and the fission reaction rate distribution in UO and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi*; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Morishita, Kazuki; Watanabe, Masashi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Yano, Yasuhide; Oki, Shigeo
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113755_1 - 113755_17, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fukushima, Masahiro; Ando, Masaki; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 199(1), p.18 - 41, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of integral experiments were conducted at FCA of JAEA, simulating LWR cores with a tight lattice cell of highly enriched MOX fuel containing more than 15% fissile plutonium. The three experimental configurations were constructed using foamed polystyrene with different void fractions to clarify the prediction accuracy of neutronic calculation codes and nuclear data among various neutron spectra. The nuclear characteristics measured in the experiments were criticality, moderator void reactivity worths, and sample reactivity worths. The preliminary analyses on experiments were conducted using a deterministic calculation code conventionally used for fast reactors with JENDL-4.0. Most reactivity worth calculations correlated well with the experimental values. Specifically for the softer neutron spectra configurations, the treatment of ultrafine energy groups obviously improved the prediction accuracy of the deterministic calculations. Furthermore, reference calculations were performed with MVP3 code by modeling the experimental setup in detail, confirming the validity of the deterministic calculations.
Sakamoto, Masahiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Kanno, Ikuo; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kaneko, Junichi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ito, Tatsuya; Xu, S.*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Kainuma, Ryosuke*
Shape Memory and Superelasticity, 9 Pages, 2025/00
Wakui, Takashi; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Jikken Rikigaku, 24(4), p.212 - 218, 2024/12
Irradiation damage is one of the main factors determining the lifetime of the mercury target vessel for spallation neutron source in J-PARC. To understand material degradation of the used vessels, it is planned to conduct an evaluation using inverse analyses with indentation tests on the structural materials of the used vessels and numerical experiments. This evaluation technique was applied to two kinds of ion-irradiated materials with different displacement damage doses, in which the irradiation condition was simulated. It could be confirmed that the ultimate strength increased, and the total elongation decreased with increasing irradiation. These trends are like the material degradation behaviors which have been reported by using small specimen's tensile tests.
 Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag, and
Ag, and  In
InNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(11), p.1415 - 1430, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron capture cross-sections of nuclides targeted for decommissioning are necessary to contribute to the evaluation of radioactivity produced. The present study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag and
Ag and  In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18
In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18 0.28 barn for
0.28 barn for  Sc(n,
Sc(n,  )
)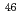 Sc, 4.34
Sc, 4.34 0.06 barn for
0.06 barn for  Cu(n,
Cu(n,  )
) Cu, 0.719
Cu, 0.719 0.011 barn for
0.011 barn for  Zn(n,
Zn(n,  )
) Zn, 4.05
Zn, 4.05 0.05 barn for
0.05 barn for  Ag(n,
Ag(n,  )
)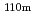 Ag and 8.53
Ag and 8.53 0.27 barn for
0.27 barn for  In(n,
In(n,  )
) 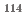 In
In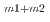 . The results for
. The results for  Sc and
Sc and  Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Sato, Yuki
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 212, p.111421_1 - 111421_8, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)