Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe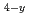 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-001, 94 Pages, 2025/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2023, along with the verification of each system, a three-dimensional reconstruction model was generated using images acquired from a moving camera on the monitoring platform in a simulated environment, and an integrated experiment was conducted to demonstrate that it is possible to present images from the optimal viewpoint for the visualization target, with the cooperation of each research theme.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Motome, Yuiko
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
The detailed computational models for nuclear criticality analyses on the first startup cores of NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), which is categorized as a TRIGA-ACPR (Annular Core Pulse Reactor), were created for the purposes of deeper understandings of safety inspection data on the neutron absorber rod worths of reactivity and improvement of determination technique of the reactivity worths. The uncertainties in effective neutron multiplication factor (k ) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k
) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029
for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029  k
k . It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k
. It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-005, 106 Pages, 2025/06
JAEA has been creating input data for pressurized water reactor (PWR) analysis with RELAP5/MOD3.3 code, mainly based on design information for the four-loop PWR's Tsuruga Power Station Unit-2 as the reference reactor of the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF). The cold leg large-break loss-of-coolant accident (LBLOCA) calculation in the flamework of the BEMUSE program is cited as a representative OECD/NEA activity related to the PWR analysis. The new regulatory requirements for PWRs in Japan include the event of loss of recirculation functions from emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in the cold leg LBLOCA. This event should be evaluated the effectiveness of measures against severe core damage. The input data for this study were made preparations to analyze the PWR LBLOCA, which is one of the design basis accidents that should be postulated in the safety design. This report describes the main features of the input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis. The PWR model comprised a reactor vessel, pressurizer (PZR), hot legs, steam generators (SGs), SG secondary-side system, crossover legs, cold legs, and ECCS. A four-loop PWR was simulated by two loops in the LBLOCA calculation. Specifically, loop-A attached with the PZR corresponded to three loops, and loop-B mounted with the break was equal to one loop. The nodalization schemes of the PWR components were referred to those of the LSTF components. Moreover, interpretations were added to the main input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis, and further information such as the basis for determining the input data was provided. In addition, transient analysis was performed employing the prepared input data for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event. The present transient analysis was confirmed to be appropriate generally by comparing with the calculation in the previous study using the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code. Furthermore, sensitivity analyses were executed exploiting the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code to clarify the effects of a discharge coefficient through the break and water injection flow rate of the alternative recirculation on the fuel rod cladding surface temperature. This report explains the results of the sensitivity analyses within the defined ranges, which complement some of the content of the previous study's calculation for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event.
Birkholzer, J. T.*; Graupner, B. J.*; Harrington, J.*; Jayne, R.*; Kolditz, O.*; Kuhlman, K. L.*; LaForce, T.*; Leone, R. C.*; Mariner, P. E.*; McDermott, C.*; et al.
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100685_1 - 100685_17, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0Sugita, Yutaka; Ono, Hirokazu; Beese, S.*; Pan, P.*; Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Jove-Colon, C.*; Lopez, C. M.*; Liang, S.-Y.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100668_1 - 100668_21, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)The international cooperative project DECOVALEX 2023 focused on the Horonobe EBS experiment in the Task D, which was undertaken to study, using numerical analyses, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (or thermo-hydro) interactions in bentonite based engineered barriers. One full-scale in-situ experiment and four laboratory experiments, largely complementary, were selected for modelling. The Horonobe EBS experiment is a temperature-controlled non-isothermal experiment combined with artificial groundwater injection. The Horonobe EBS experiment consists of the heating and cooling phases. Six research teams performed the THM or TH (depended on research team approach) numerical analyses using a variety of computer codes, formulations and constitutive laws.
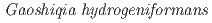 sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation
sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formationUeno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 75(6), p.006802_1 - 006802_11, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Hayano, Akira; Ono, Hirokazu; Tachi, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
, 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency launched the Horonobe International Project (HIP) utilizing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The main objectives of this project are to develop and demonstrate advanced technologies to be used in repository design, operation and closure and a realistic safety assessment in deep geological disposal, and to encourage and train the next generation of engineers and researchers. In this review, an overview of the HIP is presented.
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; Esaki, Nanse; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Li, X.; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Sato, Ikken*; Yamashita, Takuya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111217_1 - 111217_13, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sonehara, Masateru; Okano, Yasushi; Uchibori, Akihiro; Oki, Hiroshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.403 - 414, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For sodium-cooled fast reactors, understanding sodium combustion behaviour is crucial for managing sodium leakage accidents. In this study, we perform benchmark analyses of the Sandia National Laboratories (SNL) T3 experiment using the multi-dimensional thermal hydraulic code AQUA-SF. Conducted in an enclosed space with a large vessel volume of 100 m and a sodium mass flow rate of 1 kg/s, the experiment highlighted the multi-dimensional effects of local temperature increase shortly after sodium injection. This study aims to extend the capabilities of AQUA-SF by focusing on the simulation of these multi-dimensional temperature variations, in particular the formation of high temperature regions at the bottom of the vessel. The proposed models include the temporary stopping of sodium droplet ignition and spray combustion of sodium splash on the floor. Furthermore, it has been shown that additional heat source near the floor is essential to enhance the reproduction of the high temperature region at the bottom. Therefore, case studies including sensitivity analyses of spray cone angle and prolonged combustion of droplets on the floor are conducted. This comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into the dynamics of sodium combustion and safety measures in sodium-cooled fast reactors.
and a sodium mass flow rate of 1 kg/s, the experiment highlighted the multi-dimensional effects of local temperature increase shortly after sodium injection. This study aims to extend the capabilities of AQUA-SF by focusing on the simulation of these multi-dimensional temperature variations, in particular the formation of high temperature regions at the bottom of the vessel. The proposed models include the temporary stopping of sodium droplet ignition and spray combustion of sodium splash on the floor. Furthermore, it has been shown that additional heat source near the floor is essential to enhance the reproduction of the high temperature region at the bottom. Therefore, case studies including sensitivity analyses of spray cone angle and prolonged combustion of droplets on the floor are conducted. This comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into the dynamics of sodium combustion and safety measures in sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Nagatake, Taku; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.432 - 456, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)We performed electrostatic simulations of a wire-mesh sensor (WMS) for a single spherical bubble and bubbly flow to clarify the accuracy of the WMS. The electrostatic simulation for the single bubble showed the electric current density distribution and the electric current path from the excited transmitter to receivers for various bubble locations. It indicated systematic errors based on the nonuniform current density distribution around the WMS. The electrostatic simulation for the bubbly flow calculated by the computational fluid dynamics code, JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER), indicated that the WMS had difficulty in quantitatively measuring the intermediate values of the instantaneous void fraction between 0 and 1 because they cannot be estimated by previous transformation methods from the WMS signal to the void fraction, such as linear approximation or Maxwell's equation, and have a significant deviation of the void fraction of  0.2 for the WMS signal. However, the electrostatic simulation indicated that the time-averaged void fractions around the center of the flow channel can be estimated using linear approximation, and the time-averaged void fraction near the wall of the flow channel can be estimated using Maxwell's equation.
0.2 for the WMS signal. However, the electrostatic simulation indicated that the time-averaged void fractions around the center of the flow channel can be estimated using linear approximation, and the time-averaged void fraction near the wall of the flow channel can be estimated using Maxwell's equation.
Usami, Hiroshi; Yoshinaga, Kyohei*; Fujikawa, Keigo*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(5), p.295 - 299, 2025/05
, 67(5), p.295 - 299, 2025/05
no abstracts in English
 phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates
phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobatesAso, Seiyu*; Matsuo, Hiroki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Morikawa, Daisuke*; Tsuda, Kenji*; Oyama, Kenji*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Noguchi, Yuji*
Physical Review B, 111(17), p.174114_1 - 174114_12, 2025/05
We investigate the crystal structures, phase transitions, and phase stability of undoped and Ca-modified NaNbO through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)-
through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)- phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO
phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO
is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.195 - 198, 2025/05
Extraction chromatgraphy technology for trivalent minor actinide (MA(III) ; Am(III) and Cm(III)) recovery from the solution generated by an extraction process in reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel has been developed. A fine particle is generated in the solution. The fine particle must be removed before MA recovery operation, because that leads clogging of the extraction chlomatography column. In order to prevent clogging the column, filtration system utilizing porous silica beads packed column has been designed. In this study, a fine particle trapping system was developed and particle removal performance of the system was experimentally evaluated using alumina particles as simulated fine particle. Column experiments revealed that the fine particle with the particle size from 0.12 to 15  m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So; Nakahara, Masaumi; Funakoshi, Tomomasa; Hoshino, Takanori; Takahatake, Yoko; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Aihara, Haruka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshida, Toshiki; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.168 - 174, 2025/05
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a project named "Systematic Treatment of RAdioactive liquid waste for Decommissioning (STRAD)" project since 2018 for fundamental and practical studies for treating radioactive liquid wastes with complicated compositions. Fundamental studies have been conducted using genuine liquid wastes accumulated in a hot laboratory of the JAEA called the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF), and treatment procedures for all liquid wastes in CPF were successfully designed on the results obtained. As the next phase of the project, new fundamental and practical studies on primarily organic liquid wastes accumulated in different facilities of JAEA are in progress. This paper reviews the representative achievements of the STRAD project and introduces an overview of ongoing studies.
 C alloy measured in the electrostatic levitation furnace onboard the international space station
C alloy measured in the electrostatic levitation furnace onboard the international space stationIshikawa, Takehiko*; Oda, Hirohisa*; Koyama, Chihiro*; Shimonishi, Rina*; Ikeuchi, Rumiko*; Paradis, P.-F.*; Okada, Jumpei*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Yamano, Hidemasa
International Journal of Microgravity Science and Application, 42(2), p.420202_1 - 420202_10, 2025/04