Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sawa, Kazuhiro*; Haseda, Masaya*; Aihara, Jun
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 89(921), p.22-00314_1 - 22-00314_6, 2023/05
In high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), Tri-isotropic (TRISO)-coated fuel particles are employed as fuel. In the high burnup coated fuel particle, stress due to fission gas pressure and irradiation-induced pyrolytic carbon (PyC) shrinkage is introduced into the coating layers and consequently the stress could cause failure of coating layers under high burnup irradiation condition. A failure model has developed to predict failure fraction of TRISO-coated particle under high burnup irradiation. In the model, failure probability is strongly dependent on the irradiation characteristics of PyC. This paper describes the outline of the failure model and evaluation result of high burnup fuel irradiation experiment by the model.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ishii, Eiichi; Ishida, Tsuyoshi*
Journal of MMIJ, 133(2), p.25 - 33, 2017/02
In the construction of a deep underground facility, the hydromechanical properties of the rock mass around an underground opening are changed significantly due to stress redistribution. This zone is called an excavation damaged zone (EDZ). In high-level radioactive waste disposal, EDZs can provide a shortcut for the escape of radionuclides to the surface environment. Therefore, it is important to develop a method for predicting the detailed characteristics of EDZs. For prediction of the EDZ in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory of Japan, we conducted borehole televiewer surveys, rock core analyses, and repeated hydraulic conductivity measurements. We observed that niche excavation resulted in the formation of extension fractures within 0.2 to 1.0 m into the niche wall, i.e., the extent of the EDZ is within 0.2 to 1.0 m into the niche wall. These results are largely consistent with the results of a finite element analysis implemented with the failure criteria considering failure mode. The hydraulic conductivity in the EDZ was increased by 3 to 5 orders of magnitude compared with the outer zone. The hydraulic conductivity in and around the EDZ has not changed significantly in the two years following excavation of the niche. These results show that short-term unloading due to excavation of the niche created a highly permeable EDZ.
Sugino, Hideharu*; Ito, Hiroto*; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(4), p.233 - 241, 2005/12
The purpose of this research is to establish the reliability evaluation method of aged nuclear power components for seismic events from a viewpoint of long-term use of the existing light water reactor nuclear power plants. For this purpose, we developed a piping failure probability evaluation code "PASCAL-SC" based on probabilistic fracture mechanics, and a probabilistic seismic hazard evaluation code "SHEAT-FM" for calculating the seismic occurrence probability of a plant site, paying attention to aging such as fatigue crack progress by the stress corrosion cracking and seismic load in primary coolant piping system. We proposed the reliability evaluation method of aged piping for seismic events by combination of these codes. Using this method, we evaluated the reliability of a weld line in the PLR(Primary Loop Recirculation system) piping of the BWR model plant for seismic events.
Ishikawa, Jun; Muramatsu, Ken; Sakamoto, Toru*
JAERI-Research 2005-021, 133 Pages, 2005/09
The THALES-2 code is an integrated severe accident analysis code in order to simulate the accident progression and transport of radioactive material for probabilistic safety assessment (PSA) of a nuclear power plant, a part of a level 3 PSA being performed at JAERI for a 1,100MWe BWR-5 with a Mark-II containment. Results and insights from the analyses were that (1) the calculated release fractions of CsI and CsOH to the environment were in the range of 0.01 to 0.1 for late containment overpressure failure cases, and the release fractions for the containment venting case were one order of magnitude smaller than that of over-pressure case and those for drywell spray recovery cases where no containment failure occurred were two orders of magnitude smaller than the containment venting cases, (2) the governing factors for source terms of Iodine and Cesium are different depending on whether the containment fails before core melt or not, (3) the containment venting, which is one of the accident management measures, can be expected to reduce source terms if suppression pool bypass is avoided.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2005/05
The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions were evaluated for a BWR Mk-II model plant. The evaluation was made for two scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area, or in the suppression pool. A probabilistic approach, Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS), was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The fragility curves connecting the steam explosion loads and containment failure were developed based on simplified assumptions on the containment failure scenarios. The mean conditional probabilities of containment failure per occurrence of a steam explosion were 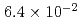 for suppression pool and
for suppression pool and 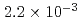 for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
Sakaki, Akihiro*; Kato, Michio; Hayashi, Koji; Fujisaki, Katsuo*; Aita, Hideki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Takada, Shoji; Shimizu, Akira; Morisaki, Norihiro; Maeda, Yukimasa; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2005-023, 72 Pages, 2005/04
In order to establish the system integration technology to connect a hydrogen production system to a high temperature gas cooled reactor, the mock-up test facility with a full-scale reaction tube for the steam reforming HTTR hydrogen production system was constructed in fiscal year 2001 and its functional test operation was performed in the year. Seven experimental test operations were performed from fiscal year 2001 to 2004. On a period of each test operation, there happened some troubles. For each trouble, the cause was investigated and the countermeasures and the improvement works were performed to succeed the experiments. The tests were successfully achieved according to plan.This report describes the improvement works on the test facility performed from fiscal year 2001 to 2004.
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Tobita, Tsutomu*
Nuclear Technology, 142(3), p.250 - 259, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)The maximum burnup of the first-loading fuel of the HTTR is limited to 3.6%FIMA to certify its integrity during the operation. In order to investigate fuel behavior under extended burnup condition, irradiation tests were performed. The thickness of buffer and SiC layers of the irradiated fuel particles were increased to keep their integrity up to over 5%FIMA. The fuel compacts were irradiated in independent capsules at the HFIR of ORNL, and at the JMTR of JAERI, respectively. The comparison of measured and calculated (R/B)s showed that additional failures occurred in both irradiation tests. A pressure vessel failure model analysis showed that no tensile stresses acted on the SiC layers even at the end of irradiation and no pressure vessel failure occurred in the intact particles. The presumed failure mechanisms are additional through-coatings failure of as-fabricated SiC-failed particles or an excessive increase of internal pressure by the accelerated irradiation. The further study is needed to clarify the failure mechanism.
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Verfondern, K.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(6), p.411 - 419, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:75.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Martin, D. G.*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya
JAERI-Research 2001-033, 19 Pages, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Verfondern, K.*; Sumita, Junya; Ueta, Shohei; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAERI-Research 2000-067, 127 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Sumita, Junya; Watanabe, Takashi*
JAERI-Data/Code 99-034, 115 Pages, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
 21, 1997, Tokai-mura, Japan
21, 1997, Tokai-mura, Japan; ; Sugimoto, Jun
JAERI-Conf 97-011, 829 Pages, 1998/01
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Yoshimuta, Shigeharu*; Tobita, Tsutomu*;
JAERI-Research 97-036, 23 Pages, 1997/05
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Shiozawa, Shusaku; Minato, Kazuo; Fukuda, Kosaku
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 33(9), p.712 - 720, 1996/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:86.73(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; Matsumoto, Kiyoshi; Hoshina, Hirofumi*
PSA95: Proc. of Probabilistic Safety Assessment Methodology and Applications, 2, p.735 - 740, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki
JAERI-M 92-021, 149 Pages, 1992/03
no abstracts in English
Nishiguchi, Isoharu; Tachibana, Yukio; Motoki, Yasuo; Shiozawa, Shusaku
JAERI-M 90-152, 31 Pages, 1990/09
no abstracts in English
; ; ; Ikawa, Katsuichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 24(6), p.429 - 434, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
;
Oyo Kikai Kogaku, 20(10), p.24 - 29, 1979/00
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro*; Haseda, Masaya*; Aihara, Jun
no journal, ,
In high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), Tri-isotropic (TRISO)-coated fuel particles are employed as fuel. In the high burnup coated fuel particle, stress due to fission gas pressure and irradiation-induced pyrolytic carbon (PyC) shrinkage is introduced into the coating layers and consequently the stress could cause failure of coating layers under high burnup irradiation condition. A failure model has developed to predict failure fraction of TRISO-coated particle under high burnup irradiation. In the model, failure probability is strongly dependent on the irradiation characteristics of PyC. This paper describes the outline of the failure model and evaluation result of high burnup fuel irradiation experiment by the model.
Zheng, X.; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
no journal, ,