Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tian, Q.*; Feng, L.*; Wu, C.*; Wen, J.*; Qiu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Yu, Q.*
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 669, p.1006 - 1014, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:44.97(Chemistry, Physical) -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:88.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
Okita, Shoichiro; Sakurai, Tatsuhiro*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Takagi, Katsuyuki*; Nakano, Takayuki*; Hino, Masahiro*
KURNS Progress Report 2023, P. 97, 2024/07
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Takano, Masahide; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.1002 - 1012, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology) /GaN interfaces with suppressed Ga-oxide interlayer via sputter deposition of SiO
/GaN interfaces with suppressed Ga-oxide interlayer via sputter deposition of SiO
Onishi, Kentaro*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Mizobata, Hidetoshi*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 62(5), p.050903_1 - 050903_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:47.87(Physics, Applied)While the formation of an GaO interlayer is key to achieving SiO
interlayer is key to achieving SiO /GaN interfaces with low defect density, it can affect the reliability and stability of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices if the annealing conditions are not properly designed. In the present study, we aimed to minimize the growth of the GaO
/GaN interfaces with low defect density, it can affect the reliability and stability of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices if the annealing conditions are not properly designed. In the present study, we aimed to minimize the growth of the GaO layer on the basis of the sputter deposition of SiO
layer on the basis of the sputter deposition of SiO on GaN. Synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectrometry measurements confirmed the suppressed growth of the GaO
on GaN. Synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectrometry measurements confirmed the suppressed growth of the GaO layer compared with a SiO
layer compared with a SiO /GaN structure formed by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Negligible GaO
/GaN structure formed by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Negligible GaO growth was also observed when subsequent oxygen annealing up to 600
growth was also observed when subsequent oxygen annealing up to 600 C was performed. A MOS device with negligible capacitance-voltage hysteresis, nearly ideal flat-band voltage, and low leakage current was demonstrated by performing oxygen and forming gas annealing at temperatures of 600
C was performed. A MOS device with negligible capacitance-voltage hysteresis, nearly ideal flat-band voltage, and low leakage current was demonstrated by performing oxygen and forming gas annealing at temperatures of 600 C and 400
C and 400 C, respectively.
C, respectively.
Saito, Shingo*; Haraga, Tomoko; Marumo, Kazuki*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Nakano, Yuta*; Tasaki-Handa, Yuiko*; Shibukawa, Masami*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 96(3), p.223 - 225, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.03(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Highly efficient and effective separation between americium (Am ) and curium ion (Cm
) and curium ion (Cm ) was achieved by two simple electrophoresis-based techniques. Am
) was achieved by two simple electrophoresis-based techniques. Am and Cm
and Cm ions were complexed with fluorophore-modified acyclic hexadentate and octadentate polyaminocarboxylates and then were electrophoretically separated and fluorescently detected in free solution with ternary complexation or in gel medium.
ions were complexed with fluorophore-modified acyclic hexadentate and octadentate polyaminocarboxylates and then were electrophoretically separated and fluorescently detected in free solution with ternary complexation or in gel medium.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-028, 54 Pages, 2022/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Tailor-made Adsorbents for Uranium Recovery from Seawater on the Basis of Uranyl Coordination Chemistry" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop a new ligand class for efficient and selective capture of uranium from seawater. On the basis of deep understanding on uranyl coordination chemistry, we design molecular structures of pentadentate ligands as functional moieties for uranium adsorption from seawater and study fundamental coordination chemistry of uranyl ion with those ligands in order to resolve current problems in uranium recovery technology …
 /Fe(0) by bacteria
/Fe(0) by bacteriaLiu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Takano, Masahide; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/10
Nuclear fuel debris, consisting primarily of nuclear fuel and structural material, was formed during the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident and exists in the cooling water accumulated in the primary containment vessels. Microorganisms living in groundwater may come into contact with the fuel debris and react with it. To assess the degradation of fuel debris, it is necessary to evaluate the interactions between microorganisms and fuel debris. Here we performed an experimental study on bacterial degradation. A mixed powder of UO and Fe(0) was used as a fuel debris simulant. Bacillus subtilis, which is widespread bacteria in nature and thought to be present at the accident site, was used. The mixed powder was exposed to the Bacillus subtilis in a liquid medium for some days. It was found that the oxidative dissolution of the U(IV) and Fe(0) was accelerated by B. subtilis. A fraction of the dissolved U(VI) was precipitated together with iron precipitates which are probably amorphous Fe(III) hydroxides. The study indicates that microorganisms would cause the degradation of fuel debris.
and Fe(0) was used as a fuel debris simulant. Bacillus subtilis, which is widespread bacteria in nature and thought to be present at the accident site, was used. The mixed powder was exposed to the Bacillus subtilis in a liquid medium for some days. It was found that the oxidative dissolution of the U(IV) and Fe(0) was accelerated by B. subtilis. A fraction of the dissolved U(VI) was precipitated together with iron precipitates which are probably amorphous Fe(III) hydroxides. The study indicates that microorganisms would cause the degradation of fuel debris.
 /GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000
/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates
) substratesMizobata, Hidetoshi*; Tomigahara, Kazuki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Letters, 121(6), p.062104_1 - 062104_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Physics, Applied)The interface properties and energy band alignment of SiO /GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000
/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates were investigated by electrical measurements and synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. They were then compared with those of SiO
) substrates were investigated by electrical measurements and synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. They were then compared with those of SiO /GaN MOS structures on Ga-polar GaN(0001). Although the SiO
/GaN MOS structures on Ga-polar GaN(0001). Although the SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) structure was found to be more thermally unstable than that on the GaN(0001) substrate, excellent electrical properties were obtained for the SiO
) structure was found to be more thermally unstable than that on the GaN(0001) substrate, excellent electrical properties were obtained for the SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) structure by optimizing conditions for post-deposition annealing. However, the conduction band offset for SiO
) structure by optimizing conditions for post-deposition annealing. However, the conduction band offset for SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) was smaller than that for SiO
) was smaller than that for SiO /GaN(0001), leading to increased gate leakage current. Therefore, caution is needed when using N-polar GaN(000
/GaN(0001), leading to increased gate leakage current. Therefore, caution is needed when using N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates for MOS device fabrication.
) substrates for MOS device fabrication.
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Sumita, Takehiro; Kitagaki, Toru; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(6), p.2785 - 2794, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Chemistry, Analytical)Remnant nuclear fuel debris in the damaged nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) has contacted the groundwater containing microorganisms for over ten years. Herein, we report the possibility of bacterial alteration of fuel debris. We investigated the physical and chemical changes of fuel debris simulants (FDS) in the powder and pellet forms via exposure to two ubiquitous bacteria, Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus subtilis. In the experiments using FDS composed of the powders of Fe(0), solid solution of CeO and ZrO
and ZrO , and SiO
, and SiO , Ce, Zr, and Si were hardly dissolved, while Fe was dissolved, a fraction of the dissolved Fe was present in the liquid phase as Fe(II) and Fe(III), and the rest was precipitated as the nano-sized particles of iron (hydr)oxides. In the experiment using P. fluorescens and FDS pellet pieces prepared by melting the Fe(0) particles and solid solution of CeO
, Ce, Zr, and Si were hardly dissolved, while Fe was dissolved, a fraction of the dissolved Fe was present in the liquid phase as Fe(II) and Fe(III), and the rest was precipitated as the nano-sized particles of iron (hydr)oxides. In the experiment using P. fluorescens and FDS pellet pieces prepared by melting the Fe(0) particles and solid solution of CeO and ZrO
and ZrO , the bacteria selectively gathered on the Fe(0) particle surface and made corrosion pits. These results suggest that bacteria in groundwater corrode the iron in fuel debris at FDNPP, change fuel debris into porous one, releasing the nano-sized iron (hydr)oxide particles into the water.
, the bacteria selectively gathered on the Fe(0) particle surface and made corrosion pits. These results suggest that bacteria in groundwater corrode the iron in fuel debris at FDNPP, change fuel debris into porous one, releasing the nano-sized iron (hydr)oxide particles into the water.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-041, 42 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of tailor-made adsorbents for uranium recovery from seawater on the basis of uranyl coordination chemistry" conducted in FY2020. On the basis of deep understanding on uranyl coordination chemistry, we design molecular structures of pentadentate ligands as functional moieties for uranium adsorption from seawater and study coordination chemistry of uranyl ion with those ligands in order to resolve current problems in uranium recovery technology from seawater and to develop novel selective and efficient adsorbents for this purpose.
Ochs, M.*; Dolder, F.*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 136, p.105161_1 - 105161_11, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:67.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Various types of radioactive wastes and environments contain organic substances that can stabilize the aqueous complexes with radionuclides and therefore lead to a decrease of sorption. The present study focuses on testing a methodology to quantify sorption reduction factors (SRFs) in the presence of organic ligands for cement systems. Three approaches for the estimation of SRFs; (1) analogy with solubility enhancement factors, (2) radionuclide speciation based on the thermodynamic calculations, and (3) experimental sorption data in ternary systems, were coupled and tested for the representative organic ligands (ISA and EDTA) and selected key radionuclides (actinides). Our approach allows to critically evaluate the dependence of SRFs for various systems on the chosen method of quantification, in accordance with the data availability for a given systems. The reliable SRFs can only be derived from the sorption measurements in ternary systems. SRF often need to be derived in the absence of such direct evidence, and estimations need to be made based on analogies and speciation information. However, such estimates may be subject to substantial uncertainties.
 O vapor on GaN surfaces
O vapor on GaN surfacesSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Sang, L.*; Harada, Yoshitomo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.189 - 198, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)GaN is an attracting material for power-electronic devices. Understanding the oxidation at GaN surface is important for improving metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices. In this study, the oxidation at GaN surfaces depending on the GaN crystal planes (+c, -c, and m-plane) was investigated by real time XPS and DFT-MD simulation. We found that H O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H
O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al
O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al Ga
Ga N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al
N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al O
O layer deposited by ALD using H
layer deposited by ALD using H O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H
O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H O and O
O and O should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al
should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al Ga
Ga N atomi layer deposition.
N atomi layer deposition.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-029, 64 Pages, 2021/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishment of the measurement system of radiation dependent mutation in organ cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells" conducted from FY2018 to 2020. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2020, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aimed to establish measurement system of radiation dependent mutation for analyze radiation effect to the human body. A distinctive feature of this study is to compare several organ cells which possess same genome DNA using human induced pluripotent stem cell. Further, using artificial intelligence technology and machine leaning method, we analyzed differences of mutation frequency during samples.
 U accumulations in
U accumulations in 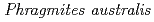 naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophores
naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophoresNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Doyama, Kohei*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Lu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
Minerals (Internet), 11(12), p.1337_1 - 1337_17, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Mine drainage is a vital water problem in the mining industry worldwide because of the heavy metal elements and low pH. Rhizofiltration using wetland plants is an appropriate method to remove heavy metals from the water via accumulation in the rhizosphere. 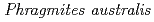 is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,
is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,  has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that
has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that  accumulated Fe, Mn, and
accumulated Fe, Mn, and  U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around
U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around  roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as
roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as 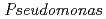 spp. and
spp. and 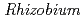 spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several
spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several 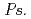 spp. and
spp. and 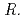 spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as
spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as 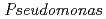 spp. and
spp. and 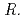 spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of
spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of  , might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in
, might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in  , and
, and 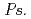 spp. and
spp. and 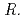 spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
Kato, Takuma*; Nagaoka, Mika; Guo, H.*; Fujita, Hiroki; Aida, Taku*; Smith, R. L. Jr.*
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(39), p.55725 - 55735, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)In this work, hydrothermal leaching was applied to simulated soils (clay minerals vermiculite, montmorillonite, kaolinite) and actual soils (Terunuma, Japan) to generate organic acids with the objective to develop an additive-free screening method for determination of Sr in soil. Stable strontium (SrCl ) was adsorbed onto soils for study and ten organic acids were evaluated for leaching Sr from simulated soils under hydrothermal conditions (120 to 200
) was adsorbed onto soils for study and ten organic acids were evaluated for leaching Sr from simulated soils under hydrothermal conditions (120 to 200 C) at concentrations up to 0.3 M. For strontium-adsorbed vermiculite (Sr-V), 0.1 M citric acid was found to be effective for leaching Sr at 150
C) at concentrations up to 0.3 M. For strontium-adsorbed vermiculite (Sr-V), 0.1 M citric acid was found to be effective for leaching Sr at 150 C and 1 h treatment time. Based on these results, the formation of organic acids from organic matter in Terunuma soil was studied. Hydrothermal treatment of Terunuma soil produced a maximum amount of organic acids at 200
C and 1 h treatment time. Based on these results, the formation of organic acids from organic matter in Terunuma soil was studied. Hydrothermal treatment of Terunuma soil produced a maximum amount of organic acids at 200 C and 0.5 h reaction time. To confirm the possibility for leaching of Sr from Terunuma soil, strontium-adsorbed Terunuma soil (Sr-S) was studied. For Sr-S, hydrothermal treatment at 200
C and 0.5 h reaction time. To confirm the possibility for leaching of Sr from Terunuma soil, strontium-adsorbed Terunuma soil (Sr-S) was studied. For Sr-S, hydrothermal treatment at 200 C for 0.5 h reaction time allowed 40% of the Sr to be leached at room temperature, thus demonstrating an additive-free method for screening of Sr in soil. The additive-free hydrothermal leaching method avoids calcination of solids in the first step of chemical analysis and has application to both routine monitoring of metals in soils and to emergency situations.
C for 0.5 h reaction time allowed 40% of the Sr to be leached at room temperature, thus demonstrating an additive-free method for screening of Sr in soil. The additive-free hydrothermal leaching method avoids calcination of solids in the first step of chemical analysis and has application to both routine monitoring of metals in soils and to emergency situations.
 C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditions
C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditionsHidaka, Akihide
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.341 - 356, 2021/10
Kobayashi, Masaki*; Anh, L. D.*; Suzuki, Masahiro*; Kaneta-Takada, Shingo*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Shibata, Goro*; Tanaka, Arata*; Tanaka, Masaaki*; Oya, Shinobu*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 15(6), p.064019_1 - 064019_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:46.19(Physics, Applied)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-061, 56 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishment of the measurement system of radiation dependent mutation in organ cells derived from human induced pluripotent cells" conducted in FY2019. In this study, we aimed to establish measurement system of radiation dependent mutation for analyze radiation effect to the human body. A distinctive feature of this study is to compare several organ cells which possess same genome DNA using human induced pluripotent stem cell. Further, using artificial intelligence technology and machine leaning method, we will analyze differences of mutation frequency during samples.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-026, 41 Pages, 2020/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Tailor-Made Adsorbents for Uranium Recovery from Seawater on the Basis of Uranyl Coordination Chemistry". On the basis of deep understanding on uranyl coordination chemistry, we design molecular structures of pentadentate ligands as functional moieties for uranium adsorption from seawater and study coordination chemistry of uranyl ion with those ligands in order to resolve current problems in uranium recovery technology from seawater and to develop novel selective and efficient adsorbents for this purpose.