Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ono, Masato; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.235 - 242, 2025/05
 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hydridosilicates featuring SiH octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH
octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH
obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH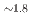 with H
with H fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH
fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH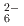 ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba
ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH
counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH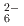 bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm
bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm , respectively. BaSiH
, respectively. BaSiH is thermally stable up to 95
is thermally stable up to 95 C above which decomposition into BaH
C above which decomposition into BaH and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH
and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (
consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (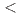 10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH
10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH
suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH .
.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Terada, Atsuhiko; Thwe Thwe, A.; Hino, Ryutaro*
JAEA-Review 2024-049, 400 Pages, 2025/03
In the aftermath of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, safety measures against hydrogen in severe accident has been recognized as a serious technical problem in Japan. As one of efforts to form a common knowledge base between nuclear engineers and experts on combustion and explosion, we issued the "Handbook of Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety (1st edition)" in 2017. For improvement of the rational advancement of hydrogen safety measures and further reliability of hydrogen safety evaluation, a CFD analysis is highly expected to produce more precisely and quantitative results. We have been developing an integrated CFD analysis code system which can analyze hydrogen diffusion, explosion-combustion and structural integrity at the severe accident especially for pressurized water reactors (PWRs). We organized the role of LP and the CFD analyses and their utilization examples of hydrogen safety validation. Based on these results, we made the "Handbook of Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety (2nd volume)". The analysis results of real scale PWR described in 2nd volume are confirmed by cross-analysis models and existing data obtained through representative small, medium and large-scale tests.
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 226, p.112198_1 - 112198_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)In recent years, the use of radiation-resistant resins of polyimide and polyether ether ketone becomes increasing as vessels for irradiation and unsealed radioisotope experiments. However, in our radiolysis experiments, the possibility of interaction between radiolysis products of water and the resin was found, suggesting concerns that the resin may affect reactions in water in radiation fields. To clarify the interaction, dichromate (Cr O
O
 ) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H
) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) formation in
) formation in  -radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr
-radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr O
O
 reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr
reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr O
O
 reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H
reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H O
O formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Lee, Y.*; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Hartl, M.*; Aso, Tomokazu; Iverson, E. B.*; Ariyoshi, Gen; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)At Japanese Spallation Neutron Source in J-PARC, the para-hydrogen fraction was measured by using Raman spectroscopy in-situ for an integrated beam power of 9.4 MW h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW
h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
Doi, Daisuke
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 91, p.1245 - 1252, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.33(Chemistry, Physical)Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/11
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steelIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Shibayama, Yuki; Hojo, Tomohiko*; Koyama, Motomichi*; Akiyama, Eiji*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 88, p.1010 - 1016, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.25(Chemistry, Physical)Terada, Atsuhiko; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Nuclear Technology, 210(10), p.1871 - 1887, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to understand dispersion of H2 leaked in packed beds of non-porous/porous particles in a partially open space practically, the dispersion of H2 in the particle layers of glass beads and soil was analytically studied using a CFD code to be compared with the experiments and to elucidate the effects of particle layer. H2 flowed out from a single leak point in the particle layer of non-porous glass beads was affected by buoyancy around the leak point, and diffused directly above the leak point in an elliptical shape faster than in the horizontal direction. After that, when it reached the air layer in the head space above the particle layer, H2 spread horizontally, formed a large concentration gradient near the boundary between the particle layer and the air layer, and further diffused in the air layer until the H2 concentration became about 1/3 or less of the concentration near the surface of particle layer. The calculations largely reproduced the experimental concentration distributions. When the particle layer was porous decomposed granite soil, the diffusion behavior of H2 in the particle layer proceeded in the same manner as in the case of glass beads. However, a large concentration gradient was formed near the boundary between the particle layer and the air layer, and then H2 diffused in the air layer until the H2 concentration became below the lower combustion limit. It was suggested through sensitivity analysis that the air permeability coefficient had a large effect on the time course of H2 concentration distribution. Based on the above, we further simulated H2 behavior in the vessel containing the H2 leaked particle layer. By inserting multiple vent pipes without considering H2 generation distribution and particle properties in the particle layer, H2 accumulated from one pipe was discharged by buoyancy without depending on the H2 generation distribution and particle properties in the particle layer, and air flowed in from the other pipe.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 31(10), p.102504_1 - 102504_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hydrogen isotope mixing phenomena in tokamak plasmas are analyzed using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. Model plasma parameters are chosen based on the hydrogen isotope pellet experiments on JET, in which hydrogen isotope mixing in the time scale of the energy confinement time occurred after injecting deuterium (D) pellets into hydrogen (H) plasmas. Two numerical experiments are conducted using plasma profiles before and after the D pellet injection. In both cases, turbulent fluctuations in the plasma core are characterized by ion temperature gradient driven turbulence, while in the latter case, trapped electron mode turbulence also exists in the outer region. In the former case, the density profile of bulk H ions is kept in a quasi-steady state, and the particle confinement time of bulk H ions is an order of magnitude longer than the energy confinement time. In the latter case, the density profiles of bulk H ions and pellet D ions show transient relaxation in the time scale of the energy confinement time, indicating the fast hydrogen isotope mixing. In the toroidal angular momentum balance, it is found that the hydrogen isotope mixing is driven by the toroidal field stress.
Takeda, Takeshi; Shibata, Taiju
JAEA-Review 2024-040, 29 Pages, 2024/09
An important theme of Japan's 6th strategic energy plan is to indicate the energy policy path towards carbon neutrality by 2050. Policy responses for Japan's nuclear energy research and development (R&D) towards 2030 contain the demonstrations of technologies for small modular reactors (SMRs) through international cooperation by 2030. In light of this energy plan, basic policy initiatives over the next 10 years have been compiled to realize Green Transformation (GX), which simultaneously achieves decarbonization and economic growth. Looking overseas, activities of SMR R&D are active internationally, mainly in the US, Canada, Europe, China, and Russia. These activities are not only by heavy industry manufactures and R&D institutes, but also by venture companies. Under these circumstances, the NEA CSNI has gathered an Expert Group on SMRs (EGSMR) to help estimate the safety effects of SMRs. The EGSMR efforts required the submission of responses to several questionnaires whose main purpose was to collect the latest information on the efforts of SMR deployment and research. The first author of this report responded to this based on information from Hitachi-GE Nuclear Energy, Ltd. and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. as well as JAEA. Most of the responses from Japan to the questionnaires are the information that serves as the basis of CSNI Technical Opinion Paper No. 21 (TOP-21). In this report, the Japan's publicly available responses to the questionnaires arranged and additional information are explained, which complements some of the content of the TOP-21. In this manner, the investigation results of R&D related to SMR in Japan, focusing on the EGSMR activities (2022-2023), are summarized. The target of this report is to provide useful information for future discussions on international cooperation concerning SMR as well as nuclear power field human resources development internationally and domestically.
 /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2024-019, 102 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a new corrosion mitigation technology using nanobubbles toward corrosion mitigation in PCV system under the influence of  /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to corrosion, which is considered to be an important factor in the aging degradation of confinement functions (PCV, negative pressure maintenance system, etc.) during the fuel debris removal process. If the chemical species (especially H
-rays radiolysis" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to corrosion, which is considered to be an important factor in the aging degradation of confinement functions (PCV, negative pressure maintenance system, etc.) during the fuel debris removal process. If the chemical species (especially H O
O ) generated by radiolysis become locally concentrated in the areas where short-range
) generated by radiolysis become locally concentrated in the areas where short-range  - and
- and  -radiation emitting nuclides come into contact, the corrosion of steels may be greatly accelerated in those areas.
-radiation emitting nuclides come into contact, the corrosion of steels may be greatly accelerated in those areas.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(8), p.1135 - 1154, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to elucidate ventilation and exhaust of hydrogen leaked in a partially open space practically, the effects of outer wind on them were studied analytically by using a CFD code in the room of experimental Half-size Hallway model, which has a H release hole on the bottom, one vent on the roof and another vent on the side: external air flowed in the room from the Door vent and then H
release hole on the bottom, one vent on the roof and another vent on the side: external air flowed in the room from the Door vent and then H was discharged outside from the Roof vent. The H
was discharged outside from the Roof vent. The H concentration distribution in the room was divided into two layers at the height of Door vent, with a high concentration layer above it and a low concentration layer below it, forming a stratified interface. When the wind speed blown into the room increased, the combination of the Realizable k-e; turbulence model and the turbulence Schmidt number of 1.0 improved the reproducibility of the analysis results of H
concentration distribution in the room was divided into two layers at the height of Door vent, with a high concentration layer above it and a low concentration layer below it, forming a stratified interface. When the wind speed blown into the room increased, the combination of the Realizable k-e; turbulence model and the turbulence Schmidt number of 1.0 improved the reproducibility of the analysis results of H concentration distribution. The trial analysis suggested that the concern that wind would increase the indoor H
concentration distribution. The trial analysis suggested that the concern that wind would increase the indoor H concentration could be reduced by using the plate with a simple structure in which two plates were crossed on the Roof vent.
concentration could be reduced by using the plate with a simple structure in which two plates were crossed on the Roof vent.
Higa, Ryota*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
Materials Transactions, 65(8), p.899 - 906, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)It is indispensable to suppress hydrogen embrittlement (HE) to develop the strength of the Al-Zn-Mg alloy. Because intergranular fracture (IGF) is mainly observed when HE occurs in the alloy, we need to understand the IGF initiation to suppress HE. In the present study, we investigated the stress, strain, and H concentration, which influence the IGF initiation, in actual fractured regions by simulation of a crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis in a 3D image-based model, which was created based on 3D polycrystalline microstructure data obtained from X-ray imaging technique. Combining the simulation and in-situ observation of the tensile test sample by X-ray CT, we examined the stress, strain, and H concentration, and discussed the IG crack initiation condition. As a result, it is revealed that stress normal to grain boundary induced by crystal plasticity dominates IG crack initiation while the accumulation of H due to stress has little impact on it.
Nagatsuka, Kentaro; Noguchi, Hiroki; Nagasumi, Satoru; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Sakaba, Nariaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 425, p.113338_1 - 113338_11, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:93.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)HTGR has a potential to contribute to decarbonization of hard-to-abate industries by supplying a large amount of hydrogen and high temperature heat or steam without carbon dioxide emission. JAEA has been conducting R&Ds for HTGR technologies with High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). This paper shows that HTTR's tests including the loss of core cooing test as a joint the OECD/NEA international research project and a HTTR heat application test plan which demonstrate hydrogen production by coupling the HTTR with a hydrogen production test facility. Additionally, aiming for operation start from the latter half of 2030s, the basic design of the HTGR demonstration reactor has been shown. The Japan's HTGR technology capabilities established by the HTTR project will be fully utilized for the construction of HTGR demonstration reactor.
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*
Nuclear Technology, 210(8), p.1427 - 1443, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The retention of hydrogen (H ) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H
) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H
retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H
O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H
O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H
bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H observed with and without stirring the slurry after
observed with and without stirring the slurry after  Co
Co  -irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H2 bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.
-irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H2 bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.
Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Kato, Atsushi; Hayakawa, Masato; Shimoyama, Kazuhito; Ara, Kuniaki; Hatakeyama, Nozomu*; Yamauchi, Kanau*; Eda, Yuhei*; Yui, Masahiro*
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 56(3), p.893 - 899, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:57.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)