Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 72(10.11), p.441 - 448, 2023/10
Rapid analytical method for the determination of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes has been developed. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS was applied to the analysis of Zr isotopes in simulated high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Sample preparation time was dramatically reduced by using a DGA resin as the adsorbent for Zr. Direct quantification of Zr isotopes in this resin sample was carried out by LA-ICP-MS. Laser settings were optimized to obtain a reliable isotope ratio of the sample by LA-ICP-MS. Quantification of Zr isotopes in the simulated HLW solution by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) was examined. The amount of Zr-90 in the sample obtained by IDMS corresponded to a value calculated from the given concentration of Zr in the sample within uncertainty. Thus, this method can be applied for the quantification of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes.
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Ishiniwa, Hiroko*; Wada, Toshihiro*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analyst, 148(18), p.4291 - 4299, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.37(Chemistry, Analytical)Quantitative imaging of trace elements was successfully performed by online isotope dilution laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (online LA-ICP-IDMS). The sample aerosols produced by LA are mixed online with the mist created from an isotopically enriched spike solution via an in-house cyclonic spray chamber, which has a gas port on the top. Quantification was continuously achieved in each spot; subsequently, quantitative imaging was realized. Fe and Sr were selected as the model elements, and their spot quantifications based on online-isotope dilution. The method was applied to actual biological hard tissues, and the results were compared with electron probe microanalyzer data.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ito, Daichi*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Sakata, Shuhei*; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Koshi*; Imura, Takumi*; Motai, Satoko*; Ono, Takeshi*
Lithos, 440-441, p.107026_1 - 107026_14, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.60(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We propose a new method for elucidating zircon growth in granitic plutons, based on variations in three-dimensional 3D cathodoluminescence (CL) patterns, U-Pb ages, titanium concentration, and Th/U ratios. We focused on the zircon growth processes in the Okueyama granite (OKG) in central Kyushu, Japan, to obtain interpretations of magma chamber processes that result in the formation of granitic plutons. The OKG consists of three lithofacies: biotite granite (BG), hornblende granite (HG), and hornblende granodiorite (HGD). To determine the 3D internal structure and growth pattern of a zircon crystal, we performed CL observations for multi-sections of the samples. Simultaneously, we also determined the zircon U-Pb age and titanium concentration of the center sections of the samples. The 3D distribution of the oscillatory zoning can be used to determine the crystal nucleus. The simultaneous determination of zircon U-Pb ages and Ti concentrations of the granite samples indicates the time-temperature (t-T) history of granitic magma before its solidification. The t-T histories of the BG, HG, and HGD represented similar cooling behaviors within the magma chamber: rapid cooling from the zircon crystallization temperature to the closure temperature of the biotite K-Ar system between 16 Ma and 10 Ma. The variations in the Th/U ratios against temperature also demonstrate a different trend at the boundary of approximately 670  C. Fractional crystallization in the magma chamber progressed significantly at temperatures above 670
C. Fractional crystallization in the magma chamber progressed significantly at temperatures above 670  C; below 670
C; below 670  C, crystallization progressed slowly, indicating only minimal changes in the magma composition. The variations in the Th/U ratio against temperature in the BG, HG, and HGD portrayed common tendencies, indicating the same behavior in the progression of fractional crystallization among the three lithofacies, which in turn, represented the same behavior within the entire magma chamber.
C, crystallization progressed slowly, indicating only minimal changes in the magma composition. The variations in the Th/U ratio against temperature in the BG, HG, and HGD portrayed common tendencies, indicating the same behavior in the progression of fractional crystallization among the three lithofacies, which in turn, represented the same behavior within the entire magma chamber.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Yamazaki, Hayato*; Ishibashi, Kozue*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Sando, Kazusa*; Imura, Takumi*; Ono, Takeshi*
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 226, p.105075_1 - 105075_9, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.12(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Simultaneous determination of the U-Pb age of zircon and concentration of titanium in a single analysis spot, using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with laser ablation sample introduction, produces paired age and temperature data of zircon crystallisation, potentially revealing time-temperature ( ) histories for evolved magma. The Kurobegawa granite, central Japan, contains abundant mafic magmatic enclaves (MMEs). We applied this method to evaluate MMEs and their host (enclosing) granites. Cooling behaviour common to both MMEs and host rocks was found between 1.5 and 0.5 Ma. Rapid cooling from the zircon crystallisation temperature to the closure temperature of biotite K-Ar system was within
) histories for evolved magma. The Kurobegawa granite, central Japan, contains abundant mafic magmatic enclaves (MMEs). We applied this method to evaluate MMEs and their host (enclosing) granites. Cooling behaviour common to both MMEs and host rocks was found between 1.5 and 0.5 Ma. Rapid cooling from the zircon crystallisation temperature to the closure temperature of biotite K-Ar system was within  1 million year. Combining the obtained
1 million year. Combining the obtained  paths of MMEs and host rocks with petrological information can provide insights into magma chamber processes. This suggests that MME flotation, migration, and spread through the magma chamber ceased at 1.5-0.5 Ma, indicating the emplacement age of the Kurobegawa granitic pluton, as no large-scale reheating episodes have occurred since then.
paths of MMEs and host rocks with petrological information can provide insights into magma chamber processes. This suggests that MME flotation, migration, and spread through the magma chamber ceased at 1.5-0.5 Ma, indicating the emplacement age of the Kurobegawa granitic pluton, as no large-scale reheating episodes have occurred since then.
Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Umeda, Koji*
JAEA-Testing 2021-001, 49 Pages, 2021/08
To make a contribution to safety assessment for geological disposal of high level radioactive and/or TRU waste, we need to assess long-term stability of geological environment and predict long-term changes of geotectonic events that will occur in the future, especially for Quaternary period ( 2.6 million years ago-present). In the most case, we investigate chronological data of geological events by radiometric dating. When some geological samples have no objects to which radiometric dating method can be applied (e.g., zircon, biotite, wood fragments and plant residues), we can use tephrochronology, which is geological dating method using each layer of tephra (erupted volcanic ash), for dating of geological layers. This chronological method is essential in Japan, where volcanism is very active. Tephra is usually characterized by petrographic characteristics and/or chemical composition (mainly major elements) of volcanic glasses and/or minerals in tephra. In Tono Geoscience Center (Japan Atomic Energy Agency), we develop an analytical technique of chemical composition including trace elements of volcanic glasses for detailed tephra identification. In this paper, we report a sample preparation procedure and analytical methods of chemical compositions of individual volcanic glass shards by using an electron probe microanalyzer and a laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer.
2.6 million years ago-present). In the most case, we investigate chronological data of geological events by radiometric dating. When some geological samples have no objects to which radiometric dating method can be applied (e.g., zircon, biotite, wood fragments and plant residues), we can use tephrochronology, which is geological dating method using each layer of tephra (erupted volcanic ash), for dating of geological layers. This chronological method is essential in Japan, where volcanism is very active. Tephra is usually characterized by petrographic characteristics and/or chemical composition (mainly major elements) of volcanic glasses and/or minerals in tephra. In Tono Geoscience Center (Japan Atomic Energy Agency), we develop an analytical technique of chemical composition including trace elements of volcanic glasses for detailed tephra identification. In this paper, we report a sample preparation procedure and analytical methods of chemical compositions of individual volcanic glass shards by using an electron probe microanalyzer and a laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer.
 Cs in spent Cs adsorbent used for the decontamination of radiocesium-containing water by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Cs in spent Cs adsorbent used for the decontamination of radiocesium-containing water by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryAsai, Shiho*; Ohata, Masaki*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Yomogida, Takumi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Chemistry, 92(4), p.3276 - 3284, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.21(Chemistry, Analytical)The long-term safety assessment of spent Cs adsorbents produced during the decontamination of radiocesium-containing water at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant requires one to estimate their  Cs content prior to final disposal.
Cs content prior to final disposal.  Cs is usually quantified by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), which necessitates the elution of Cs from Cs adsorbents. However, this approach suffers from the high radiation dose from
Cs is usually quantified by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), which necessitates the elution of Cs from Cs adsorbents. However, this approach suffers from the high radiation dose from  Cs. To address this challenge, we herein employed laser ablation ICP-MS for direct quantitation of
Cs. To address this challenge, we herein employed laser ablation ICP-MS for direct quantitation of  Cs in Cs adsorbents and used a model Cs adsorbent prepared by immersion of a commercially available Cs adsorbent into radiocesium-containing liquid waste to verify the developed technique. The use of the
Cs in Cs adsorbents and used a model Cs adsorbent prepared by immersion of a commercially available Cs adsorbent into radiocesium-containing liquid waste to verify the developed technique. The use of the  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio and
Cs ratio and  Cs radioactivity obtained by gamma spectrometry achieved simple and precise quantitation of
Cs radioactivity obtained by gamma spectrometry achieved simple and precise quantitation of  Cs and the resulting
Cs and the resulting  Cs activity of 0.36 Bq agreed well with that in the original radiocesium-containing liquid waste.
Cs activity of 0.36 Bq agreed well with that in the original radiocesium-containing liquid waste.
 Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MS
Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MSAsai, Shiho; Ohata, Masaki*; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(5), p.973 - 983, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:58.34(Biochemical Research Methods)Determination of radiopalladium  Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of
Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of  Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study,
Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study, 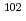 Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of
Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of  Pd/
Pd/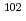 Pd. The amount of
Pd. The amount of  Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kimura, Junichi*; Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Danhara, Toru*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Chang, Q.*; Miyazaki, Takashi*; et al.
Geochemical Journal, 52(6), p.531 - 540, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.35(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Asai, Shiho; Limbeck, A.*
Talanta, 135, p.41 - 49, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:58.68(Chemistry, Analytical)A new analytical method for chondrite-normalized Rare earth elements (REE) plot has been developed in this study. Cation-exchange resin particles were used as a substrate to retain REE for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). In LA analysis, formation of oxide and hydroxide of the light REE and Ba which causes spectral interferences in the heavy REE measurement was effectively attenuated, compared to conventional solution nebulization ICP-MS. To evaluate the applicability of the proposed method, the REE-adsorbed particles prepared by immersing them in a U-bearing solution were measured with LA-ICP-MS. Additionally, each concentration of REE in the U standard solution was determined with solution nebulization ICP-MS. The chondrite-normalized plot obtained through LA-ICP-MS analysis exhibited close agreement with that obtained through the solution nebulization ICP-MS of the REE-separated solution within the uncertainties.
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
Determinations of radioisotopes in fuel debris and radioactive wastes are important for decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Difficult-to-measure radioisotopes such as Sr-90 have been measured by radiometric analysis and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), the methods have not achieved the distribution of the radioisotopes on the sample's surface due to its digestion process of the samples before measurements. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS can obtain the distribution information of radionuclides directly on the surface of solid samples. In contrast, the quantification with the method is difficult caused by the spectral interferences and matrix effects from samples. In this study, a quantification method was developed combined with LA-ICP-MS and isotope dilution method. The proposed method was applied for Sr-90 quantification.
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Yokota, Hiromi; Matsueda, Makoto; Ishiniwa, Hiroko*; Fujimoto, Katsushige*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
Fuel debris is considered a heterogeneous mixture of nuclear fuel, control rods and reactor structural materials that has cooled and solidified, and it is important to understand its composition (elements and isotopes) and distribution to formulate storage, treatment and disposal methods after fuel debris removal. Mass spectrometric imaging using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) is useful for the aforementioned fuel debris analysis because it can visualise the distribution of elements and isotopes at the 10 - 10
- 10
 g/g level with a spatial resolution of 10-100
g/g level with a spatial resolution of 10-100  m. However, the number of data is enormous when the number of measurement points is large. In this study, an automatic peak detection method using the asymmetric least squares method with a penalty term was developed, data processing for LA-ICP-MS was automated and an intuitive GUI was constructed.
m. However, the number of data is enormous when the number of measurement points is large. In this study, an automatic peak detection method using the asymmetric least squares method with a penalty term was developed, data processing for LA-ICP-MS was automated and an intuitive GUI was constructed.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kokubu, Yoko; Murakami, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Takahiro; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Miyazaki, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Chronological and geochemical studies of carbonates, which are commonly found as fracture filling minerals in rocks, can provide information about geochemical conditions present during formation including in deep subsurface environments. A dating technique for the carbonates using laser ablation-multiple collector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICPMS) is still immature partly because of a lack of a consensus international carbonate standard for the in-situ dating technique. In this study, we performed a survey on the carbonate standard materials that may be suitable for high precision U-Th-Pb dating using LA-MC-ICPMS. We examined carbonate standard materials JCp-1 and JCt-1 issued by the Geological Survey of Japan (GSJ). Based on solution-based bulk analysis using MC-ICP-MS, heterogeneities in Pb isotope compositions were confirmed. Nevertheless, the 206Pb-based isotopic compositions were all within 1.2 per mill variations acceptable for a standard used for age determination using LA-MC-ICPMS. Additional tests on the heterogenities in U-Th-Pb compositions of the carbonate standards along with determinations of other trace elements using a 2D imaging LA-ICP-MS are ongoing. Examinations on both natural standards and synthetic standards are ongoing for further efforts in determination of the standard suitable for U-Th-Pb dating of carbonates.
Kitahara, Yasuko*; Inose, Akira*; Makiishi, Noriko*; Nagoshi, Masayasu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Cs in Cs adsorbent used for water decontamination by laser-ablation ICP-MS
Cs in Cs adsorbent used for water decontamination by laser-ablation ICP-MSAsai, Shiho*; Ohata, Masaki*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Yomogida, Takumi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
A large amount of spent Cs adsorbents used for decontaminating water in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station are stored in the site. To dispose them safely, the estimation of  Cs activity along with that of
Cs activity along with that of  Cs is indispensable.
Cs is indispensable.  Cs is generally measured by ICP-MS, which required the sample to be prepared in liquid form and thus the elution of Cs from the Cs adsorbents is essential. However, this approach suffers from the high radiation dose from
Cs is generally measured by ICP-MS, which required the sample to be prepared in liquid form and thus the elution of Cs from the Cs adsorbents is essential. However, this approach suffers from the high radiation dose from  Cs. In this study, we quantified
Cs. In this study, we quantified  Cs in a Cs adsorbent using the
Cs in a Cs adsorbent using the  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio obtained by LA-ICP-MS and
Cs ratio obtained by LA-ICP-MS and  Cs radioactivity obtained by gamma spectrometry. To evaluate the applicability, we employed a
Cs radioactivity obtained by gamma spectrometry. To evaluate the applicability, we employed a  Cs -containing water sample to prepare a model spent Cs adsorbent with a certified
Cs -containing water sample to prepare a model spent Cs adsorbent with a certified  Cs activity. The resulting
Cs activity. The resulting  Cs activity of 0.36 Bq calculated by
Cs activity of 0.36 Bq calculated by  Cs /
Cs / Cs ratio of 0.41
Cs ratio of 0.41  0.02 and
0.02 and  Cs activity agreed well with that of the originally determined
Cs activity agreed well with that of the originally determined  Cs activity in the model spent Cs adsorbent, demonstrating that the proposed technique has high validity to
Cs activity in the model spent Cs adsorbent, demonstrating that the proposed technique has high validity to  Cs determination of a real sample.
Cs determination of a real sample.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Yuguchi, Takashi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Ishibashi, Kozue*; Ogita, Yasuhiro*; Ito, Daichi*; Ono, Takeshi*; Kagami, Saya; Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Sueoka, Shigeru
no journal, ,
Dating and trace elements analysis of zircons provide us the evidences of past thermal history about their growth events, such as timing and temperature of magmatism and crystallization. In granitic rocks, because the proposed closure temperature of zircon U-Pb ( 900
900  C) is often higher than crystallization temperature of the zircon, the zircon U-Pb age means the timing of crystallization. To clarify the growth history of granitic pluton, Yuguchi et al. (2016) performed the observation of internal structure of zircon (collected from the Toki granite, central Japan) using cathodoluminescence, deriving crystallization temperature and age using Ti-in-zircon thermometry and U-Pb dating. It is important to discuss the emplacement by such an approach to understand the history of upheaval and exhumation of igneous complex. In this study, for simultaneously estimating crystallization age and temperature of zircon, we performed U-Pb isotopic analysis and quantitative analysis of Titanium, in the same position of zircon, using LA-ICP-MS after the cathodoluminescence observation. As preliminary experiments, we analyzed zircons collected from Japan (e.g., Okue, Tono, Toki and Kurobegawa granites) to estimate their thermal history. We could estimate the crystallization ages and temperatures of zircons of Okue (556-946
C) is often higher than crystallization temperature of the zircon, the zircon U-Pb age means the timing of crystallization. To clarify the growth history of granitic pluton, Yuguchi et al. (2016) performed the observation of internal structure of zircon (collected from the Toki granite, central Japan) using cathodoluminescence, deriving crystallization temperature and age using Ti-in-zircon thermometry and U-Pb dating. It is important to discuss the emplacement by such an approach to understand the history of upheaval and exhumation of igneous complex. In this study, for simultaneously estimating crystallization age and temperature of zircon, we performed U-Pb isotopic analysis and quantitative analysis of Titanium, in the same position of zircon, using LA-ICP-MS after the cathodoluminescence observation. As preliminary experiments, we analyzed zircons collected from Japan (e.g., Okue, Tono, Toki and Kurobegawa granites) to estimate their thermal history. We could estimate the crystallization ages and temperatures of zircons of Okue (556-946 C in 11.1-16.1 Ma), Tono (613-901
C in 11.1-16.1 Ma), Tono (613-901 C in 110.2-127.4 Ma), Toki (575-734
C in 110.2-127.4 Ma), Toki (575-734 C in 69.4-79.9 Ma) and Kurobegawa (636-779
C in 69.4-79.9 Ma) and Kurobegawa (636-779 C in 0.46-1.85 Ma), respectively.
C in 0.46-1.85 Ma), respectively.
Nagata, Mitsuhiro*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kagami, Saya; Oto, Shigeru*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Sr isotopic analysis of apatite by LA-ICP-MS to constrain the chemical composition of the original magma
Sr isotopic analysis of apatite by LA-ICP-MS to constrain the chemical composition of the original magmaKagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Sasao, Eiji; Yuguchi, Takashi*; Chang, Q.*
no journal, ,
The fracture frequency distribution in granitic plutons depends on lithofacies, which reflect the chemical composition of the original magma. The initial Sr isotopic ratio of the whole rock is a valid indicator to identify the chemical composition of the magma. The apatite Sr isotopic composition probably records a primary Sr isotopic composition of the original magma because Rb is incompatible element for apatite. In this study, we developed a method for in situ Sr isotopic analysis of apatite by LA-ICP-MS. We adopted the technique of introducing desolvated solutions and solid samples into the ICP mass spectrometer. The correction for mass discrimination effects in the solid sample analysis by LA was attempted based on the isotope analysis of the solution. A gas line for mixing N into Ar sample carrier gas was installed to suppress the oxide production rate and improve the ionization efficiency of Sr. Our results of the analysis on the apatite reference materials were consistent with previous studies. In addition, we confirmed that this method can be applied to apatite samples with lower Sr mass fraction than above apatite reference materials and grain sizes of approximately 100
into Ar sample carrier gas was installed to suppress the oxide production rate and improve the ionization efficiency of Sr. Our results of the analysis on the apatite reference materials were consistent with previous studies. In addition, we confirmed that this method can be applied to apatite samples with lower Sr mass fraction than above apatite reference materials and grain sizes of approximately 100  m. The developed method enables the evaluation of differences in the chemical composition of the original magma and then provides the constraint on the relationship between lithofacies and fracture frequency distribution by combination with chemical and geological information of granitic rocks.
m. The developed method enables the evaluation of differences in the chemical composition of the original magma and then provides the constraint on the relationship between lithofacies and fracture frequency distribution by combination with chemical and geological information of granitic rocks.
Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishibashi, Kozue*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ito, Daichi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Koshi*; Ono, Takeshi*; Yuguchi, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Daichi*; Ishibashi, Kozue*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Koshi*; Ono, Takeshi*; Yuguchi, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English