Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2023-027, 126 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on rational treatment/disposal of contaminated concrete waste considering leaching alteration" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to understand migration behaviors of radionuclides in relation to the properties of concrete altered by leaching, to develop migration model of radionuclides, and to evaluate waste management scenarios, focusing on underground concrete structures in contact with contaminated water.
 , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:80.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2022-038, 102 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on rational treatment/disposal of contaminated concrete waste considering leaching alteration" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to understand migration behaviors of radionuclides in relation to the properties of concrete altered by leaching, to develop a model to predict concentration profiles, and to analyze waste management scenarios, with a focus on underground concrete structures in contact with contaminated water. Migration behaviors depend on radionuclides and their chemical species. Sorption of I is less significant on C-S-H and C-A-S-H than on hardened cement paste with two orders of magnitude smaller distribution coefficient
is less significant on C-S-H and C-A-S-H than on hardened cement paste with two orders of magnitude smaller distribution coefficient  , while
, while  of U was the same …
of U was the same …
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2021-070, 98 Pages, 2022/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on rational treatment/disposal of contaminated concrete waste considering leaching alteration" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to understand migration behaviors of radionuclides in relation to the properties of concrete materials altered due to leaching, to develop a model to simulate the migration behaviors based on the experimental findings, and to analyze waste management scenarios for radioactive concrete. The focus of the study is the underground concrete structures of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, which is in contact with contaminated water.
Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Katsuyama, Kozo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.383 - 398, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:69.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakayoshi, Akira; Jegou, C.*; De Windt, L.*; Perrin, S.*; Washiya, Tadahiro
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 360, p.110522_1 - 110522_18, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:82.17(Nuclear Science & Technology)Garcia-Lodeiro, I.*; Lebon, R.*; Machoney, D.*; Zhang, B.*; Irisawa, Keita; Taniguchi, Takumi; Namiki, Masahiro*; Osugi, Takeshi; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kinoshita, Hajime*
Proceedings of 3rd International Symposium on Cement-based Materials for Nuclear Wastes (NUWCEM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2018/11
Irisawa, Keita; Meguro, Yoshihiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(3), p.365 - 372, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)Irisawa, Keita; Komatsuzaki, Toshio; Kawato, Yoshimi; Sakakibara, Tetsuro; Nakazawa, Osamu; Meguro, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2015-008, 28 Pages, 2015/03
In JAEA, 16,671 drums of intermediate-radioactive bituminized waste products (BWPs) have been stored in asphalt solidification storages. As a way of reduction of uncertainty in assessment of disposal of the BWPs, a processing technique of separation of nitrate salts from the BWP by means of an aqueous leaching method was studied. As elemental techniques for the denitration process, (1) crushing techniques of a BWP and (2) denitration techniques for the crushed BWP by the aqueous leaching method were investigated. In order to promote leaching amounts of nitrates, the BWP was crushed, and the grain size distribution was investigated by sieving. Moreover, leaching behaviors of nitrate, nitrite and elements as radionuclides including in the BWP were investigated.
Nakayama, Shinichi; Iida, Yoshihisa; Nagano, Tetsushi; Akimoto, Toshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(4), p.227 - 237, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Leaching behavior of synthetic bituminized waste form was studied to inquire data for performance assessment of the geologic disposal. Laboratory-scale leaching tests were performed. The bituminized samples were contacted with an alkaline solution representing cement-contacting groundwater, with a saline solution simulating seawater for a possible repository construction at the coastal area, and with deionized water as reference. The release of soluble components, Na and Cs, was enhanced by the swelling, and considered to be diffusion controlled in the swelled layers of the specimens. The release of insoluble components such as Ba and Np was solubility-limited in addition to control by the progression of leaching. Neptunium, a redox-sensitive element, showed a distinct difference in release reflecting the difference between the anoxic and atmospheric conditions. The concentrations of Pu were below the detection limit (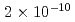 mol/L) under all of the leaching conditions in this study.
mol/L) under all of the leaching conditions in this study.
Abe, Ken*; Kojima, Takuji; ; ; ; ; Sakai, Takuro;
Radiation Detectors and Their Uses, p.323 - 328, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
; Takeda, Tsuneo; Muraoka, Susumu; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 33(3), p.268 - 270, 1996/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kato, Shohei; Yanase, Yoshiaki; Honda, Tetsutaro*
IRPA9: 1996 International Congress on Radiation Protection, Proceedings, 3, p.354 - 356, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Murata, Isao; Shiozawa, Shusaku;
Nuclear Technology, 106, p.265 - 273, 1994/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; ; ; Endo, Yasuichi; Shiozawa, Shusaku;
JAERI-M 91-207, 34 Pages, 1991/12
no abstracts in English
; ; Takeda, Tsuneo; Muraoka, Susumu;
Hoshasei Haikibutsu Kenkyu Renrakukai Rombunshu, VI, p.64 - 75, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; Matsuzuru, Hideo
JAERI-M 89-200, 26 Pages, 1989/12
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Haruto; Muraoka, Susumu
JAERI-M 89-192, 74 Pages, 1989/11
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Hiromichi; Onuki, Toshihiko; ;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 30(8), p.684 - 686, 1988/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:19.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; Matsuzuru, Hideo;
JAERI-M 88-089, 36 Pages, 1988/05
no abstracts in English