Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Nagasumi, Satoru; Hasegawa, Toshinari; Kawai, Hiromi*; Wakisaka, Shinji*; Nagase, Sota*; Nakamura, Kento*; Yaguchi, Hiroki*; Ishii, Toshiaki; Nakano, Yumi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-008, 23 Pages, 2024/07
Five people from three universities participated in the 2023 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the analysis of HTTR core, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, the analysis of Iodine deposition behavior in primary cooling system and the feasibility study of energy storage system for HTGRs. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience and some students found it useful for their own research. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ho, H. Q.; Kitagawa, Kanta*; Fukuda, Takahito*; Ito, Ryo*; Nemoto, Masaya*; Kusunoki, Hayato*; Nomura, Takuro*; Nagase, Sota*; Hashimoto, Haruki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-013, 19 Pages, 2023/06
Eight people from five universities participated in the 2022 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the feasibility study for nuclear battery, the burn-up analysis of HTTR core, the feasibility study for  Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Isogawa, Hiroki*; Naoi, Motomasa*; Yamasaki, Seiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Katayama, Kazunari*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2022-015, 18 Pages, 2022/07
As a summer holiday practical training 2021, the impact of 10 years long-term shutdown on critical control rod position of the HTTR and the delayed neutron fraction (
 ) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0
) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0 0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as
0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am, 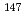 Pm,
Pm, 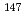 Sm,
Sm,  Gd. Regarding the
Gd. Regarding the 
 calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the
calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the 
 value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.
value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.
 Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response function
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response functionSato, Shunsuke*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*; Suyama, Kenya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.615 - 623, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new non-destructive method for evaluating  Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.  Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which
Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which  Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of
Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.
Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.  Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified
Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified  Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Mitsui, Wataru*; Yamamoto, Yudai*; Nakagawa, Kyoichi*; Ho, H. Q.; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nagasumi, Satoru; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Kenzhina, I.*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-016, 16 Pages, 2021/09
As a summer holiday practical training 2020, the feasibility study for nuclear design of a nuclear battery using HTTR core was carried out, and the downsizing of reactor core were studied by the MVP-BURN. As a result, it is clear that a 1.6 m radius reactor core, containing 54 (18 3 layers) fuel blocks with 20% enrichment of
3 layers) fuel blocks with 20% enrichment of  U, and BeO neutron reflector, could operate continuously for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW. Number of fuel blocks of this compact core is 36% of the HTTR core. As a next step, the further downsizing of core by changing materials of the fuel block will be studied.
U, and BeO neutron reflector, could operate continuously for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW. Number of fuel blocks of this compact core is 36% of the HTTR core. As a next step, the further downsizing of core by changing materials of the fuel block will be studied.
Ikeda, Reiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nakano, Yumi*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Fujimoto, Nozomu*
JAEA-Technology 2021-015, 32 Pages, 2021/09
Burnup calculation of the HTTR considering temperature distribution and detailed burning regions was carried out using MVP-BURN code. The results show that the difference in k , as well as the difference in average density of some main isotopes, is insignificant between the cases of uniform temperature and detailed temperature distribution. However, the difference in local density is noticeable, being 6% and 8% for
, as well as the difference in average density of some main isotopes, is insignificant between the cases of uniform temperature and detailed temperature distribution. However, the difference in local density is noticeable, being 6% and 8% for  U and
U and  Pu, respectively, and even 30% for the burnable poison
Pu, respectively, and even 30% for the burnable poison  B. Regarding the division of burning regions to more detail, the change of k
B. Regarding the division of burning regions to more detail, the change of k is also small of 0.6%
is also small of 0.6% k/k or less. The small burning region gives a detailed distribution of isotopes such as
k/k or less. The small burning region gives a detailed distribution of isotopes such as  U,
U,  Pu, and
Pu, and  B. As a result, the effect of graphite reflector and the burnup behavior could be evaluated more clearly compared with the previous study.
B. As a result, the effect of graphite reflector and the burnup behavior could be evaluated more clearly compared with the previous study.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Nakashima, Koki*; Nakagawa, Naoki*; Ho, H. Q.; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Kenzhina, I.*; Chikhray, Y.*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-008, 16 Pages, 2020/08
As a summer holiday practical training 2019, the feasibility study for nuclear design of a nuclear battery using HTTR core was carried out, and the  U enrichment and burnable poison of the fuel, which enables continuous operation for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW, were studied by the MVP-BURN. As a result, it is clear that a fuel with
U enrichment and burnable poison of the fuel, which enables continuous operation for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW, were studied by the MVP-BURN. As a result, it is clear that a fuel with  U enrichment of 12%, radius of burnable poison and natural boron concentration of 1.5 cm and 2wt% are required. As a next step, the downsizing of core will be studied.
U enrichment of 12%, radius of burnable poison and natural boron concentration of 1.5 cm and 2wt% are required. As a next step, the downsizing of core will be studied.
Kugo, Teruhiko
Advanced Monte Carlo for Radiation Physics, Particle Transport Simulation and Applications, p.821 - 826, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Kojima, Kensuke; Okumura, Keisuke
no journal, ,
The MOSRA system has been developing to improve the applicability of the neutronic characteristic analyses. The cell calculation module MOSRA-SRAC is a core module of MOSRA, and applicability tests for realistic problems are required. As a test, we joined the benchmark "Burnup Credit Criticality Benchmark Phase IIIC". The benchmark requested the neutronic characteristics for a BWR fuel assembly with gadolinium, which had been used in the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Because of a restriction of MOSRA-SRAC, the geometry was partially homogenized. To verify the module's applicability including the homogenization effects, the multiplication factor and the nuclide compositions were compared with the well-validated code MVP-BURN. As the results, the applicability of MSORA-SRAC for the assembly was verified. Additionally, it was also shown that the homogenization effects were smaller than the difference due to the calculation methods.
Ikeda, Reiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Reiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English