Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study山下 享介*; 古賀 紀光*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 藤井 英俊*; 梅澤 修*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
被引用回数:0Ferrite-austenite duplex stainless steels offer excellent strength and ductility, making them suitable for extreme environments. In this study,  neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 他4名*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) equi-atomic multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties from cryogenic to room temperatures. At room temperature, deformation is dominated by dislocation slip, while at cryogenic temperatures (CTs), reduced stacking fault energy enhances strain hardening with twinning. This study uses in-situ neutron diffraction to analyze the temperature-dependent deformation behavior of Al (CoNiV)
(CoNiV)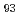 , a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
, a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:84.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dual-phase (DP) steel, composed of soft ferrite and hard martensite, offers excellent strength-ductility balance and low cost. This study found that refining the DP microstructure enhanced both yield strength and strain hardening, improving strength and ductility. Digital image correlation (DIC) revealed strain localization in ferrite, but refinement reduced strain differences between ferrite and martensite, suppressing crack initiation. More ferrite/martensite interfaces promoted plasticity in martensite via enhanced deformation constraint.  neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining
neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining  -DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
-DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
大橋 智典*; 坂巻 竜也*; 舟越 賢一*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; 服部 高典; Yuan, L.*; 鈴木 昭夫*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
0-6GPa, 1000-1300Kのドライおよび含水Na Si
Si O
O 融体の構造と高温高圧から回収したガラスの構造をその場中性子回折及びX線回折により調べた。また、0-10GPa, 3000Kの融体の構造をab-initio分子動力学シミュレーションにより調べた。その場中性子実験から、-O-D-O-架橋種の形成によりD-O距離が圧縮とともに増加することが明らかになり、分子動力学シミュレーションでも再現された。圧力による-O-D-O-形成は、水素がより強固に取り込まれることを反映しており、実験的に観測されたケイ酸塩融体中の水の高い溶解度のメカニズムとして働く。一方、0-10GPa, 3000KにおけるドライNa
融体の構造と高温高圧から回収したガラスの構造をその場中性子回折及びX線回折により調べた。また、0-10GPa, 3000Kの融体の構造をab-initio分子動力学シミュレーションにより調べた。その場中性子実験から、-O-D-O-架橋種の形成によりD-O距離が圧縮とともに増加することが明らかになり、分子動力学シミュレーションでも再現された。圧力による-O-D-O-形成は、水素がより強固に取り込まれることを反映しており、実験的に観測されたケイ酸塩融体中の水の高い溶解度のメカニズムとして働く。一方、0-10GPa, 3000KにおけるドライNa Si
Si O
O の圧縮は、Si-O-Si角の曲げに支配される。さらに、含水Na
の圧縮は、Si-O-Si角の曲げに支配される。さらに、含水Na Si
Si O
O 融体の分子動力学シミュレーションから、圧力上昇とともに、2(
融体の分子動力学シミュレーションから、圧力上昇とともに、2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na およびSi-O
およびSi-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na で示される反応により、ナトリウムイオンがネットワーク修飾の役割を果たさなくなることを示唆している。
で示される反応により、ナトリウムイオンがネットワーク修飾の役割を果たさなくなることを示唆している。
友田 陽*; Harjo, S.; 徐 平光; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; Wang, Y.*
Metals, 15(6), p.610_1 - 610_19, 2025/05
被引用回数:0Lattice parameters of product and matrix phases in steels have been measured using in situ X-ray and neutron diffraction during forward and reverse transformations. These parameters are influenced by temperature, transformation-induced internal stresses, alloying element partitioning, crystal defects, and magnetic strains. Disentangling these contributions is essential for understanding lattice behavior. This review explores internal strain (stress) associated with ferrite, pearlite, bainite, martensite, and reverse austenite transformations, emphasizing the distinction between diffusional and displacive mechanisms. It also examines how plastic deformation of austenite affects subsequent bainite or martensite formation. The roles of dislocations and vacancies are identified as critical areas for further research.
 phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates
phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates阿蘇 星侑*; 松尾 拓紀*; 米田 安宏; 森川 大輔*; 津田 健治*; 大山 研司*; 石垣 徹*; 野口 祐二*
Physical Review B, 111(17), p.174114_1 - 174114_12, 2025/05
高分解能放射光X線・中性子回折、収束電子線回折、密度汎関数理論(DFT)計算を組合せた解析により、Ca修飾NaNbO と非ドープNaNbO
と非ドープNaNbO の結晶構造、phase転移、相安定性を調べた。その結果、Ca修飾によって反強誘電体(AFE)-
の結晶構造、phase転移、相安定性を調べた。その結果、Ca修飾によって反強誘電体(AFE)- 相が200Kから800Kの広い温度範囲で安定化されること、NaNbO
相が200Kから800Kの広い温度範囲で安定化されること、NaNbO は格子膨張を伴う温度誘起等方圧によって安定化されるのに対し、Ca修飾NaNbO
は格子膨張を伴う温度誘起等方圧によって安定化されるのに対し、Ca修飾NaNbO は格子収縮を伴う組成誘起化学圧力によって安定化されることが示された。
は格子収縮を伴う組成誘起化学圧力によって安定化されることが示された。
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 他3名*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
The need for lightweight materials with mechanical integrity at ultralow temperatures drives the development of advanced alloys for cryogenic use. Additive manufacturing via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) offers a scalable way to create alloys with tailored properties. Here, we show that LPBF-processed Al10SiMg exhibits a high ultimate tensile strength (395 MPa) and uniform elongation (25%) at 15 K. These enhancements stem from grain refinement, increased geometrically necessary dislocations, and stress partitioning between the Al matrix and the stiffer Si phase, aiding strain accommodation.  neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
Pandian, K.*; Neikter, M.*; Ekh, M.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Woracek, R.*; Hansson, T.*; Pederson, R.*
JOM, 77(4), p.1803 - 1815, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To produce dense Ti-6Al-4V components, electron beam powder bed fusion is typically followed by post-heat treatment like hot isostatic pressing (HIP). Standard HIP at 920 C/100 MPa for 2 h coarsens the microstructure and reduces yield strength, while low-temp HIP at 800
C/100 MPa for 2 h coarsens the microstructure and reduces yield strength, while low-temp HIP at 800 C/200 MPa for 2 h limits coarsening and retains strength comparable to as-built material. A coarser microstructure negatively affects tensile properties. Tensile tests at various temperatures suggest that thermally activated slip systems may influence elongation, requiring further study. In situ neutron time-of-flight diffraction during tensile loading enables analysis of strain evolution and slip plane activity. A two-phase elastic-plastic self-consistent model was used to compare with experiments. Results show basal slip {0002} activated at 20
C/200 MPa for 2 h limits coarsening and retains strength comparable to as-built material. A coarser microstructure negatively affects tensile properties. Tensile tests at various temperatures suggest that thermally activated slip systems may influence elongation, requiring further study. In situ neutron time-of-flight diffraction during tensile loading enables analysis of strain evolution and slip plane activity. A two-phase elastic-plastic self-consistent model was used to compare with experiments. Results show basal slip {0002} activated at 20 C, pyramidal slip {10-11} at 350
C, pyramidal slip {10-11} at 350 C, and
C, and  phase carrying higher stress than
phase carrying higher stress than  in the plastic regime.
in the plastic regime.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; 服部 高典
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)X線回折、中性子回折、ラマン散乱、第一原理計算を用いて、ReO の高圧力下での挙動を15GPaまで包括的に調べた。常圧
の高圧力下での挙動を15GPaまで包括的に調べた。常圧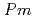 =3
=3 構造は0.7GPaで空間群
構造は0.7GPaで空間群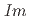 =3の立方晶相に連続的に相転移し、その後少なくとも15GPaまで安定であることがわかった。過去この圧力領域で報告されていた単斜晶
=3の立方晶相に連続的に相転移し、その後少なくとも15GPaまで安定であることがわかった。過去この圧力領域で報告されていた単斜晶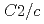 構造や菱面体晶
構造や菱面体晶 =3
=3 構造への転移は、試料に高輝度放射光X線を照射したことによる試料の劣化によるものであり、人工的なものであることが分かった。また今回、
構造への転移は、試料に高輝度放射光X線を照射したことによる試料の劣化によるものであり、人工的なものであることが分かった。また今回、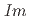 =3相の構造の圧力依存性と正確な状態方程式および天然試料と同位体濃縮
=3相の構造の圧力依存性と正確な状態方程式および天然試料と同位体濃縮 O試料のラマン散乱データを示した。このデータから、リジッドなReO
O試料のラマン散乱データを示した。このデータから、リジッドなReO 八面体が圧力とともに回転することによって、相転移および高密度化が起こることが分かった。
八面体が圧力とともに回転することによって、相転移および高密度化が起こることが分かった。
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; 服部 高典; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)二次元ファンデルワールス強磁性体Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
(FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
青木 勝敏*; 町田 晃彦*; 齋藤 寛之*; 服部 高典
高圧力の科学と技術, 35(1), p.4 - 11, 2025/03
鉄は水素と反応して、高温高圧下で体心立方、面心立方、六方最密充填、二重六方最密充填構造の固溶体を形成する。中性子回折は、金属格子中に溶解した水素原子の占有位置と占有率を決定するための最も強力なツールである。水素の占有位置や占有率を含む構造パラメータは、中性子回折データのリートベルト解析によって精密化される。本原稿では、10年以上にわたって蓄積してきた鉄水素化物のリートベルト精密化に関するノウハウを紹介する。
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; 服部 高典; 阿部 淳*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)アルダー-エン反応は、アルケンとアリル水素との化学反応であり、C-C結合を構築する効率的な方法である。従来、この反応には触媒、高温、あるいは光触媒が必要であった。本研究では、触媒を用いずに室温下で加圧することで成功した1-ヘキセンのアルダー-エン反応を報告する。1-ヘキセンは4.3GPaで結晶化し、18GPaで重合してオレフィンを形成する。ガスクロマトグラフィー-質量分析法により、1-ヘキセンが高圧下でのアルダー-エン反応により二量体を生成することを発見した。その場中性子回折から、この反応過程はトポケミカル則に従わないことがわかった。理論計算により、1つのC-H  結合と2つのアルケン
結合と2つのアルケン 結合を含む6員環遷移状態が示され、そのエネルギーは20GPaまで圧縮すると明らかに減少した。本研究は、触媒を用いずに室温でアルダー-エン反応を実現する新規かつ有望な方法を提供し、この重要な反応の応用を拡大するものである。
結合を含む6員環遷移状態が示され、そのエネルギーは20GPaまで圧縮すると明らかに減少した。本研究は、触媒を用いずに室温でアルダー-エン反応を実現する新規かつ有望な方法を提供し、この重要な反応の応用を拡大するものである。
 neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation
neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 北條 智彦*; 興津 貴隆*; 藤井 英俊*
ISIJ International, 64(14), p.2051 - 2060, 2024/12
被引用回数:0An Fe-0.15C-5Mn-0.5Si-0.05Nb steel annealed at 660 C and 685
C and 685 C showed L
C showed L ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L
ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L ders strain and hardening behavior.
ders strain and hardening behavior.  neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed
neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed  1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L
1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
物質科学研究センター
JAEA-Review 2024-037, 141 Pages, 2024/11
JRR-3(Japan Research Reactor No.3)には、日本原子力研究開発機構(原子力機構)が所管する15台の中性子ビーム利用実験装置が設置されており、装置高度化を含めた原子力機構の独自利用を行うとともに施設供用装置として外部利用者に供し、様々な研究成果を創出している。本報告書は、運転再開後の令和3年度、令和4年度の独自利用研究および中性子ビーム利用実験装置の高度化などの技術開発の進捗状況を取りまとめたものである。
Harjo, S.; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.205 - 208, 2024/11
This study aimed to elucidate the effect of grain size on the deformation behavior of TRIP steel. We prepared metastable austenitic Fe-24Ni-0.3C steel samples with average grain sizes of 35 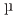 m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5
m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5 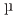 m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Hydrogen embrittlement has long been an obstacle to the development of safe infrastructure. However, in contrast to hydrogen's embrittling effect, recent research has revealed that the addition of hydrogen improves both the strength and uniform elongation of AISI Type 310S austenitic stainless steel. A detailed understanding of how hydrogen affects the deformation mechanism of this steel could pave the way for the development of more advanced materials with superior properties. In the present study,  neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:96.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using a hybrid method of in situ neutron diffraction and digital image correlation, we found that ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel exhibits Luders deformation after yielding, in which the deformation behavior changes from a cooperation mechanism involving dislocation slip and martensitic transformation to one primarily governed by martensitic transformation, as the temperature decreases from 295 K to 77 K. Such martensitic transformation-governed Luders deformation delays the activation of plastic deformation in both the austenite parent and martensite product, resulting in delayed strain hardening. This preserves the strain-hardening capability for the later stage of deformation, thereby maintaining a remarkable elongation of 29% while achieving a high tensile strength of 1.87 GPa at 77 K.
Zhang, Y.-J.*; 梅田 岳昌*; 諸岡 聡; Harjo, S.; 宮本 吾郎*; 古原 忠*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(10), p.3921 - 3936, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, a series of eutectoid steels with Mn addition up to 2 mass% were isothermally transformed at various temperatures from 873 K to 973 K to clarify the pearlite growth kinetics and the underlying thermodynamics at its growth front. The microscopic observation indicates the acceleration in pearlite growth rate and refinement in lamellar spacing by decreasing the transformation temperature or the amount of Mn addition. After analyzing the solute distribution at pearlite growth front via three-dimensional atom probe, no macroscopic Mn partitioning across pearlite/austenite interface is detected, whereas Mn segregation is only observed at ferrite/austenite interface. Furthermore, in-situ neutron diffraction measurements performed at elevated temperatures reveals that the magnitude of elastic strain generated during pearlite transformation is very small.