Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 他4名*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) equi-atomic multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties from cryogenic to room temperatures. At room temperature, deformation is dominated by dislocation slip, while at cryogenic temperatures (CTs), reduced stacking fault energy enhances strain hardening with twinning. This study uses in-situ neutron diffraction to analyze the temperature-dependent deformation behavior of Al (CoNiV)
(CoNiV)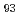 , a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
, a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
柳澤 宏司; 求 惟子
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
中性子吸収棒の反応度価値に関する安全検査データのより深い理解と反応度価値の測定技術の向上のために、TRIGA-ACPR(環状炉心パルス炉)に分類されるNSRR(原子炉安全性研究炉)の初回起動炉心の臨界解析用詳細計算モデルを作成した。本モデルの形状、材料、運転データの誤差から伝播する中性子実効増倍率(keff)の不確かさを、最新の核データライブラリJENDL-5及び旧版のJENDLライブラリとMVP第3版コードを用いて詳細に評価した。その結果、本モデルにおけるk の全体的な不確かさは、0.0027から0.0029
の全体的な不確かさは、0.0027から0.0029 k
k の範囲と評価した。本モデルは、TRIGA-ACPRのk
の範囲と評価した。本モデルは、TRIGA-ACPRのk のベンチマークとして利用されることが期待される。さらに、全体的な不確かさは、NSRRで測定された吸収棒価値よりも十分小さいことを確認した。よって、本モデルはNSRRにおける吸収棒反応度価値に関する今後の解析にも適用できる。
のベンチマークとして利用されることが期待される。さらに、全体的な不確かさは、NSRRで測定された吸収棒価値よりも十分小さいことを確認した。よって、本モデルはNSRRにおける吸収棒反応度価値に関する今後の解析にも適用できる。
Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
被引用回数:1Dual-phase (DP) steel, composed of soft ferrite and hard martensite, offers excellent strength-ductility balance and low cost. This study found that refining the DP microstructure enhanced both yield strength and strain hardening, improving strength and ductility. Digital image correlation (DIC) revealed strain localization in ferrite, but refinement reduced strain differences between ferrite and martensite, suppressing crack initiation. More ferrite/martensite interfaces promoted plasticity in martensite via enhanced deformation constraint.  neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining
neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining  -DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
-DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
中村 詔司; 遠藤 駿典; Rovira Leveroni, G.; 木村 敦; 芝原 雄司*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
本研究は、生成放射能を評価するために、廃止措置で問題となる核種について熱中性子捕獲断面積を測定するものである。本件では、対象核種の中から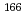 Hoを選定し、京大原子炉にて放射化法によりその熱中性子捕獲断面積を測定した。今回、
Hoを選定し、京大原子炉にて放射化法によりその熱中性子捕獲断面積を測定した。今回、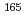 Ho(n,
Ho(n, )
) Ho反応について2.79
Ho反応について2.79 0.04 barnを得た。従来の報告値は3.4
0.04 barnを得た。従来の報告値は3.4 0.5(b)に対して、誤差1.4
0.5(b)に対して、誤差1.4 に向上して導出することができた。また副産物として、
に向上して導出することができた。また副産物として、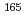 Ho(n,
Ho(n, )
)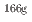 Ho反応について61.2
Ho反応について61.2 0.6 barnを得た。
0.6 barnを得た。 Hoと
Hoと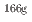 Hoの生成の断面積を合わせて、64.0
Hoの生成の断面積を合わせて、64.0 0.6 barnを求めた。今回の結果は、TOF法による過去の報告値64.4
0.6 barnを求めた。今回の結果は、TOF法による過去の報告値64.4 2.8(b)や、最近の評価値64.69 barn、64.4
2.8(b)や、最近の評価値64.69 barn、64.4 1.2 barnを誤差の範囲で支持した。
1.2 barnを誤差の範囲で支持した。
福田 航大; 小原 徹*; 須山 賢也
Nuclear Technology, 211(5), p.963 - 973, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)An application of the boiling water reactor (BWR) to an offshore floating nuclear power plant (OFNP) is discussed in Japan. The BWR-type OFNP has some challenges for practical use, although it has high economic efficiency because of downsizing and simplification. One challenge is understanding reactor kinetics under conditions specific to the marine environment. This study quantitatively clarifies the total and spatial changes in power when the BWR is inclined during regular operation. Therefore, the TRAC/RELAP Advanced Computational Engine (TRACE) and Purdue Advanced Reactor Core Simulator (PARCS) codes were used to perform a three-dimensional neutronics-thermal-hydraulics-coupled transient analysis. The calculation model is based on Peach Bottom II. This study clarifies the changing trend in total and local BWR power by inclination with simplified modeling and conditions. Reasons for such changes are discussed based on changes in several thermal-hydraulic parameters. The difference in BWR power against the inclinations is small. Thus, it was implied that the BWR-type OFNP is expected to have a stable power supply capability during natural disasters. Finally, requires further studies to support the obtained conclusions are discussed.
 phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates
phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates阿蘇 星侑*; 松尾 拓紀*; 米田 安宏; 森川 大輔*; 津田 健治*; 大山 研司*; 石垣 徹*; 野口 祐二*
Physical Review B, 111(17), p.174114_1 - 174114_12, 2025/05
高分解能放射光X線・中性子回折、収束電子線回折、密度汎関数理論(DFT)計算を組合せた解析により、Ca修飾NaNbO と非ドープNaNbO
と非ドープNaNbO の結晶構造、phase転移、相安定性を調べた。その結果、Ca修飾によって反強誘電体(AFE)-
の結晶構造、phase転移、相安定性を調べた。その結果、Ca修飾によって反強誘電体(AFE)- 相が200Kから800Kの広い温度範囲で安定化されること、NaNbO
相が200Kから800Kの広い温度範囲で安定化されること、NaNbO は格子膨張を伴う温度誘起等方圧によって安定化されるのに対し、Ca修飾NaNbO
は格子膨張を伴う温度誘起等方圧によって安定化されるのに対し、Ca修飾NaNbO は格子収縮を伴う組成誘起化学圧力によって安定化されることが示された。
は格子収縮を伴う組成誘起化学圧力によって安定化されることが示された。
長谷 竹晃; 小菅 義広*; 相楽 洋*; 中岫 翔; 能見 貴佳; 奥村 啓介
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.41 - 46, 2025/05
This paper provides an overview of plutonium quantification in irradiated fuel including fuel debris at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, named Dual Time Measurement (DTM) method. Spontaneous fission nuclides in irradiated fuel decrease exponentially with the passage of time according to the mainly half-life of Cm-244 (half-life of about 18.11 years). By measuring neutrons two times with long time intervals, Pu-240 effective mass (half-life of about 6,500 years) and Cm-244 mass can be quantified. Pu mass can be quantified by utilizing the correlation between ratio of Cm-244/ Pu-240 effective mass and Pu/ Pu-240 effective mass. The applicability of DTM method was evaluated numerically. The results show that long time interval was required to reduce the random errors. In the case that the interval between the first and second measurements is 32 years, Pu-240 effective mass and Pu can be quantified with uncertainties of 10-50% depending on the presence of water in storage canister and the burnup condition of irradiated fuel including the mixture of several burnup compositions in fuel debris.
 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)SiH 八面体部位を特徴とするヒドリドケイ酸塩は、水素貯蔵と水素化物イオン伝導に関連する潜在的な性質を持つかなり新しい化合物のクラスである。ここでは、Zintl相水素化物BaSiH
八面体部位を特徴とするヒドリドケイ酸塩は、水素貯蔵と水素化物イオン伝導に関連する潜在的な性質を持つかなり新しい化合物のクラスである。ここでは、Zintl相水素化物BaSiH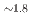 を4GPa以上の圧力でH
を4GPa以上の圧力でH 流体と反応させ、その後常圧まで減圧して得られた新しい代表的なBaSiH
流体と反応させ、その後常圧まで減圧して得られた新しい代表的なBaSiH について報告する。SiH
について報告する。SiH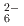 イオンはBa
イオンはBa 対イオンによって八面体に配位している。Ba原子とSi原子の配置は理想的なfcc NaCl構造からわずかにずれている。IRとラマンスペクトルからSiH
対イオンによって八面体に配位している。Ba原子とSi原子の配置は理想的なfcc NaCl構造からわずかにずれている。IRとラマンスペクトルからSiH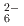 の屈曲と伸縮モードがそれぞれ800-1200と1400-1800cm
の屈曲と伸縮モードがそれぞれ800-1200と1400-1800cm の範囲で観測された。BaSiH
の範囲で観測された。BaSiH は95
は95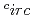 Cまで熱的に安定であり、それ以上ではBaH
Cまで熱的に安定であり、それ以上ではBaH とSiに分解する。DFT計算により、直接バンドギャップは2.5eVであることが示された。BaSiH
とSiに分解する。DFT計算により、直接バンドギャップは2.5eVであることが示された。BaSiH の発見により、ギガパスカル圧力(10GPa以下)のシリサイドの水素化反応からアクセス可能なヒドリドケイ酸塩の化合物クラスが固まった。BaSiH
の発見により、ギガパスカル圧力(10GPa以下)のシリサイドの水素化反応からアクセス可能なヒドリドケイ酸塩の化合物クラスが固まった。BaSiH の構造的性質は、超伝導ポリハイドライドBaSiH
の構造的性質は、超伝導ポリハイドライドBaSiH を予測されるより高い圧力で水素化するための中間体(あるいは前駆体)であることを示唆している。
を予測されるより高い圧力で水素化するための中間体(あるいは前駆体)であることを示唆している。
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 他3名*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
The need for lightweight materials with mechanical integrity at ultralow temperatures drives the development of advanced alloys for cryogenic use. Additive manufacturing via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) offers a scalable way to create alloys with tailored properties. Here, we show that LPBF-processed Al10SiMg exhibits a high ultimate tensile strength (395 MPa) and uniform elongation (25%) at 15 K. These enhancements stem from grain refinement, increased geometrically necessary dislocations, and stress partitioning between the Al matrix and the stiffer Si phase, aiding strain accommodation.  neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
Pandian, K.*; Neikter, M.*; Ekh, M.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Woracek, R.*; Hansson, T.*; Pederson, R.*
JOM, 77(4), p.1803 - 1815, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To produce dense Ti-6Al-4V components, electron beam powder bed fusion is typically followed by post-heat treatment like hot isostatic pressing (HIP). Standard HIP at 920 C/100 MPa for 2 h coarsens the microstructure and reduces yield strength, while low-temp HIP at 800
C/100 MPa for 2 h coarsens the microstructure and reduces yield strength, while low-temp HIP at 800 C/200 MPa for 2 h limits coarsening and retains strength comparable to as-built material. A coarser microstructure negatively affects tensile properties. Tensile tests at various temperatures suggest that thermally activated slip systems may influence elongation, requiring further study. In situ neutron time-of-flight diffraction during tensile loading enables analysis of strain evolution and slip plane activity. A two-phase elastic-plastic self-consistent model was used to compare with experiments. Results show basal slip {0002} activated at 20
C/200 MPa for 2 h limits coarsening and retains strength comparable to as-built material. A coarser microstructure negatively affects tensile properties. Tensile tests at various temperatures suggest that thermally activated slip systems may influence elongation, requiring further study. In situ neutron time-of-flight diffraction during tensile loading enables analysis of strain evolution and slip plane activity. A two-phase elastic-plastic self-consistent model was used to compare with experiments. Results show basal slip {0002} activated at 20 C, pyramidal slip {10-11} at 350
C, pyramidal slip {10-11} at 350 C, and
C, and  phase carrying higher stress than
phase carrying higher stress than  in the plastic regime.
in the plastic regime.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; 服部 高典
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)X線回折、中性子回折、ラマン散乱、第一原理計算を用いて、ReO の高圧力下での挙動を15GPaまで包括的に調べた。常圧
の高圧力下での挙動を15GPaまで包括的に調べた。常圧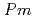 =3
=3 構造は0.7GPaで空間群
構造は0.7GPaで空間群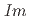 =3の立方晶相に連続的に相転移し、その後少なくとも15GPaまで安定であることがわかった。過去この圧力領域で報告されていた単斜晶
=3の立方晶相に連続的に相転移し、その後少なくとも15GPaまで安定であることがわかった。過去この圧力領域で報告されていた単斜晶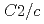 構造や菱面体晶
構造や菱面体晶 =3
=3 構造への転移は、試料に高輝度放射光X線を照射したことによる試料の劣化によるものであり、人工的なものであることが分かった。また今回、
構造への転移は、試料に高輝度放射光X線を照射したことによる試料の劣化によるものであり、人工的なものであることが分かった。また今回、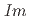 =3相の構造の圧力依存性と正確な状態方程式および天然試料と同位体濃縮
=3相の構造の圧力依存性と正確な状態方程式および天然試料と同位体濃縮 O試料のラマン散乱データを示した。このデータから、リジッドなReO
O試料のラマン散乱データを示した。このデータから、リジッドなReO 八面体が圧力とともに回転することによって、相転移および高密度化が起こることが分かった。
八面体が圧力とともに回転することによって、相転移および高密度化が起こることが分かった。
阿部 一英
JAEA-Review 2024-065, 26 Pages, 2025/03
日本原子力研究開発機構が保有する試験研究炉「JRR-3」は、令和3年2月26日に約10年ぶりに運転を再開した。この研究炉は供用施設として運営されており、外部からの利用者も受け入れている。利用課題の提案から成果報告書の提出までの手続きは、オンラインシステム「JRR-3 RING(Research Information NaviGator)」(https://jrr3ring.jaea.go.jp/)を通じて行われる。RINGは、課題申請、スケジュール調整、データ共有、成果報告までを一括して管理できるシステムであり、供用再開に向けた整備が進められてきた。RINGは特にビーム利用ユーザーの利便性を重視して設計されており、申請手続きの簡略化やスケジュール調整の柔軟性向上、データ管理機能の強化が特徴である。このシステムの導入によりユーザーは効率的かつ安全に研究を進めることが可能になった。今後JRR-3は国内外の多様な研究者に利用される中性子研究のプラットフォームとしての役割を拡大していく。供用再開とRINGの拡張は、中性子利用研究の活性化に寄与し、産業界や学術界との連携を推進する重要な一歩である。今回、新たに整備された機能や今後の展望について、報告する。
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; 服部 高典; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)二次元ファンデルワールス強磁性体Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
(FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
Fe中村 詔司; 芝原 雄司*; 遠藤 駿典; Rovira Leveroni, G.; 木村 敦
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)As nuclear facilities are dismantled in decommissioning, large amount of various waste is generated. Even more inconveniently, waste is radioactive due to neutron activation. Thus, the neutron capture cross-sections of nuclides targeted in decommissioning are required to evaluate the radioactivity produced. In this work,  Fe nuclide was selected among objective nuclides for decommissioning, and its thermal-neutron capture cross-section was measured by a neutron activation method at the graphite thermal column of Kyoto University Research Reactor in 5-MW operation. The thermal-neutron capture cross-section was derived using
Fe nuclide was selected among objective nuclides for decommissioning, and its thermal-neutron capture cross-section was measured by a neutron activation method at the graphite thermal column of Kyoto University Research Reactor in 5-MW operation. The thermal-neutron capture cross-section was derived using 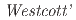 s convention. The present work obtained 1.36
s convention. The present work obtained 1.36 0.03 barns for the
0.03 barns for the  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe reaction. The present result supports the JENDL-5 evaluation within 2
Fe reaction. The present result supports the JENDL-5 evaluation within 2 . If updated with currently recommended nuclear data, some of the reported past data would support the present result.
. If updated with currently recommended nuclear data, some of the reported past data would support the present result.
青木 勝敏*; 町田 晃彦*; 齋藤 寛之*; 服部 高典
高圧力の科学と技術, 35(1), p.4 - 11, 2025/03
鉄は水素と反応して、高温高圧下で体心立方、面心立方、六方最密充填、二重六方最密充填構造の固溶体を形成する。中性子回折は、金属格子中に溶解した水素原子の占有位置と占有率を決定するための最も強力なツールである。水素の占有位置や占有率を含む構造パラメータは、中性子回折データのリートベルト解析によって精密化される。本原稿では、10年以上にわたって蓄積してきた鉄水素化物のリートベルト精密化に関するノウハウを紹介する。
田辺 鴻典*; 米田 政夫; 藤 暢輔; 北村 康則*; 三澤 毅*
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 67(3), p.198 - 202, 2025/03
, 67(3), p.198 - 202, 2025/03
鉛等で隠匿された Uに対する非破壊測定技術の開発は、長年、核セキュリティ上の最重要課題と言われてきたが、依然として現場レベルでの検知は困難な状況にある。我々は
Uに対する非破壊測定技術の開発は、長年、核セキュリティ上の最重要課題と言われてきたが、依然として現場レベルでの検知は困難な状況にある。我々は Cf回転照射法と呼ばれる新たな核物質非破壊測定手法を提案し、回転照射装置と水チェレンコフ中性子検出器で構成される運搬性の高い現場検知システムを開発、本システムによる核物質検知を実証した。本報では、開発したシステムを概説するとともに今後の展望について解説する。
Cf回転照射法と呼ばれる新たな核物質非破壊測定手法を提案し、回転照射装置と水チェレンコフ中性子検出器で構成される運搬性の高い現場検知システムを開発、本システムによる核物質検知を実証した。本報では、開発したシステムを概説するとともに今後の展望について解説する。
Guembou Shouop, C. J.; 土屋 晴文
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170189_1 - 170189_14, 2025/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The development of a compact mobile neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) instrument is in progress for measuring nuclear materials in the field of nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security. The present paper focuses on research/developments on designing the source, moderators and shielding for the table-top NRTA system utilising a  Cf spontaneous neutron. To this end, three source configurations were assessed using Monte Carlo (MC) simulations-based Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) by evaluating each configuration's neutron/gamma fluxes. Experimental validation of the MC simulation was conducted using an EJ270 plastic scintillation detector, a
Cf spontaneous neutron. To this end, three source configurations were assessed using Monte Carlo (MC) simulations-based Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) by evaluating each configuration's neutron/gamma fluxes. Experimental validation of the MC simulation was conducted using an EJ270 plastic scintillation detector, a 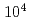 Bq
Bq  Cf source, and a thin In sample. The Monte Carlo simulations and experimental results confirmed that an optimal configuration for the table-top NRTA system involves sandwiching the
Cf source, and a thin In sample. The Monte Carlo simulations and experimental results confirmed that an optimal configuration for the table-top NRTA system involves sandwiching the  Cf source between the polyethylene (PE) moderator (PE closer to the detector) and the W reflector. Furthermore, the MC simulations showed that resonance dips from NatU and Pu (energy lines of 1.06 and 2.60 eV of
Cf source between the polyethylene (PE) moderator (PE closer to the detector) and the W reflector. Furthermore, the MC simulations showed that resonance dips from NatU and Pu (energy lines of 1.06 and 2.60 eV of  Pu and 0.30 eV of
Pu and 0.30 eV of  Pu) can be observed in the Time-of-Flight spectra obtained using the table-top NRTA system with an appropriate collimator for a small pellet sample. The preliminary experimental results with a 2 mm thick In sample displayed the 1.46 eV resonance dip of
Pu) can be observed in the Time-of-Flight spectra obtained using the table-top NRTA system with an appropriate collimator for a small pellet sample. The preliminary experimental results with a 2 mm thick In sample displayed the 1.46 eV resonance dip of  In, showing that the table-top NRTA system using a
In, showing that the table-top NRTA system using a  Cf neutron source can measure TOF spectra and observe dips caused by low energy resonances in a sample. These findings suggest the system is well-suited for measuring small pellet samples of Pu and U.
Cf neutron source can measure TOF spectra and observe dips caused by low energy resonances in a sample. These findings suggest the system is well-suited for measuring small pellet samples of Pu and U.
谷川 聖史; 瀬谷 和仁*; 浅川 直也*; 林 宏幸*; 堀籠 和志; 向 泰宣; 北尾 貴彦; 中村 仁宣; Henzlova, D.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-014, 63 Pages, 2025/02
プルトニウム転換技術開発施設の廃液処理工程で発生したスラッジ中のPu量を評価する上で、スラッジは生成上、多くの不純物(Na, Fe, Ni等)を含み不均質であるため、従来の破壊分析ではサンプリングによる代表性が乏しく、Pu量測定に係る測定不確かさが大きかった(約24%)。この測定不確かさを低減させるために、日本原子力研究開発機構と米国ロスアラモス国立研究所は共同で中性子を利用した非破壊測定装置のPlutonium Scrap Multiplicity Counter (PSMC)を用いた測定技術の開発を進めた。MOX粉末を用いた模擬スラッジやモンテカルロ法により検証等を行いPSMC検出器パラメーター(predelay, doubles gatefraction等)を最適化し、高分解能ガンマ線分光分析を組み合わせて測定した結果、含有不純物の影響はないことが確認でき、従来法と比べ新たに設定した非破壊測定方法における測定不確かさは約6.5%まで低減できた。さらに、PSMC測定値の妥当性を評価するため、IAEA立ち合いの下、ガンマ線を測定しPu量を評価するIn Situ Object Counting System (ISOCS)を用いた比較測定した結果、ISOCSとPSMCの測定値は両方の測定不確かさの範囲内で一致したため、PSMCによる測定値の妥当性が確認された。これらの結果より、本非破壊測定技術はスラッジのように不純物を多く含み、サンプリングの代表性が乏しいアイテムに有効であり、スラッジの計量管理に適用することが認められた。