Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a comprehensive study of the high pressure behaviour of ReO using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure
using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure 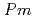
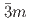 structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group
structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group 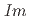
 and rhombohedral
and rhombohedral 
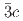 structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the
structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the 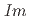
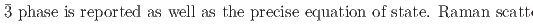 O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO
O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO octahedra.
octahedra.
 -CsOH
-CsOHRizaal, M.; Luu, V. N.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
Hirooka, Shun; Horii, Yuta; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Vauchy, R.; Hayashizaki, Kohei; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1313 - 1323, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:80.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Additive MOX pellets are fabricated by a conventional dry powder metallurgy method. Nd O
O and Sm
and Sm O
O are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
 Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from
Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from  -MoO
-MoO to water
to waterQuach, N. M.*; Ngo, M. C.*; Yang, Y.*; Nguyen, T. B.*; Nguyen, V. T.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Do, T. M. D.*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(10), p.4057 - 4064, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:62.75(Chemistry, Analytical)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 (
Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 ( Mo). Production of
Mo). Production of  Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived
Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived  Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of
Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of  Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous
Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting
wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting  Mo. Porous
Mo. Porous  -MoO
-MoO wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of
wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of  Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous
Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of
wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of  Mo extraction in the porous
Mo extraction in the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was comparable to that of commercial
wire was comparable to that of commercial  -MoO
-MoO powder.
powder.
 -MoO
-MoO whiskers in
whiskers in  Mo/
Mo/ Tc radioisotope production and
Tc radioisotope production and  Mo/
Mo/ Tc extraction using hot atoms
Tc extraction using hot atomsNgo, M. C.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Do, T. M. D.*; Seki, Misaki; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Niihara, Koichi*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(32), p.13140 - 13147, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:54.36(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.
Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.  Tc is a daughter product of the
Tc is a daughter product of the  Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce
Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n,
Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n, ) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n,
) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n, ) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,
) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,  -MoO
-MoO whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and
whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and  -MoO
-MoO particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce
particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the
Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc. As a result,
Tc. As a result,  -MoO
-MoO whisker yielded higher
whisker yielded higher  Mo extraction rate than that from
Mo extraction rate than that from  -MoO
-MoO . In addition, by comparing the dissolved
. In addition, by comparing the dissolved  Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of
Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of  -MoO
-MoO whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of
whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of  -MoO
-MoO being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,
being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,  -MoO
-MoO is considered a promising irradiation target for producing
is considered a promising irradiation target for producing  Mo/
Mo/ Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
 and Zr at precisely controlled high temperatures
and Zr at precisely controlled high temperaturesShirasu, Noriko; Sato, Takumi; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.697 - 714, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Interaction tests between UO and Zr were performed at precisely controlled high temperatures between 1840 and 2000
and Zr were performed at precisely controlled high temperatures between 1840 and 2000  C to understand the interaction mechanism in detail. A Zr rod was inserted in a UO
C to understand the interaction mechanism in detail. A Zr rod was inserted in a UO crucible and then heat-treated at a fixed temperature in Ar-gas flow for 10 min. After heating in the range of 1890 to 1930
crucible and then heat-treated at a fixed temperature in Ar-gas flow for 10 min. After heating in the range of 1890 to 1930  C, the Zr rod was deformed to a round shape, in which the post-analysis detected the significant diffusion of U into the Zr region and the formation of a dominant
C, the Zr rod was deformed to a round shape, in which the post-analysis detected the significant diffusion of U into the Zr region and the formation of a dominant  -Zr(O) matrix and a small amount of U-Zr-O precipitates. The abrupt progress of liquefaction was observed in the sample heated at around 1940
-Zr(O) matrix and a small amount of U-Zr-O precipitates. The abrupt progress of liquefaction was observed in the sample heated at around 1940  C or higher. The higher oxygen concentration in the
C or higher. The higher oxygen concentration in the  -Zr(O) matrix suppressed the liquefaction progress, due to the variation in the equilibrium state. The U-Zr-O melt formation progressed by the selective dissolution of Zr from the matrix, and the selective diffusion of U could occur via the U-Zr-O melt.
-Zr(O) matrix suppressed the liquefaction progress, due to the variation in the equilibrium state. The U-Zr-O melt formation progressed by the selective dissolution of Zr from the matrix, and the selective diffusion of U could occur via the U-Zr-O melt.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Osaka University*
JAEA-Review 2021-046, 77 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of technology to simultaneously measure viscosity and surface tension of molten materials in reactor core" conducted from FY2018 to FY2020. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2020, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. Since (U, Zr)O and boride, molten materials in reactor core, exist at extremely high temperature, chemical reactions between the vessel and these molten materials are unavoidable. Therefore, it is difficult to measure the thermophysical property of these materials. In the present study, droplets are produced by heating and melting the samples levitated by a gas levitation method, then the droplets are collided with a substrate.
and boride, molten materials in reactor core, exist at extremely high temperature, chemical reactions between the vessel and these molten materials are unavoidable. Therefore, it is difficult to measure the thermophysical property of these materials. In the present study, droplets are produced by heating and melting the samples levitated by a gas levitation method, then the droplets are collided with a substrate.
Project 6 Meeting Members for Tsukuba International Strategic Zone
JAEA-Review 2021-016, 102 Pages, 2021/11
In December 2011, the Prime Minister designated Tsukuba and some areas in Ibaraki Prefecture as "Comprehensive Special Zones". In the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone, nine advanced research and development (R&D) projects are underway with the goal of promoting industrialization of life innovation and green innovation utilizing the science and technology in Tsukuba. In these projects, the domestic production of medical radioisotope (Technetium-99m,  Tc) was certified as a new project in October 2013, and R&D have been performed in collaboration with related organizations with Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) as the project leader. Japan is the third largest consumer of molybdenum-99 (
Tc) was certified as a new project in October 2013, and R&D have been performed in collaboration with related organizations with Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) as the project leader. Japan is the third largest consumer of molybdenum-99 ( Mo) after the United States and Europe, and all
Mo) after the United States and Europe, and all  Mo are imported. Supply will be insufficient if overseas reactors are shut down due to trouble or if transportation (air and land transportations) is stopped due to volcanic eruptions and some accidents. Thus, early domestic production of
Mo are imported. Supply will be insufficient if overseas reactors are shut down due to trouble or if transportation (air and land transportations) is stopped due to volcanic eruptions and some accidents. Thus, early domestic production of  Mo is strongly required. This project is a technology development aimed at domestic production of
Mo is strongly required. This project is a technology development aimed at domestic production of  Mo, which is a raw material of
Mo, which is a raw material of  Tc used as a diagnostic agent. This report summarizes the activities carried out in the first and second phase of the domestic production of medical radioisotope (
Tc used as a diagnostic agent. This report summarizes the activities carried out in the first and second phase of the domestic production of medical radioisotope ( Tc) (here referred to as the "Project 6") in Tsukuba International Strategic Zone (FY2014-2020).
Tc) (here referred to as the "Project 6") in Tsukuba International Strategic Zone (FY2014-2020).
Myagmarjav, O.; Shibata, Ai*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Takegami, Hiroaki
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(56), p.28435 - 28449, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:13.75(Chemistry, Physical)Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Suzuki, Masahiro; Tachihara, Joji; Takato, Kiyoto; Okita, Takatoshi; Satone, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Michitaka*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 8(3), p.21-00022_1 - 21-00022_9, 2021/06
To reduce the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box and the external exposure dose, the technology of the MOX powder adhesion prevention by the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of the glove box has been developed. The surface analysis by means of atomic force microscopy (AFM) showed that the acrylic test piece surface coated with nanoparticles had a higher root mean square roughness value than that non-coated with nanoparticles. Due to the formation of nano-sized tiny rugged surface, the nanoparticle coating reduced the minimum adhesion force between the UO particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5
particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5  m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Osaka University*
JAEA-Review 2020-038, 41 Pages, 2020/12
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Technology to Simultaneously Measure Viscosity and Surface Tension of Molten Materials in Reactor Core" conducted in FY2019.
 H monitoring in radioactive gaseous waste
H monitoring in radioactive gaseous wasteFurutani, Misa; Kometani, Tatsunari; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Ueno, Yumi; Sato, Junya; Iwai, Yasunori*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 55(2), p.97 - 101, 2020/06
Herein, an oxidation catalyst was introduced after heating it to 600 C to oxidize tritium gas (HT) existing in exhaust into tritiated water vapor (HTO). This study aims to establish a safer
C to oxidize tritium gas (HT) existing in exhaust into tritiated water vapor (HTO). This study aims to establish a safer  H monitoring system by lowering the heating temperature required for the catalyst. In these experiments, which were conducted in the Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, cupric oxide, hydrophobic palladium/silicon dioxide (Pd/SiO
H monitoring system by lowering the heating temperature required for the catalyst. In these experiments, which were conducted in the Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, cupric oxide, hydrophobic palladium/silicon dioxide (Pd/SiO ), and platinum/aluminum oxide (Pt/Al
), and platinum/aluminum oxide (Pt/Al O
O ) catalysts were ventilated using standard hydrogen gas. After comparing the oxidation efficiency of each catalyst at different temperatures, we found that the hydrophobic Pd/SiO
) catalysts were ventilated using standard hydrogen gas. After comparing the oxidation efficiency of each catalyst at different temperatures, we found that the hydrophobic Pd/SiO and Pt/Al
and Pt/Al O
O catalysts could oxidize HT into HTO at 25
catalysts could oxidize HT into HTO at 25 C.
C.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Osaka University*
JAEA-Review 2019-025, 36 Pages, 2020/01
CLADS, JAEA, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Technology to Simultaneously Measure Viscosity and Surface Tension of Molten Materials in Reactor Core". Since (U,Zr)O and boride, molten materials in reactor core, exist at extremely high temperature, chemical reactions between the vessel and these molten materials are unavoidable. Therefore, it is difficult to measure the thermophysical property of these materials. In the present study, droplets are produced by heating and melting the samples levitated by a gas levitation method, then the droplets are collided with a substrate. From the instant behavior of the collision, a new technology to simultaneously derive the viscosity and surface tension will be developed.
and boride, molten materials in reactor core, exist at extremely high temperature, chemical reactions between the vessel and these molten materials are unavoidable. Therefore, it is difficult to measure the thermophysical property of these materials. In the present study, droplets are produced by heating and melting the samples levitated by a gas levitation method, then the droplets are collided with a substrate. From the instant behavior of the collision, a new technology to simultaneously derive the viscosity and surface tension will be developed.
 TiO
TiO during DT neutron irradiation by use of an improved tritium collection method
during DT neutron irradiation by use of an improved tritium collection methodEdao, Yuki; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 112, p.480 - 485, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:51.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The accurate measurement of behavior of bred tritium released from a tritium breeder is indispensable to understand the behavior for a design of a tritium extraction system. The tritium collection method combined a CuO bed and water bubbles was not suitable to measure transient behavior of tritium released from Li TiO
TiO during neutron irradiation because tritium released behavior was changed to be delayed due to adsorption of oxidized tritium on the CuO. Hence, the tritium collection method with hydrophobic catalyst instead of the CuO was demonstrated and succeeded the accurate release measurement of tritium from Li
during neutron irradiation because tritium released behavior was changed to be delayed due to adsorption of oxidized tritium on the CuO. Hence, the tritium collection method with hydrophobic catalyst instead of the CuO was demonstrated and succeeded the accurate release measurement of tritium from Li TiO
TiO . With the method, we assessed the behavior of tritium release under the various conditions since tritium should be released from Li
. With the method, we assessed the behavior of tritium release under the various conditions since tritium should be released from Li TiO
TiO as the form of HT as much as possible from the view point of the fuel cycle. Our results indicated; promotion of isotopic exchange reaction on the surface of Li
as the form of HT as much as possible from the view point of the fuel cycle. Our results indicated; promotion of isotopic exchange reaction on the surface of Li TiO
TiO by addition of hydrogen in sweep gas is mandatory in order to release tritium smoothly from Li
by addition of hydrogen in sweep gas is mandatory in order to release tritium smoothly from Li TiO
TiO irradiated with neutrons; the favorable sweep gas to release as the form of HT was hydrogen added inert gas; and the temperature of Li
irradiated with neutrons; the favorable sweep gas to release as the form of HT was hydrogen added inert gas; and the temperature of Li TiO
TiO was the dominant parameter to control the chemical form of tritium released from the Li
was the dominant parameter to control the chemical form of tritium released from the Li TiO
TiO .
.
 C monitoring in gaseous radioactive waste
C monitoring in gaseous radioactive wasteUeno, Yumi; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Sato, Junya; Iwai, Yasunori
Hoken Butsuri, 51(1), p.7 - 11, 2016/03
In the Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in order to oxidize  C, which exists in various chemical forms in exhaust, into
C, which exists in various chemical forms in exhaust, into  CO
CO , a copper oxide (CuO) catalyst is introduced after heating to 600
, a copper oxide (CuO) catalyst is introduced after heating to 600 C. Our goal was to establish a safer
C. Our goal was to establish a safer  C monitoring system by lowering the heating temperature required for the catalyst; therefore, we developed a new hydrophobic palladium/silicon dioxide (Pd/SiO
C monitoring system by lowering the heating temperature required for the catalyst; therefore, we developed a new hydrophobic palladium/silicon dioxide (Pd/SiO ) catalyst that makes the carrier's surface hydrophobic. In these experiments, catalysts CuO, platinum/aluminum oxide (Pt/Al
) catalyst that makes the carrier's surface hydrophobic. In these experiments, catalysts CuO, platinum/aluminum oxide (Pt/Al O
O ), palladium/zirconium dioxide (Pd/ZrO
), palladium/zirconium dioxide (Pd/ZrO ), hydrophobic Pd/SiO
), hydrophobic Pd/SiO , and hydrophilic Pd/SiO
, and hydrophilic Pd/SiO were ventilated with standard methane gas, and we compared the oxidation efficiency of each catalyst at different temperatures. As a result, we determined that the hydrophobic Pd/SiO
were ventilated with standard methane gas, and we compared the oxidation efficiency of each catalyst at different temperatures. As a result, we determined that the hydrophobic Pd/SiO catalyst had the best oxidation efficiency. By substituting the currently used CuO catalyst with the hydrophobic Pd/SiO
catalyst had the best oxidation efficiency. By substituting the currently used CuO catalyst with the hydrophobic Pd/SiO catalyst, we will be able to lower the working temperature from 600
catalyst, we will be able to lower the working temperature from 600 C to 300
C to 300 C and improve the safety of the monitoring process.
C and improve the safety of the monitoring process.
Seya, Michio; Kobayashi, Naoki; Naoi, Yosuke; Hajima, Ryoichi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Harada, Hideo
Book of Abstracts, Presentations and Papers of Symposium on International Safeguards; Linking Strategy, Implementation and People (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA-ISCN has been implementing basic development programs of the advanced NDA technologies for nuclear material (NM) since 2011JFY (Japanese Fiscal Year), which are (1) NRF (Nuclear resonance fluorescence) NDA technology using laser Compton scattered (LCS)  -rays (intense mono-energetic
-rays (intense mono-energetic  -rays), (2) Alternative to
-rays), (2) Alternative to  He neutron detection technology using ZnS/B
He neutron detection technology using ZnS/B O
O ceramic scintillator, and (3) NRD (Neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (Neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (Neutron resonance capture analysis). These programs are going to be finished in 2014JFY and have demonstration tests in February - March 2015.
ceramic scintillator, and (3) NRD (Neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (Neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (Neutron resonance capture analysis). These programs are going to be finished in 2014JFY and have demonstration tests in February - March 2015.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc production by (n,
Tc production by (n, ) method
) methodNishikata, Kaori; Kimura, Akihiro; Ishida, Takuya; Shiina, Takayuki*; Ota, Akio*; Tanase, Masakazu*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Technology 2014-034, 34 Pages, 2014/10
As a part of utilization expansion after the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR) re-start, research and development (R&D) on the production of medical radioisotope  Mo/
Mo/ Tc by (n,
Tc by (n,  ) method using JMTR has been carried out in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
) method using JMTR has been carried out in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.  Mo is usually produced by fission method. On the other hand,
Mo is usually produced by fission method. On the other hand,  Mo/
Mo/ Tc production by the (n,
Tc production by the (n,  ) method has advantages for radioactive waste, cost reduction and non-proliferation. However, the specific radioactivity per unit volume by the (n,
) method has advantages for radioactive waste, cost reduction and non-proliferation. However, the specific radioactivity per unit volume by the (n,  ) method is low compared with the fission method, and that is the weak point of the (n,
) method is low compared with the fission method, and that is the weak point of the (n,  ) method. This report summarizes the investigation of raw materials, the fabrication tests of high-density MoO
) method. This report summarizes the investigation of raw materials, the fabrication tests of high-density MoO pellets by the plasma sintering method for increasing of
pellets by the plasma sintering method for increasing of  Mo contents and the characterization of sintered high-density MoO
Mo contents and the characterization of sintered high-density MoO pellets.
pellets.
Seya, Michio; Kureta, Masatoshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Nakamura, Hironobu; Harada, Hideo; Hajima, Ryoichi
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/07
JAEA has been implementing development programs of basic technologies of the following advanced NDA (non-destructive assay) of nuclear material (NM) for nuclear safeguards and security. (1) Alternative to  He neutron detection using ZnS/B
He neutron detection using ZnS/B O
O ceramic scintillator, (2) NRD (neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (neutron resonance capture analysis), (3) NRF (nuclear resonance fluorescence)-NDA using laser Compton scattered (LCS)
ceramic scintillator, (2) NRD (neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (neutron resonance capture analysis), (3) NRF (nuclear resonance fluorescence)-NDA using laser Compton scattered (LCS)  -rays (intense mono-energetic
-rays (intense mono-energetic  -rays). The development program (1) is for NDA systems that use ZnS/B
-rays). The development program (1) is for NDA systems that use ZnS/B O
O ceramic scintillator as alternative neutron detector to
ceramic scintillator as alternative neutron detector to  He for coming shortage of its supply. The program (2) is for a NDA system of isotopic composition measurement (non-destructive mass spectroscopy) in targets such as particle-like melted fuel debris using NRTA and NRCA. The program (3) is for NDA systems using a specific NRF reaction of certain Pu/U isotope caused by mono-energetic LCS
He for coming shortage of its supply. The program (2) is for a NDA system of isotopic composition measurement (non-destructive mass spectroscopy) in targets such as particle-like melted fuel debris using NRTA and NRCA. The program (3) is for NDA systems using a specific NRF reaction of certain Pu/U isotope caused by mono-energetic LCS  -ray with energy tuned to the specific excited state of the isotope. This paper introduces above three programs.
-ray with energy tuned to the specific excited state of the isotope. This paper introduces above three programs.
 TiO
TiO
Nakazawa, Tetsuya; Naito, Akira*; Aruga, Takeo; Grismanovs, V.*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1398 - 1403, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:92.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 TiO
TiO pebbles with different diameters
pebbles with different diametersTsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Satoru*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1065 - 1069, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English