Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Idham, M. F.*; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, R.*; Maamoun, I.; Eljamal, O.*
Journal of Water Process Engineering (Internet), 50, p.103289_1 - 103289_16, 2022/12
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:95.02(Engineering, Environmental)Due to synthesis variation affecting various graphene oxide (GO) physicochemical parameters and cost efficiency aspects, the present study investigated the influence of GO precursor components for GO precipitated nZVI nanocomposite (nZVI/GO) and optimized removal conditions to remove chloramphenicol (CAP) from water. In order to synthesize nZVI/GO nanocomposites, four methods of GO precursor synthesis were used, denoted GO1, GO2, GO3, and GO4. A novel synthesis process is introduced based on economic and time-less-consuming protocols to produce GO precursor. A series of desorption experiments were also implemented in various eluents to clarify the CAP removal mechanism. Interestingly, this study demonstrated the substantial impact of GO precursor on the nanocomposite performance in eliminating CAP. The introduced novel GO successfully served as an excellent nZVI precipitation medium and enhanced CAP removal efficiency. Empirical optimization demonstrated that nZVI/GO4-1:1 could eliminate up to 91% of 100 mg/L CAP by dosage as low as 0.25 g/L at pH 5. nZVI/GO4 displayed CAP removal stability throughout a more comprehensive pH range, and remarkable recyclability, making it more promising and practical than bare nZVI and other analyzed nanocomposites. Kinetics data demonstrated a high degree of compatibility with the pseudo-first-order (PFO) and pseudo-second-order (PSO). Through kinetics and statistical analyses, desorption experiments, FTIR spectroscopy, and EDX analysis, nZVI/GO4 removed some of the CAP through the adsorption mechanism controlled by physisorption and chemisorption. In contrast, the oxidation mechanism eliminated the remaining CAP.
西原 哲夫; 羽田 一彦
日本原子力学会誌, 41(5), p.571 - 578, 1999/05
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:40.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)高温ガス炉水素製造システムでは、原子炉で発生したトリチウムの製品水素への移行を可能な限り低減する必要がある。さらに、水素製造システムでは、過剰に供給する水蒸気を再利用することによりトリチウム水が蓄積され、さらに製品水素のトリチウム量を増加させる可能性がある。そこで、製品水素を非放射性物質として位置づける観点から製品水素のトリチウム濃度の目標値を5Bq/g-H と定めた。そして、その目標値を満足させるためには、水素を生成する反応器のみならず、原子炉1次系と水素製造システムの間に設ける中間熱交換器もトリチウム透過量を抑制する必要があり、この手段として酸化膜やコーティングが有効であること、並びに、水素製造システムでリサイクル水のトリチウムを回収する必要はないことを明らかにした。
と定めた。そして、その目標値を満足させるためには、水素を生成する反応器のみならず、原子炉1次系と水素製造システムの間に設ける中間熱交換器もトリチウム透過量を抑制する必要があり、この手段として酸化膜やコーティングが有効であること、並びに、水素製造システムでリサイクル水のトリチウムを回収する必要はないことを明らかにした。
 を含むジルカロイ酸化膜の特性; ジルカロイ-4管の酸化膜
を含むジルカロイ酸化膜の特性; ジルカロイ-4管の酸化膜本橋 治彦; 古田 照夫
JAERI-M 83-132, 15 Pages, 1983/08
ジルカロイ-4管が水素・水蒸気の混合気流中、1000 Cで酸化した時に生成する層状酸化膜の特性を20
Cで酸化した時に生成する層状酸化膜の特性を20 C~1300
C~1300 Cの温度でX線回折法により調べた。室温におけるX線回析図形の解析から、正方晶ZrO
Cの温度でX線回折法により調べた。室温におけるX線回析図形の解析から、正方晶ZrO を含む層状酸化膜中の単斜晶ZrO
を含む層状酸化膜中の単斜晶ZrO は340
は340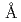 の小さな結晶子となり0.03%の大きな格子歪を持ちそして111の格子面間隔が標準物質より0.7%大きくなっていることを明らかにした。また高温X線回折から正方晶ZrO
の小さな結晶子となり0.03%の大きな格子歪を持ちそして111の格子面間隔が標準物質より0.7%大きくなっていることを明らかにした。また高温X線回折から正方晶ZrO を含む層状酸化膜中の単斜晶ZrO
を含む層状酸化膜中の単斜晶ZrO はゆるやに相変化を起こすことがわかった。この相変化の起こる温度は正方晶ZrO
はゆるやに相変化を起こすことがわかった。この相変化の起こる温度は正方晶ZrO を含まない酸化膜中の単斜晶ZrO
を含まない酸化膜中の単斜晶ZrO の相変化温度より低くなっている。これらの事実から正方晶ZrO
の相変化温度より低くなっている。これらの事実から正方晶ZrO を含む層状酸化膜の生成は酸化膜の結晶子の微細化と大きな格子歪か生じる事と相関性があることを明らかにした。
を含む層状酸化膜の生成は酸化膜の結晶子の微細化と大きな格子歪か生じる事と相関性があることを明らかにした。