Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; 江崎 蘭世; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
It remains an open question whether or not the scalar spin chirality itself can exhibit a Hall-type transport. In this work, we show that the answer is yes: The scalar spin chirality is Hall-transported in Kagome ferromagnets and antiferromagnets under an external bias, engendering a phenomenon which we dub the scalar spin chirality Nernst effect. Our findings call for the need to lift the conventional assumption that the scalar spin chirality is a static quantity in order to discover the active roles of the scalar spin chirality in transport properties.
高畠 容子; 渡部 創; 渡部 雅之; 佐野 雄一; 竹内 正行
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.195 - 198, 2025/05
高レベル放射性廃液からの抽出クロマトグラフィ法によるマイナーアクチノイドの回収に係る研究開発を実施している。高レベル放射性廃液中では微粒子が発生する。抽出クロマトグラフィのカラムの閉塞を防ぐため、それを取り除く技術の開発が必要である。シリカビーズ充填カラムにおける微粒子の除去性能を実験的に評価した。シリカビーズ充填カラムにて、アルミナ粉末を回収したところ、0.12から15 mの微粒子がカラム閉塞の原因であることが分かり、またシリカビーズを充填したカラムによる微粒子除去は実現可能であることが示された。
mの微粒子がカラム閉塞の原因であることが分かり、またシリカビーズを充填したカラムによる微粒子除去は実現可能であることが示された。
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 一場 雄太*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(4), p.389 - 400, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Understanding the distribution of radioactive substances and dose-equivalent rates during the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) is crucial for developing detailed decontamination plans and minimizing worker exposure to radiation. This study used an integrated Radiation Imaging System comprising a Compton camera, survey meter, and simultaneous localization and mapping device to visualize the dose-equivalent rate and radioactive contamination distribution around the startup transformer of Unit 3 at the FDNPS. While previous measurements using this system have helped visualize radioactive hotspots where radioactive contamination has accumulated in pipes or specific equipment, this demonstration test helped visualize the radioactive contamination widely distributed on the ground or concrete surfaces inside the nuclear power station. Furthermore, the reconstructed image intensity of radioactive contamination was compared with the dose rate at the target surface, showing for the first time the possibility of creating a calibration curve between the two.
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer and
ssbauer and  SR studies of Sm
SR studies of Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge
筒井 智嗣; 伊藤 孝; 中村 仁*; 吉田 実生*; 小林 義男*; 依田 芳卓*; 中村 惇平*; 幸田 章宏*; 東中 隆二*; 青木 大*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.55_1 - 55_9, 2024/12
 Sm SR-based M
Sm SR-based M ssbauer and muon spin relaxation (
ssbauer and muon spin relaxation ( SR) spectroscopies have been applied to Sm
SR) spectroscopies have been applied to Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge . The temperature dependence of the
. The temperature dependence of the  Sm SR-based M
Sm SR-based M ssbauer spectra in the paramagnetic state implies the presence of dynamical nuclear Zeeman and/or quadrupole interactions. The time differential
ssbauer spectra in the paramagnetic state implies the presence of dynamical nuclear Zeeman and/or quadrupole interactions. The time differential  SR spectra also exhibit a marked temperature dependence in the paramagnetic state, indicating the presence of magnetic fluctuation in Sm
SR spectra also exhibit a marked temperature dependence in the paramagnetic state, indicating the presence of magnetic fluctuation in Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge at least. These results in the present work infer that the dynamical hyperfine interactions observed using the mutually complementary spectroscopic methods are connected with the mechanism of the heavy fermion behavior in Sm
at least. These results in the present work infer that the dynamical hyperfine interactions observed using the mutually complementary spectroscopic methods are connected with the mechanism of the heavy fermion behavior in Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge .
.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 大浦 正利*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.856 - 870, 2024/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:91.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, understanding the distribution of radioactive substances and dose-equivalent rates is crucial to develop detailed decontamination plans and minimize worker exposure. In this study, we remotely visualized radioactive hotspots and dose-equivalent rate distribution in Unit 1 reactor building of the station using a Mecanum wheel robot equipped with a Compton camera, simultaneous localization and mapping device, and survey meter. We successfully visualized high-concentration radiation hotspots on the U-shaped piping of the drywell humidity control system and the atmospheric control piping in the ceiling in front of the transverse in-core probe room. Furthermore, the hotspot location was identified in three dimensions using the Compton camera used to analyze the atmospheric control piping. By simultaneously analyzing the dose-equivalent rate data acquired by the survey meter and the hotspot locations visualized by the Compton camera, it was confirmed that the hotspots caused elevated dose-equivalent rates in the surrounding area. Using this robot system in unexplored areas, such as the higher floors of reactor buildings, in future will enable us to obtain information on radiation hotspot locations and dose-equivalent rate distribution.
関 剛斎*; 内田 健一*; 高梨 弘毅
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 36(33), p.333001_1 - 333001_11, 2024/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:12.05(Physics, Condensed Matter)Spin caloritronics, a research field studying on the interconversion between a charge current (J ) and a heat current (J
) and a heat current (J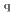 ) mediated by a spin current (J
) mediated by a spin current (J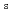 ) and/or magnetization (M), has attracted much attention not only for academic interest but also for practical applications. Newly discovered spin-caloritronic phenomena such as the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) have stimulated the renewed interest in the thermoelectric phenomena of a magnet, which have been known for a long time, e.g. the anomalous Nernst effect (ANE). These spin-caloritronic phenomena involving the SSE and the ANE have provided with a new direction for thermoelectric conversion exploiting J
) and/or magnetization (M), has attracted much attention not only for academic interest but also for practical applications. Newly discovered spin-caloritronic phenomena such as the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) have stimulated the renewed interest in the thermoelectric phenomena of a magnet, which have been known for a long time, e.g. the anomalous Nernst effect (ANE). These spin-caloritronic phenomena involving the SSE and the ANE have provided with a new direction for thermoelectric conversion exploiting J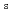 and/or M. Importantly, the symmetry of ANE allows the thermoelectric conversion in the transverse configuration between J
and/or M. Importantly, the symmetry of ANE allows the thermoelectric conversion in the transverse configuration between J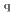 and J
and J . Although the transverse configuration is totally different from the conventional longitudinal configuration based on the Seebeck effect and has many advantages, we are still facing several issues that need to be solved before developing practical applications. The primal issue is the improvement of conversion efficiency. In the case of ANE-based applications, a material with a large anomalous Nernst coefficient (S
. Although the transverse configuration is totally different from the conventional longitudinal configuration based on the Seebeck effect and has many advantages, we are still facing several issues that need to be solved before developing practical applications. The primal issue is the improvement of conversion efficiency. In the case of ANE-based applications, a material with a large anomalous Nernst coefficient (S ) is the key for solving the issue. This review article introduces the increase of S
) is the key for solving the issue. This review article introduces the increase of S can be achieved by forming superlattice structures, which has been demonstrated for several kinds of materials combinations. The overall picture of studies on spin caloritronics is first surveyed. Then, we mention the pioneering work on the transverse thermoelectric conversion in superlattice structures, which was performed using Fe-based metallic superlattices, and show the recent studies for the Ni-based metallic superlattices and the ordered alloy-based metallic superlattices.
can be achieved by forming superlattice structures, which has been demonstrated for several kinds of materials combinations. The overall picture of studies on spin caloritronics is first surveyed. Then, we mention the pioneering work on the transverse thermoelectric conversion in superlattice structures, which was performed using Fe-based metallic superlattices, and show the recent studies for the Ni-based metallic superlattices and the ordered alloy-based metallic superlattices.
吉川 龍志; 今井 康友*; 菊地 紀宏; 田中 正暁; 大島 宏之
Nuclear Technology, 210(5), p.814 - 835, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)ナトリウム冷却高速炉安全性強化研究では、燃料ピンの構造健全性を評価するために各種運転条件下におけるワイヤスペーサ型燃料集合体内熱流動特性の解明が重要である。そこで有限要素法による集合体詳細熱流動解析コードSPIRALが開発されている。本研究では、SPIRALにおける壁近傍低Re数効果を考慮したハイブリッド型乱流モデルの妥当性を確認するために、層流-乱流遷移条件及び乱流条件を含む異なるRe数条件下の37本ピンバンドルナトリウム実験の再現解析を実施した。SPIRALによる予測された温度分布はナトリウム実験で測定され温度と一致した。以上によって、SPIRALにおけるハイブリッド型乱流モデルの広範囲Re数条件下ナトリウム冷却集合体熱流動評価への適用性を確認した。
石田 真也; 田上 浩孝; 岡野 靖; 山野 秀将; 久保 重信; 飛田 吉春
Proceedings of 11th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research Conference (ERMSAR 2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/05
The new detailed fuel pin model has been developed in the SIMMER-V code to simulate thermal and mechanical behavior of the fuel pin from accident initiation to fuel pin failure. The SIMMER code has mainly been developed to simulate the event progression in Transition Phase (TP), and the Initiating Phase (IP) was simulated by the SAS4A code and the results of the SAS4A code were taken over as the initial conditions of the SIMMER code. The transfer of data between codes causes discontinuities due to differences in geometric models and analysis models. There is an additional issue that SIMMER has no analytical model applicable to reactor cores with complex geometry. To solve these issues, the improved SIMMER code, SIMMER-V, is being developed by introducing a detailed and flexible model to simulate fuel pin failure in the IP. This paper describes the development of the new detailed fuel pin model, the construction of the verification matrix, and the results of the verification.
伊藤 孝; 門野 良典*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose a model to describe the fluctuations in the internal magnetic field due to ion dynamics observed in muon spin relaxation ( SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter
SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter  (where
(where 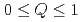 ). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the
). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the  SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI
SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI [with FA referring to HC(NH
[with FA referring to HC(NH )
) ], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI
], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with
lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with 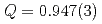 , and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying
, and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying  SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
 Cs contamination of Japanese mustard spinach by resuspended particles in areas with different contamination conditions
Cs contamination of Japanese mustard spinach by resuspended particles in areas with different contamination conditions辰野 宇大*; 吉村 和也; 二瓶 直登*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(3), p.1089 - 1096, 2024/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Resuspended matters occur the secondary radioactive contamination of the crops in Fukushima Prefecture. We investigated the Cs-137 contamination derived from the resuspended matters to Japanese mustard spinaches in the multiple sites. In the less contaminated site, because Cs-137 of the surface ground soil was low, contamination of crops by the soil particles might be small. In the highly contaminated area, Cs-137 deposition of the soil particles might increase. However, the soil particles had no significant effect on Cs-137 contamination to crops. This was because the grown crop might cover the soil and reduce the Cs-137 deposition on the soil.
 CoSi
CoSi山内 宏樹; Sari, D. P.*; 安井 幸夫*; 坂倉 輝俊*; 木村 宏之*; 中尾 朗子*; 大原 高志; 本田 孝志*; 樹神 克明; 井川 直樹; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
 -Mn-type family alloys Mn
-Mn-type family alloys Mn
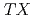 have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn
have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N
RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N el temperature
el temperature  = 190 K. Mn
= 190 K. Mn CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest
CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest  in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15
in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15  of Mn
of Mn CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn
CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient
CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient  . We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn
. We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn CoSi by using neutron scattering,
CoSi by using neutron scattering,  SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn
SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of
RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of  SR above
SR above  becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature
becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature 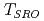 is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn
is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
 system.
system.
伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 下村 浩一郎*
Physical Review B, 108(22), p.224301_1 - 224301_11, 2023/12
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:62.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In positive muon spin rotation and relaxation ( SR) spectroscopy, positive muons (
SR) spectroscopy, positive muons ( ) implanted into solid oxides are conventionally treated as immobile spin-probes at interstitial sites below room temperature. This is because each
) implanted into solid oxides are conventionally treated as immobile spin-probes at interstitial sites below room temperature. This is because each  is thought to be tightly bound to an oxygen atom in the host lattice to form a muonic analogue of the hydroxy group. On the basis of this concept, anomalies in
is thought to be tightly bound to an oxygen atom in the host lattice to form a muonic analogue of the hydroxy group. On the basis of this concept, anomalies in  SR spectra observed in oxides have been attributed in most cases to the intrinsic properties of host materials. On the other hand, global
SR spectra observed in oxides have been attributed in most cases to the intrinsic properties of host materials. On the other hand, global  diffusion with an activation energy of
diffusion with an activation energy of  0.1~eV has been reported in some chemically-substituted perovskite oxides at cryogenic temperatures, although the reason for the small activation energy despite the formation of the strong O
0.1~eV has been reported in some chemically-substituted perovskite oxides at cryogenic temperatures, although the reason for the small activation energy despite the formation of the strong O bond has not yet been quantitatively understood. In this study, we investigated interstitial
bond has not yet been quantitatively understood. In this study, we investigated interstitial  diffusion in the perovskite oxide lattice using KTaO
diffusion in the perovskite oxide lattice using KTaO cubic perovskite as a model system. We used the
cubic perovskite as a model system. We used the  SR method and density functional theory calculations along with the harmonic transition state theory to study this phenomenon both experimentally and theoretically. Experimental activation energies for global
SR method and density functional theory calculations along with the harmonic transition state theory to study this phenomenon both experimentally and theoretically. Experimental activation energies for global  diffusion obtained below room temperature were less than a quarter of the calculated classical potential barrier height for a bottleneck
diffusion obtained below room temperature were less than a quarter of the calculated classical potential barrier height for a bottleneck  transfer path. The reduction in the effective barrier height could be explained by the harmonic transition state theory with a zero-point energy correction; a significant difference in zero-point energies for
transfer path. The reduction in the effective barrier height could be explained by the harmonic transition state theory with a zero-point energy correction; a significant difference in zero-point energies for  at the positions in the O
at the positions in the O bonding equilibrium state and a bond-breaking transition state was the primary cause of the reduction. This suggests that the assumption of immobile
bonding equilibrium state and a bond-breaking transition state was the primary cause of the reduction. This suggests that the assumption of immobile  in solid oxides is not always satisfied since such a significant decrease in diffusion barrier height can also occur in other oxides.
in solid oxides is not always satisfied since such a significant decrease in diffusion barrier height can also occur in other oxides.
廣畑 貴文*; Lloyd, D. C.*; 窪田 崇秀*; 関 剛斎*; 高梨 弘毅; 介川 裕章*; Wen, Z.*; 三谷 誠司*; 小泉 洸生*
IEEE Access, 11, p.117443 - 117459, 2023/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:20.14(Computer Science, Information Systems)Spintronic devices are expected to replace the recent nanoelectronic memories and sensors due to their efficiency in energy consumption and functionality with scalability. To date, spintronic devices, namely magnetoresistive junctions, employ ferromagnetic materials by storing information bits as their magnetization directions. However, in order to achieve further miniaturization with maintaining and/or improving their efficiency and functionality, new materials development is required: 1) increase in spin polarization of a ferromagnet or 2) replacement of a ferromagnet by an antiferromagnet. Antiferromagnetic materials have been used to induce an exchange bias to the neighboring ferromagnet but they have recently been found to demonstrate a 100% spin-polarized electrical current, up to THz oscillation and topological effects. In this review, the recent development of three types of antiferromagnets is summarized with offering their future perspectives towards device applications.
山崎 匠*; 関 剛斎*; 窪田 崇秀*; 高梨 弘毅
Applied Physics Express, 16(8), p.083003_1 - 083003_4, 2023/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:12.23(Physics, Applied)We report the effect of the epitaxial growth of NiO films on its spin current transmission. Two sample series of Pt/NiO/CoFeB, including epitaxial and polycrystalline NiO, were prepared using different deposition conditions. The spin current transmission of NiO is evaluated using the thermo-spin effects in the trilayers. Epitaxial NiO exhibits a non-monotonic behavior in the NiO thickness dependence of spin current transmission, while this behavior is smeared out in polycrystalline NiO. The non-monotonic behavior implies the presence of multiple spin transport mechanisms, which becomes apparent with epitaxial growth.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.1013 - 1026, 2023/08
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:96.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) suffered a meltdown in the aftermath of the large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake that occurred on 11 March 2011. A massive amount of radioactive substance was spread over a wide area both inside and outside the FDNPS site. In this study, we present an approach for visualizing a radioactive hotspot on a standby gas-treatment system filter train, a highly contaminated piece of equipment in the air-conditioning room of the Unit 2 reactor building of FDNPS, using radiation imaging based on a Compton camera. In addition to fixed-point measurements using only the Compton camera, data acquisition while moving using an integrated Radiation Imaging System (iRIS), which combines a Compton camera with a simultaneous localization and mapping device and a survey meter, enabled the three-dimensional visualization of the hotspot location on the filter train. In addition, we visualized the hotspot and quantitatively evaluated its radioactivity. Notably, the visualized hotspot location and estimated radioactivity value are consistent with the accident investigation report of the FDNPS. Finally, the extent to which the radioactivity increased the ambient dose equivalent rate in the surrounding environment was explored.
 Sn
Sn S
S -based shandite films
-based shandite filmsLau, Y.-C.*; 池田 絢哉*; 藤原 宏平*; 小沢 耀弘*; Zheng, J.*; 関 剛斎*; 野村 健太郎*; Du, L.*; Wu, Q.*; 塚崎 敦*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(6), p.064429_1 - 064429_11, 2023/08
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:72.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic Weyl semimetals (mWSMs) are characterized by linearly dispersive bands with chiral Weyl node pairs associated with broken time-reversal symmetry. One of the hallmarks of mWSMs is the emergence of large intrinsic anomalous Hall effect. On heating the mWSM above its Curie temperature, the magnetism vanishes while exchange-split Weyl point pairs collapse into doubly degenerate gapped Dirac states. Here, we reveal the attractive potential of these Dirac nodes in paramagnetic state for efficient spin current generation at room temperature via the spin Hall effect. Ni and In are introduced to separately substitute Co and Sn in a prototypal mWSM Co Sn
Sn S
S shandite film and tune the Fermi level. Composition dependence of spin Hall conductivity for paramagnetic shandite at room temperature resembles that of anomalous Hall conductivity for ferromagnetic shandite at low temperature; exhibiting peak-like dependence centering around the Ni-substituted Co
shandite film and tune the Fermi level. Composition dependence of spin Hall conductivity for paramagnetic shandite at room temperature resembles that of anomalous Hall conductivity for ferromagnetic shandite at low temperature; exhibiting peak-like dependence centering around the Ni-substituted Co Ni
Ni Sn
Sn S
S and undoped Co
and undoped Co Sn
Sn S
S compositions, respectively. The observed spin Hall and anomalous Hall conductivity maxima at different compositions reflect optimum Fermi-level positioning relative to the paramagnetic Dirac and magnetic Weyl states, suggesting the common origin and intercorrelation between the two Hall effects. Our findings highlight a strategy for the quest of spin Hall materials, guided by the abundant experimental anomalous Hall-effect data of ferromagnets in the literature.
compositions, respectively. The observed spin Hall and anomalous Hall conductivity maxima at different compositions reflect optimum Fermi-level positioning relative to the paramagnetic Dirac and magnetic Weyl states, suggesting the common origin and intercorrelation between the two Hall effects. Our findings highlight a strategy for the quest of spin Hall materials, guided by the abundant experimental anomalous Hall-effect data of ferromagnets in the literature.
上羽 智之; 伊藤 昌弘*; 石谷 行生*
JAEA-Technology 2023-006, 36 Pages, 2023/05
日本原子力研究開発機構で開発しているBAMBOOコードは、高速炉用のワイヤスペーサ型炉心燃料集合体における燃料ピンバンドルの変形を解析するコードである。本研究では、燃料ピンとダクトとの相互作用により生じた隣接する燃料ピン同士や最外周の燃料ピンとダクトとの接触部に対して摩擦を考慮するモデルを開発した。これは、BAMBOOの接触・分離解析の中で摩擦力を考慮するモデルであり、摩擦が生じた場合に解析が数値的に不安定になる状況を避けるため、収束計算によって摩擦力を徐々に変化させていき確定するようにした。モデルの解析機能確認の結果、現実的な摩擦係数を適用した場合、ピン-ダクト接触時期やピンバンドル内の変位の方向について摩擦の影響が僅かに認められた。
沖田 将一朗; 水田 直紀; 高松 邦吉; 後藤 実; 吉田 克己*; 西村 洋亮*; 岡本 孝司*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Adoption of SiC-matrix fuel elements in future pin-in-block type HTGR designs will enhance oxidation resistance of the fuel element in the event of the air ingress accident, one of the most worrisome accidents in HTGRs. This would eliminate the need for the graphite sleeves used in the current pin-in-block type HTGR designs and enable high power density core designs with sleeveless and direct coolable fuel structure. Such a concept itself has been suggested by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the past. However, JAEA has not yet demonstrated the feasibility for a core design with the SiC-matrix fuel elements. The present work is intended to demonstrate the feasibility for a new core design upgraded from an existing conceptual core design, called HTR50S, with 50 MW thermal power and reactor outlet temperature of 750 C. The new core design uses SiC-matrix fuel elements and increases the reactor power density to 1.2 times higher than the original HTR50S design. The feasibility is determined by whether the core satisfies the target values in nuclear and thermal-hydraulic designs by performing burn-up calculation with the whole core model and fuel temperature calculations. The calculation results showed that the new core design satisfied these target values on the reactor shutdown margin, the temperature coefficient of reactivity, and the maximum fuel temperature during normal operation.
C. The new core design uses SiC-matrix fuel elements and increases the reactor power density to 1.2 times higher than the original HTR50S design. The feasibility is determined by whether the core satisfies the target values in nuclear and thermal-hydraulic designs by performing burn-up calculation with the whole core model and fuel temperature calculations. The calculation results showed that the new core design satisfied these target values on the reactor shutdown margin, the temperature coefficient of reactivity, and the maximum fuel temperature during normal operation.

中村 惇平*; 川北 至信; 岡部 博孝*; Li, B.*; 下村 浩一郎*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 175, p.111199_1 - 111199_8, 2023/04
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:22.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Muon spin rotation ( SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe
SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe . The detailed investigation of the
. The detailed investigation of the  SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
 SR) methods
SR) methods伊藤 孝; 下村 浩一郎*
Hydrogenomics; The Science of Fully Utilizing Hydrogen (Internet), p.43 - 49, 2023/03
A brief introduction to the muon spin rotation, relaxation, and resonance ( SR) methods is given for researchers and students involved in hydrogen science research. The text includes several examples of how the
SR) methods is given for researchers and students involved in hydrogen science research. The text includes several examples of how the  SR methods can be used to elucidate the behavior of hydrogen in materials.
SR methods can be used to elucidate the behavior of hydrogen in materials.