Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Adachi, Nozomu*; Ueno, Haruki*; Onoe, Katsuhiko*; Morooka, Satoshi; Todaka, Yoshikazu*
ISIJ International, 61(8), p.2320 - 2322, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.97(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) C operation of the HTTR
C operation of the HTTRSakaba, Nariaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Takeda, Tetsuaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 353(1-2), p.42 - 51, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The permeation of hydrogen isotopes through the Hastelloy XR high-temperature alloy adopted for the heat transfer pipes of the intermediate heat exchanger in the HTTR, is one of the concerns in the hydrogen production system, which will be connected to the HTTR in the near future. The hydrogen permeation between the primary and secondary coolant through the Hastelloy XR was evaluated using the actual hydrogen concentration observed during the initial 950 C operation of the HTTR. The hydrogen permeability of the Hastelloy XR was estimated conservatively high as follows. The activation energy E
C operation of the HTTR. The hydrogen permeability of the Hastelloy XR was estimated conservatively high as follows. The activation energy E and pre-exponential factor F
and pre-exponential factor F of the permeability of hydrogen were E
of the permeability of hydrogen were E = 65.8 kJ/mol and F
= 65.8 kJ/mol and F = 7.8
= 7.8 10
10 m
m (STP)/(m
(STP)/(m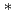 s
s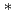 Pa
Pa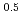 ), respectively, in the temperature range from 707K to 900K.
), respectively, in the temperature range from 707K to 900K.
Kawamura, Yoshinori; Enoeda, Mikio; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.809 - 814, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:69.07(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium bred in the solid breeder blanket of a fusion reactor is extracted by passing of a helium sweep gas. Tritium is separated from sweep gas at the blanket tritium recovery system. Palladium membrane diffuser is one of the applicable processes for the blanket tritium recovery system. It is usually applied for hydrogen purification system such as TEP in ITER. However, it has been reported that the rate controlling step changes at lower hydrogen pressure such as the blanket sweep gas condition, and discussion about application for the blanket sweep gas condition is not enough. Recently, conceptual design of the demonstration reactor, named "DEMO2001", has been proposed from JAERI. In this report, the application of the Pd diffuser for the blanket sweep gas condition is discussed based on the condition of DEMO 2001.
 O
O -SiO
-SiO including CrPO
including CrPO , Out-of-pile tests
, Out-of-pile testsKulsartov, T. V.*; Hayashi, Kimio; Nakamichi, Masaru*; Afanasyev, S. E.*; Shestakov, V. P.*; Chikhray, Y. V.*; Kenzhin, E. A.*; Kolbaenkov, A. N.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.701 - 705, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:92.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Matsuhiro, Kenjiro; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.625 - 628, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.452 - 455, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.10(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium behavior released in ITER hot cell has been investigated numerically. Tritium behavior was evaluated by a combined analytical methods of a tritium transport analysis with the one dimensional diffusion model in the multi-layer wall (concrete and epoxy paint) and a tritium concentration analysis with the complete mixing model by the ventilation in the hot cell under the simulated hot cell operational conditions. As the results, tritium concentration in the hot cell volume decreases rapidly from 300 DAC (Derived Air Concentration) less than 1 DAC in several days after removing the tritium release source. Tritium inventory in the wall is estimated to be about 0.1 PBq for 20 years operation. On the other hand, Tritium permeation through the epoxy painted concrete wall will be negligible. Finally, as to the effect of epoxy paint on the tritium permeation and inventory, it is found that the epoxy paint can reduce tritium inventory by about two orders of magnitude relative to bare concrete wall.
Kawamura, Yoshinori; Iwai, Yasunori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.654 - 657, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Adding some amount of hydrogen to the helium sweep gas is effective for tritium extraction from blanket, but it causes permeation of tritium to a cooling system. In the design study of a demonstration reactor in JAERI, tritium leakage has been estimated to be about 20% of bred tritium under typical sweep gas conditions. If these tritiums are recovered under the ITER-WDS condition, tritium leakage limitation has to be less than 0.3% of typical case. Water vapor addition to the sweep gas is effective not only for blanket tritium extraction but also for permeation prevention. The reaction rate of isotope exchange is larger than the case of H , and the equilibrium constant is also expected to be about 1.0. When the H/T ratio is 100, tritium inventory of breeder material is larger than the case of H
, and the equilibrium constant is also expected to be about 1.0. When the H/T ratio is 100, tritium inventory of breeder material is larger than the case of H addition. However it is not so large. In case of H
addition. However it is not so large. In case of H O sweep, separation of tritiated water from helium seems to be easyer, but the process that changes HTO to HT is necessary.
O sweep, separation of tritiated water from helium seems to be easyer, but the process that changes HTO to HT is necessary.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
A hydrogen production system connected to the High-Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) is being designed to be able to produce hydrogen using a nuclear heat of 10 MW supplied by the HTTR. The HTTR hydrogen production system is first connected to a nuclear reactor in the world, hence an mock-up model test is planned to carry out prior to the demonstration test of the HTTR hydrogen production system. In parallel to the mock-up model test, the following tests as an essential problem, a corrosion test of a reforming tube, a permeation test of hydrogen isotopes through a heat exchanger tube, an integrity test of a high-temperature isolation valve, and a performance test of a hydrogen permselective membrane are carried out to obtain detailed data for a safety review and development of analytical codes. This paper describes the present status of the component tests on the R&D of the HTTR hydrogen production system.
 C operation of the HTTR
C operation of the HTTRSakaba, Nariaki; Matsuzawa, Takaharu*; Hirayama, Yoshiaki*; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takeda, Tetsuaki
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
The permeation of hydrogen isotopes through the Hastelloy XR high-temperature alloy adopted for the heat exchanger pipes of the intermediate heat exchanger in the HTTR (High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor) is one of the concerns in the hydrogen production system, which will be connected to the HTTR in the near future. An evaluation of the hydrogen permeation between the primary and secondary coolant through the Hastelloy XR was performed using the hydrogen concentration data observed during the initial 950 C operation of the HTTR. The hydrogen permeability of the Hastelloy XR was estimated conservatively high as follows. The activation energy E
C operation of the HTTR. The hydrogen permeability of the Hastelloy XR was estimated conservatively high as follows. The activation energy E and pre-exponential factor F
and pre-exponential factor F of the permeability of hydrogen were E
of the permeability of hydrogen were E = 62 kJ/mol and F
= 62 kJ/mol and F = 3.6
= 3.6 10
10 cm
cm (NTP)/(cm s Pa
(NTP)/(cm s Pa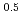 ), respectively, in the temperature range from 735K to 940K. The results implied that some oxidized film had been formed on the surface of the heat exchanger pipes of the intermediate heat exchanger.
), respectively, in the temperature range from 735K to 940K. The results implied that some oxidized film had been formed on the surface of the heat exchanger pipes of the intermediate heat exchanger.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho*; Matsuhiro, Kenjiro; Fischer, U.*; Hayashi, Takumi; Mori, Seiji*; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishitani, Takeo; Shimizu, Katsusuke*; Simakov, S.*; et al.
JAERI-Review 2005-005, 40 Pages, 2005/03
The International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is being jointly planned to provide an accelerator-based Deuterium-Lithium (Li) neutron source to produce intense high energy neutrons (2 MW/m ) up to 200 dpa and a sufficient irradiation volume (500 cm
) up to 200 dpa and a sufficient irradiation volume (500 cm ) for testing the candidate materials and components up to about a full lifetime of their anticipated use in ITER and DEMO. To realize such a condition, 40 MeV deuteron beam with a current of 250 mA is injected into high speed liquid Li flow with a speed of 20 m/s. In target system, radioactive species such as 7Be, tritium and activated corrosion products are generated. In addition, back wall operates under severe conditions of neutron irradiation damage (about 50 dpa/y). In this paper, the thermal and thermal stress analyses, the accessibility evaluation of the IFMIF Li loop, and the tritium inventory and permeation of the IFMIF Li loop are summarized as JAERI activities on the IFMIF target system performed in FY2004.
) for testing the candidate materials and components up to about a full lifetime of their anticipated use in ITER and DEMO. To realize such a condition, 40 MeV deuteron beam with a current of 250 mA is injected into high speed liquid Li flow with a speed of 20 m/s. In target system, radioactive species such as 7Be, tritium and activated corrosion products are generated. In addition, back wall operates under severe conditions of neutron irradiation damage (about 50 dpa/y). In this paper, the thermal and thermal stress analyses, the accessibility evaluation of the IFMIF Li loop, and the tritium inventory and permeation of the IFMIF Li loop are summarized as JAERI activities on the IFMIF target system performed in FY2004.
Yoshida, Hajime; Kosaku, Yasuo*; Enoeda, Mikio; Abe, Tetsuya; Akiba, Masato
JAERI-Research 2005-003, 13 Pages, 2005/03
Hydrogen permeation fluxes of the reduced activation ferritic steel F82H were quantitatively measured by a newly proposed method, vacuum thermo-balance method, for a precise estimation of tritium leakage in a fusion reactor. We prepared sample capsules made of F82H, which enclosed hydrogen gas. The hydrogen in the capsules permeated through the capsule wall, and subsequently desorbed from the capsule surface during isothermal heating. The vacuum thermo-balance method allows simultaneous measurement of the hydrogen permeation flux by two independent methods, namely, the net weight reduction of the sample capsule and exhaust gas analysis. Thus the simultaneous measurements by two independent methods increase the reliability of the permeability measurement. The ratio of the hydrogen permeation fluxes obtained by the net weight reduction to that measured by the exhaust gas analysis was in the range from 1/4 to 1/1 in this experiment. It has been demonstrated that the vacuum thermo-balance method is effective for the measurement of hydrogen permeation rate of F82H.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.183 - 187, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:82.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Takeda, Tetsuaki; Iwatsuki, Jin*
Nuclear Technology, 146(1), p.83 - 95, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The objective of this study is to investigate the effect of the existence of hydrogen in a pipe outside on the amount of permeated deuterium through the pipe. It was found that the amount of permeated deuterium decreases with increasing the partial pressure of hydrogen in the pipe outside when the partial pressure of deuterium in the pipe is lower than 100 Pa and that of hydrogen in the pipe outside is higher than 10 kPa. The amount of permeated deuterium on counter permeation was predicted quantitatively by using an effectiveness factor for diffusivity of deuterium in metals and by taking into account the equilibrium state for hydrogen, deuterium and HD molecules on the metal surface. From the results obtained in this study, it is supposed that the amount of tritium transferred from the primary circuit of the HTTR to the hydrogen production system will be reduced by the existence of high-pressure hydrogen in the catalyst pipe of the steam reformer.
Matsuhiro, Kenjiro; Ando, Masami; Nakamura, Hiroo; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
JAERI-Research 2004-003, 12 Pages, 2004/03
The effect of neutron irradiation damage on tritium permeation through reduced-activation ferritic steel (F82H) at IFMIF target backwall has been estimated. From the results, it has been found that the effective diffusion coefficient of hydrogen in F82H will decrease by 10 % to 20 % under neutron irradiation. Therefore, the amount of tritium permeation for several hundred seconds at the beginning of permeation will be smaller than 80 % to 90 % of that before neutron irradiation. The amount of tritium permeation of F82H at IFMIF target backwall is 1.3x10 g/d (4.7x10
g/d (4.7x10 Bq/d). It is 30 times larger than that of 316SS, and is about 8 % of tritium permeation at main loop of IFMIF.
Bq/d). It is 30 times larger than that of 316SS, and is about 8 % of tritium permeation at main loop of IFMIF.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka
JAERI-Research 2003-024, 24 Pages, 2003/11
Re-evaluation of tritium permeation through vertical target of divertor under the ITER operation condition was carried out using tritium transport properties in the candidate materials such as the diffusion coefficient and the trapping factors in tungsten for armor, and the surface recombination coefficient on copper for the heat sink obtained by authors' recent investigation (authors' data), which simulated the plasma-facing conditions of ITER. Evaluation with the data set of previous evaluation was also carried out for comparison (previous data). The permeation analysis was carried out individually by classifying into the armor region (Carbon Fiber Composites and tungsten) and the slit region without armor (3% of armor surface area) assuming the incident flux and temperature for each region. As the results of the permeation analysis, estimated permeation amount with the authors' data was one order less than that with the previous data at the end of lifetime of the divertor due to authors' small diffusion coefficient of tritium in tungsten. It also indicated the possibility that permeation through the slit region of the armor tiles could dominate total permeation through the vertical target, since tritium permeation amount through tungsten armor with the authors' data was estimated to be reduced drastically smaller than that with the previous evaluation data. The result of a little tritium permeation amount through the vertical target with the authors' data ensured the conservatism of the current evaluation of tritium concentration in the primary cooling water in ITER divertor, as it indicated the possibility of direct drainage of the divertor primary cooling water.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka; Sugisaki, Masayasu*
JAERI-Research 2003-018, 32 Pages, 2003/09
Tritium transport behavior in materials, which is essential for the safety evaluation of the fusion reactor, has to be evaluated by either tritium properties or extrapolated value from protium or deuterium (D) to tritium (T) using the isotope effect theory. However, there are still some uncertainties on estimation of T behavior in materials, because there are only a few T transport properties data in materials, and it is not completely proven the application of the isotope effect theory to T due to the lack of T data. Therefore, in order to understand the tritium transport properties in materials, isotope effects on diffusion and surface recombination between T and D in/on nickel, whose hydrogen transport properties were well known, were investigated by comparing the obtained properties of T with those of D measured under the same conditions with the ion driven permeation method. Though obtained diffusion coefficient of T was larger than that of D, and activation energy of diffusion of T was smaller than that of D as the contrary to the classical diffusion theory, those were shown to be explained with a modified diffusion theory by introducing higher vibration temperatures in nickel than previous reported values. In addition, the isotope effect on surface recombination coefficient between D and T was shown to be explained using a modified solution model as well as diffusion.
Ogawa, Hiroaki*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
JAERI-Research 2002-037, 48 Pages, 2002/12
The difference in hydrogen permeation among candidate cladding materials such as 25Cr-35Ni stainless steel, Nb liner and reference materials such as 18Cr-8Ni SS, and Zr of Zircaloy base metal were evaluated by low energy plasma permeation simulated to hydrogen excited by heavy neutron irradiation. RF excitation source was arranged for the experimental apparatus in cooperating with temperature and bias control. Comparing with the thermodynamic gas driven permeation (GDP) in the same hydrogen pressure, the hydrogen permeation rate by the plasma driven permeation (PDP) was markedly accelerated at low to medium temperature range. The temperature dependency showed a knick at around 530K due to hydrogen-defect interactions. Comparing with Zr, Nb showed the high hydrogen solubility without the degradation by hydrate formation that is required to a getter material. The difference in PDP among candidates was analyzed with a new dissolution model for hydrogen.
Shiozawa, Shusaku; Ogawa, Masuro; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Onuki, Kaoru; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Hayashi, Koji; Kubo, Shinji; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 17th KAIF/KNS Annual Conference, p.557 - 567, 2002/04
The research and development program on nuclear production of hydrogen was started on January in 1997 as a study consigned by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. A hydrogen production system connected to the HTTR is being designed to be able to produce hydrogen of about 4000 m3/h by steam reforming of natural gas, using a nuclear heat of 10 MW supplied by the HTTR. In order to confirm controllability, safety and performance of key components in the HTTR hydrogen production system, the facility for an out-of-pile test was constructed on the scale of approximately 1/30 of the HTTR hydrogen production system. Essential tests are also carried out to obtain detailed data for safety review and development of analytical codes. Other basic studies on the hydrogen production technology of thermochemical water splitting called an iodine sulfur (IS) process, has been carried out for more effective and various uses of nuclear heat. This paper describes the present status and a future plan on the R&D of the HTTR hydrogen production systems in JAERI.
Enoeda, Mikio; Ohara, Yoshihiro; Akiba, Masato; Sato, Satoshi; Hatano, Toshihisa; Kosaku, Yasuo; Kuroda, Toshimasa*; Kikuchi, Shigeto*; Yanagi, Yoshihiko*; Konishi, Satoshi; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2001-078, 120 Pages, 2001/12
This report is a summary of the design works, which was discussed in the design workshop held in 2000 for the demonstration (DEMO) blanket aimed to strengthen the commercial competitiveness and technical feasibility simultaneously. The DEMO blanket must supply the feasibility and experience of the total design of the power plant and the materials. This conceptual design study was performed to determine the updated strategy and goal of the R&D of the DEMO blanket which applies the supercritical water cooling proposed in A-SSTR, taking into account the recent progress of the plasma research and reactor engineering technology.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Ohira, Shigeru; Nishi, Masataka
JAERI-Research 2001-042, 21 Pages, 2001/09
Study on Implantation Driven Permeation (IDP) behavior of deuterium through pure beryllium was investigated as a part of the research to predict the tritium permeation through the first wall components of ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor). The permeation experiments were carried out with two beryllium specimens, one was an unannealed specimen and the other was that annealed at 1173 K. The permeation flux was measured as a function of specimen temperature and incident ion flux. Surface analysis of specimen was also carried out after the permeation experiment. Permeation was observed only with the annealed specimen and no significant permeation was observed with unannealed specimen under the present experimental condition (maximum temperature: 685K, detection limit: 1x10 Datoms/m
Datoms/m s). It could be attributed that the intrinsic lattice defects, which act as diffusion preventing site, decreased with the specimen annealing. Based on the result of steady and transient permeation behavior and surface analysis, it was estimated that the deuterium permeation implanted into annealed beryllium was controlled by surface recombination due to the oxide layer on the surface of the permeated side.
s). It could be attributed that the intrinsic lattice defects, which act as diffusion preventing site, decreased with the specimen annealing. Based on the result of steady and transient permeation behavior and surface analysis, it was estimated that the deuterium permeation implanted into annealed beryllium was controlled by surface recombination due to the oxide layer on the surface of the permeated side.