Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2025-037, 103 Pages, 2025/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2023, this report summarizes the research results of the "A study on the methodology for rational treatment/disposal of contaminated concrete waste considering volume reduction of waste" conducted in FY2023. The present study aims to evaluate rational waste management strategies incorporating reuse and recycling focusing on radioactive concrete waste, which will be massively generated from dismantling. Feasibility and challenges of aggregate recycling are considered assuming a typical recycled aggregate production technique, based on the characteristics of the concrete. In 2023, the migration behaviors of radionuclides and ions in cementitious materials having interfacial transition zones (ITZ) were investigated through diffusion and leaching experiments using radioactive and non-radioactive tracers and modeled by random walk particle tracking method with a sampling technique using a probabilistic distribution model for two media with an interface. Properties of surrogate contaminated concrete samples prepared by immersing in Cs solution were examined. Migration of ions was studied for surrogate contaminated aggregates and recycled concrete using the surrogate. In addition, surrogate waste package was prepared using by-product powder to study mechanical and chemical properties as well as leaching behavior of radionuclides. Information on properties of the contaminated concrete and tools to estimate the amount of concrete were organized in order to evaluate different waste management scenarios incorporating reuse/recycling.
Yamaguchi, Yuji; Niikura, Megumi*; Mizuno, Rurie*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Harada, Masahide; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Haga, Katsuhiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 567, p.165801_1 - 165801_11, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00As part of the development of a sample radioactivity calculation program, we have measured radionuclide production probabilities in negative muon nuclear capture to update experimental data and to validate a calculation dataset obtained by a Monte Carlo simulation code. The probabilities have been obtained by an activation experiment on  Al,
Al, 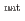 Si,
Si,  Co, and
Co, and 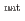 Ta targets. The obtained probabilities expand the validation scope to the radionuclide production processes outside of the existing data coverage. By comparing the resultant probabilities with the calculated dataset, it has been revealed that the dataset is generally on the safe side in radioactivity estimation and needs to be corrected in the following three cases: (i) isomer production; (ii) radionuclide production by the multiple neutron emission; (iii) radionuclide production by particle emissions involving a proton. The present probabilities and the new findings on the correction provide valuable clues to improvements of the simulation models.
Ta targets. The obtained probabilities expand the validation scope to the radionuclide production processes outside of the existing data coverage. By comparing the resultant probabilities with the calculated dataset, it has been revealed that the dataset is generally on the safe side in radioactivity estimation and needs to be corrected in the following three cases: (i) isomer production; (ii) radionuclide production by the multiple neutron emission; (iii) radionuclide production by particle emissions involving a proton. The present probabilities and the new findings on the correction provide valuable clues to improvements of the simulation models.
Kinase, Masami
Radioisotopes, 74(2), p.233 - 238, 2025/07
no abstracts in English
Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Sugihara, Kenta*; Hirano, Yukinori*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Saito, Shigeru; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Technology 2024-026, 123 Pages, 2025/03
Based on the design of the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) at the J-PARC Transmutation Experimental Facility, a conceptual study was conducted on the J-PARC proton beam irradiation facility. This research was carried out based on the recommendations of the Nuclear Transmutation Technology Evaluation Task Force of the MEXT. The recommendations state that it is desirable to consider facility specifications that can make the most of the benefits of using the existing J-PARC proton accelerator while also solving the engineering issues of the ADS. We considered facilities that could respond to a variety of needs while reducing the facilities that were not needed in the TEF-T design. In order to clarify these diverse needs, we investigated the usage status of representative accelerator facilities around the world. As a result, it became clear that the main purposes of these facilities were (1) Material irradiation, (2) Soft error testing of semiconductor devices using spallation neutrons, (3) Production of RI for medical use, and (4) Proton beam use, and we investigated the facilities necessary for these purposes. In considering the facility concept, we assumed a user community in 2022 and reflected user opinions in the facility design. This report summarizes the results of the conceptual study of the proton irradiation facility, various needs and responses to them, the roadmap for facility construction, and future issues.
Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/11
Takeda, Takeshi; Shibata, Taiju
JAEA-Review 2024-040, 29 Pages, 2024/09
An important theme of Japan's 6th strategic energy plan is to indicate the energy policy path towards carbon neutrality by 2050. Policy responses for Japan's nuclear energy research and development (R&D) towards 2030 contain the demonstrations of technologies for small modular reactors (SMRs) through international cooperation by 2030. In light of this energy plan, basic policy initiatives over the next 10 years have been compiled to realize Green Transformation (GX), which simultaneously achieves decarbonization and economic growth. Looking overseas, activities of SMR R&D are active internationally, mainly in the US, Canada, Europe, China, and Russia. These activities are not only by heavy industry manufactures and R&D institutes, but also by venture companies. Under these circumstances, the NEA CSNI has gathered an Expert Group on SMRs (EGSMR) to help estimate the safety effects of SMRs. The EGSMR efforts required the submission of responses to several questionnaires whose main purpose was to collect the latest information on the efforts of SMR deployment and research. The first author of this report responded to this based on information from Hitachi-GE Nuclear Energy, Ltd. and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. as well as JAEA. Most of the responses from Japan to the questionnaires are the information that serves as the basis of CSNI Technical Opinion Paper No. 21 (TOP-21). In this report, the Japan's publicly available responses to the questionnaires arranged and additional information are explained, which complements some of the content of the TOP-21. In this manner, the investigation results of R&D related to SMR in Japan, focusing on the EGSMR activities (2022-2023), are summarized. The target of this report is to provide useful information for future discussions on international cooperation concerning SMR as well as nuclear power field human resources development internationally and domestically.
Nagatsuka, Kentaro; Noguchi, Hiroki; Nagasumi, Satoru; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Sakaba, Nariaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 425, p.113338_1 - 113338_11, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)HTGR has a potential to contribute to decarbonization of hard-to-abate industries by supplying a large amount of hydrogen and high temperature heat or steam without carbon dioxide emission. JAEA has been conducting R&Ds for HTGR technologies with High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). This paper shows that HTTR's tests including the loss of core cooing test as a joint the OECD/NEA international research project and a HTTR heat application test plan which demonstrate hydrogen production by coupling the HTTR with a hydrogen production test facility. Additionally, aiming for operation start from the latter half of 2030s, the basic design of the HTGR demonstration reactor has been shown. The Japan's HTGR technology capabilities established by the HTTR project will be fully utilized for the construction of HTGR demonstration reactor.
 Mg,
Mg,  Si,
Si,  Fe,
Fe,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Zn
ZnSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 549, p.165299_1 - 165299_12, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Maeda, Shigetaka
Hoshasen Kagaku Furonteia, (5), P. 17, 2024/02
Regarding Actinium-225, which is one of the medical radioisotopes and has been attracting attention today, we will report on the domestic movement toward domestic production, the research and development plan and progress for production of Actinium-225 using the experimental fast reactor Joyo.
Konno, Chikara
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.121 - 126, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:51.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced in 2017 and those of 22 nuclei for neutron and 25 nuclei for proton were bundled in the PHITS code. Recently it was found that the following five data in the JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files had any problems; ACE files for  N and
N and  O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
Fukahori, Tokio; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(12), p.726 - 727, 2023/12
, 65(12), p.726 - 727, 2023/12
The Investigative Committee on Nuclear Data investigates and observes global trends in nuclear research and development and conducts comprehensive examinations of Japanese nuclear data activities from a broader perspective, as well as cooperation with domestic and foreign academic institutions in a wide range of fields other than the Atomic Energy Society. We aim to establish a system for communication, information exchange, and interdisciplinary cooperation. In this report, we will report on three of the main activities for the 2021-2022 term: a request list site for nuclear data, human resource development, and roadmap production.
 Ti and
Ti and  Nb at 0.8 and 3.0 GeV
Nb at 0.8 and 3.0 GeVSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 545, p.165153_1 - 165153_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.82(Instruments & Instrumentation)Arai, Masaji; Maeda, Shigetaka
Rinsho Hoshasen, 68(10), p.963 - 970, 2023/10
Ac-225 is attracting attention as an alpha-emitting medical radioisotope. Since its demand is expected to increase, domestic production of Ac-225 is required from the viewpoint of Japan's medical research and economic security. To establish the technical bases for the Ac-225 production, JAEA has evaluated the radioactivity that can be produced in the experimental fast reactor Joyo and designed the concept that upgrades the existing facilities for transporting the irradiated target from Joyo to a neighboring PIE facility rapidly. Efficient Actinium-225 Separation from Ra-226 irradiated in a fast reactor was studied. This study has revealed that Joyo can sufficiently produce Ac-225 as a raw material for pharmaceuticals.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ho, H. Q.; Kitagawa, Kanta*; Fukuda, Takahito*; Ito, Ryo*; Nemoto, Masaya*; Kusunoki, Hayato*; Nomura, Takuro*; Nagase, Sota*; Hashimoto, Haruki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-013, 19 Pages, 2023/06
Eight people from five universities participated in the 2022 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the feasibility study for nuclear battery, the burn-up analysis of HTTR core, the feasibility study for  Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Ishii, Katsunori; Aoki, Takeshi; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Noguchi, Hiroki; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
Nomoto, Yasunobu; Mizuta, Naoki; Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Okita, Shoichiro; Ishii, Katsunori; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Tanaka, Masato; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
 Ni and
Ni and  Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV
Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeVTakeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.17 - 27, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems and so on, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations, JENDL/HE-2007 and so on.
Fukahori, Tokio; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 64(7), p.413 - 414, 2022/07
, 64(7), p.413 - 414, 2022/07
The Investigation Advisory Committee on Nuclear Data monitors global nuclear research and development trends, and conducts collaborative nuclear data activities with domestic and foreign academic institutions in a wide range of fields. The aims are to contact, to exchange information, and to build an interdisciplinary cooperation system. Reported are the activities on the request list site, human resources development, and roadmap creation regarding nuclear data directly related to future nuclear data research activities, among the main activities in the 2019-2020 period.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita; Iwamoto, Hiroki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 98(5), p.216 - 221, 2022/05
For the realization of accelerator-driven transmutation systems (ADS) and the construction of the ADS target test facility (TEF-T) at J-PARC, it is necessary to study the proton beam handling technology and neutronics for protons in the GeV energy region. Accordingly, the Nuclear Transmutation Division of J-PARC has studied these issues with using J-PARC's accelerator facilities, and so on. This paper introduces these topics.
Nakano, Keita; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sugawara, Takanori; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-018, 41 Pages, 2022/03
Neutronic analysis of beam window of the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) proposed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducted using PHITS and DCHAIN-PHITS codes. We investigate gas production of hydrogen and helium isotopes in the beam window, displacement per atom of beam window material, and heat generation in the beam window. In addition, distributions of produced nuclides, heat density, and activity are derived. It was found that at the maximum 12500 appm H production, 1800 appm He production, and damage of 62.1 DPA occurred in the beam window by the ADS operation. On the other hand, the maximum heat generation in the beam window was 374 W/cm . In the analysis of LBE,
. In the analysis of LBE,  Bi and
Bi and  Po were found to be the dominant nuclides in decay heat and radioactivity. Furthermore, the heat generation in the LBE by the proton beam was maximum around 5 cm downstream of the beam window, which was 945 W/cm
Po were found to be the dominant nuclides in decay heat and radioactivity. Furthermore, the heat generation in the LBE by the proton beam was maximum around 5 cm downstream of the beam window, which was 945 W/cm .
.