Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Pu
Pu O
O powder using master sintering curve theory
powder using master sintering curve theoryNakamichi, Shinya; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 595, p.155072_1 - 155072_11, 2024/07
Shimazaki, Yosuke; Jidaisho, Tatsuya; Ishii, Toshiaki; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2024-005, 23 Pages, 2024/06
HTTR has newly assumed Beyond Design Basis Accident (BDBA) as part of conformity assessment with the new regulatory standards and has established measures to prevent the spread of BDBA. Among these measures, to prevent the spread of BDBA caused by cooling water leaks from spent fuel storage pool, the Oarai Research Institute's fire engine was selected as an equipment to prevent the spread of BDBA, and required performances such as pumping water performance were determined. After all required performances were confirmed by inspections, the fire engine passed the operator's pre-use inspection and contributed to the restart of the HTTR operations.
 C
CNguyen, B. V. C.*; Murakami, Kenta*; Chena, L.*; Phongsakorn, P. T.*; Chen, X.*; Hashimoto, Takashi; Hwang, T.*; Furusawa, Akinori; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 39, p.101639_1 - 101639_9, 2024/06
Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Imai, Yasutomo*; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nuclear Technology, 210(5), p.814 - 835, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the study of safety enhancement on advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor, it is essential to clarify the thermal-hydraulics under various operation conditions in a fuel assembly (FA) with the wire-wrapped fuel pins to assess the structural integrity of the fuel pin. A finite element thermal-hydraulics analysis code named SPIRAL has been developed to analyze the detailed thermal-hydraulics phenomena in a FA. In this study, the numerical simulations of the 37-pin bundle sodium experiments at different Re number conditions, including a transitional condition between laminar and turbulent flows and turbulent flow conditions, were performed to validate the hybrid turbulence model equipped in SPIRAL. The temperature distributions predicted by SPIRAL was consistent with those measured in the experiments. Through the validation study, the applicability of the hybrid turbulence model in SPIRAL to thermal-hydraulic evaluation of sodium-cooled FA in the wide range of Re number was confirmed.
Kurisaka, Kenichi
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00377_1 - 23-00377_14, 2024/04
This study aims to understand the time-dependent change in the occurrence rate of leak from steam generator (SG) tubes in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The target SFRs in the present paper are Phenix in France and BN-600 in Russia. By reviewing publicly available literature that show data from the SFRs, we have investigated the numbers of tube-to-tubeplate welds and tube-to-tube welds, heat transfer areas of tube base metal, operating hours of SGs, dates when SG tube leak occurred, locations of leak, and corrective actions taken after tube leak events, such as replacement of the module, in which a leak occurred. Based on these, we have estimated the time to leak and quantitatively analyzed the time-dependent change of the occurrence rates of SG tube leak for each of the above-mentioned parts by hazard plotting method. The results show that the rates of both Phenix and BN-600 decreased over time. For Phenix, this is probably thanks to improved welding and SG operating conditions. For BN-600, it seems that in many cases, the probable cause of the leak was initial defects that developed to failure during the early stage of reactor operation, and that no special countermeasure was taken in the later stages. Therefore, it would be natural to assume that the rate simply decreased over time. The rate of leak at tube-to-tube welds in Phenix shows significant increase in a short term after a certain period of time. This can be caused by thermal stress repeatedly exerted on the materials.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Kawata, Manabu; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2024-001, 206 Pages, 2024/03
In the assessment of seismic safety and the design of building structures in nuclear facilities, lumped mass models have been used as standard methods. Recent advances in computer capabilities allow the use of three-dimensional finite element (3D FE) models to account for the 3D behavior of buildings, material nonlinearity, and the nonlinear soil-structure interaction effect. While 3D analysis method has many advantages, it is necessary to ensure its reliability as a new approach. The International Atomic Energy Agency performed an international benchmark study using the 3D FE analysis model for reactor building of Unit 7 at TEPCO's Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station based on recordings from the Niigataken Chuetsu-oki Earthquake in 2007. Multiple organizations from different countries participated in this study and the variation in their analytical results was significant, indicating an urgent need to improve the reliability of the analytical results by standardization of the analytical methods using 3D FE models. Additionally, it has been pointed out that it is necessary to understand the 3D behavior in the seismic fragility assessment of buildings and equipment, using realistic seismic response analysis method based on 3D FE models. In view of these considerations, a guideline for the seismic response analysis method using a 3D FE model was developed by incorporating the latest knowledge and findings in this area. The purpose of the guideline is to improve the reliability of the seismic response analysis method using 3D FE model of reactor buildings. The guideline consists of a main body, commentaries, and appendixes. The standard procedures, recommendations, key points to note, and technological bases for conducting seismic response analysis on reactor buildings using 3D FE models are provided in the guideline. In addition, the guideline will be revised reflecting the latest knowledge.
Zablackaite, G.; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Kido, Kentaro; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 56(2), p.536 - 545, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Sugita, Yusuke; Yamaguchi, Yutaka
Nuclear Technology, 210(1), p.55 - 71, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study has developed an estimation method for residual sodium film and sodium lumps on dummy fuel pins in Monju and demonstrated sodium draining behavior through gaps among the pins, experimentally. The amounts of the residual sodium on the surface of the pins were measured using the three-type test specimens: (a) single pin, (b) 7-pin assembly, and (c) 169-pin assembly. The experiments revealed that the withdrawal speed of the pins and improvement of the sodium wetting increased drastically the amounts of the residual sodium. Furthermore, the experiments using the 169-pin assembly measured the practical amounts of the residual sodium in the dummy fuel assembly of short length and demonstrated sodium draining behavior through the dummy fuel assembly. The estimation method includes four models: a viscosity flow model, Landau-Levich-Derjaguin (LLD) model, an empirical equation related to the Bretherton model, and a capillary force model in a tube. The calculation predicted comparable amounts of the residual sodium with the experiments. An uncertain of the sodium wetting effects were close to 1.8 times the estimation values of the LLD model. With this estimation method, the amounts of the residual sodium on the unloaded Monju dummy fuel assembly can be evaluated.
 Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag, and
Ag, and  In
InNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 16 Pages, 2024/00
Neutron capture cross-sections of nuclides targeted for decommissioning are necessary to contribute to the evaluation of radioactivity produced. The present study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag and
Ag and  In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18
In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18 0.28 barn for
0.28 barn for  Sc(n,
Sc(n,  )
)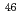 Sc, 4.34
Sc, 4.34 0.06 barn for
0.06 barn for  Cu(n,
Cu(n,  )
) Cu, 0.719
Cu, 0.719 0.011 barn for
0.011 barn for  Zn(n,
Zn(n,  )
) Zn, 4.05
Zn, 4.05 0.05 barn for
0.05 barn for  Ag(n,
Ag(n,  )
)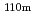 Ag and 8.53
Ag and 8.53 0.27 barn for
0.27 barn for  In(n,
In(n,  )
) 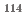 In
In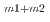 . The results for
. The results for  Sc and
Sc and  Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1514 - 1525, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study aims to clarify the effect of fuel particle radius on the criticality transient behavior and the total number of fissions in water-moderated solid fuel dispersion systems. Neutronics/thermal hydraulics-coupled kinetics analysis was performed in a hypothetical fuel debris system, where small fuel particles aggregate in water and become supercritical. Results showed that the number of fissions is 10 times larger when the fuel particle radius is reduced by one order of magnitude under conditions where heat transfer, i.e. from fuel to water, is emphasized. Moreover, there is a possibility that lower reactivity could give a larger number of fissions when the fuel particle size is very small. In addition, the number of fissions may be overestimated or underestimated to an unexpected extent unless appropriate fuel particle size is set on the analysis.
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 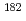 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Kamide, Hideki; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Hayafune, Hiroki; Kubo, Shigenobu; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Maeda, Seiichiro; Sagayama, Yutaka; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; et al.
Jisedai Genshiro Ga Hiraku Atarashii Shijo; NSA/Commentaries, No.28, p.14 - 36, 2023/10
Developments of next generation nuclear reactors, e.g., Fast Reactor, and High Temperature Gas cooled Reactor, are in progress. They can contribute to markets of electricity and industrial heat utilization in the world including Japan. Here, current status of reactor developments in Japan and also situation in the world are summarized, especially for activities of Generation IV International Forum (GIF), developments of Fast Reactor and High Temperature Gas cooled Reactor in Japan, and SMR movements in the world.
Okita, Shoichiro; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
Lu, K.; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Li, Y.; Masaki, Koichi*; Takagoshi, Daiki*; Nagai, Masaki*; Nannichi, Takashi*; Murakami, Kenta*; Kanto, Yasuhiro*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.22-00484_1 - 22-00484_13, 2023/08
Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki*; Shimada, Asako; Lind, T.*; Bentaib, A.*; Sogalla, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Albright, L.*; Clayton, D.*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4782 - 4795, 2023/08
Kosaka, Wataru; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Yanagisawa, Hideki*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.1150 - 1163, 2023/08
The leakage of pressurized water from a steam generator (SG) and the progress after that are a key issue in the safety assessment or design of a SG in sodium-cooled fast reactor. The analysis code LEAP-III can evaluate a rate of water leakage during the long-term event progress, i.e., from the self-wastage initiated by an occurrence of a microscopic crack in a tube wall to the water leak detection and water/water-vapor blowdown. Since LEAP-III consists of semi-empirical formulae and one-dimensional equations of conservation, it has an advantage in short computation time. Thus, LEAP-III can facilitate the exploration of various new SG designs in the development of innovative reactors. However, there are several problems, such as an excessive conservative result in some case and the need for numerous experiments or preliminary analyses to determine tuning parameters of models in LEAP-III. Hence, we have developed a Lagrangian particle method code, which is characterized by a simpler computational principle and faster calculation. In this study, we have improved the existing particle pair search method for interparticle interaction in this code and developed an alternative model without the pair search. Through the trial analysis simulating in a tube bundle system, it was confirmed that new models reduced the computation time. In addition, it was shown that representative temperatures of the heat-transfer tubes evaluated by this particle method code, which is used to predict the tube failure in LEAP-III, were good agreement with that by SERAPHIM, which is a detailed mechanistic analysis method code.
Sugawara, Takanori; Kunieda, Satoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/08
This study investigates the impact of the change from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5 on neutronics analysis of transmutation systems. As the transmutation systems, the following two systems are targeted: JAEA-ADS, a lead-bismuth cooled accelerator-driven system, and MARDS, a molten salt chloride accelerator-driven system. For the JAEA-ADS, the k-eff value increased 189 pcm from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5. It was found that the revisions of various nuclides affected to this difference. For example, the revision of  N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of
N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of  Cl and
Cl and  Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Takata, Takashi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.66(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2022, P. 73, 2023/07
The present study is concerned with the neutron capture cross-sections that contribute to the evaluation of the amount of radionuclides possessing problems in decommissioning. In this study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag,
Ag,  In and
In and  W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then
W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then  rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors (
rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors ( Au,
Au,  Co and
Co and  Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92
Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92 0.10)
0.10) 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of
/sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of  Sc and
Sc and  Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-009, 165 Pages, 2023/06
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2020 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.