Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Maruyama, Yu
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
, 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
no abstracts in English
Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 209(11), p.1765 - 1784, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Takahara, Shogo; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM16) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/09
 sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory (Sweden)
Hard Rock Laboratory (Sweden)Soler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
Geologica Acta, 20(7), 32 Pages, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:46.22(Geology)Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 223, p.108503_1 - 108503_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:81.06(Engineering, Industrial)Soler, J. M.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; Svensson, U.*; Iraola, A.*; Ebrahimi, K.*; Trinchero, P.*; Molinero, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 208(6), p.1059 - 1073, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)The SKB Task Force is an international forum on modelling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing tracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A was the predictive modelling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modelling approaches and codes, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modelling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable.
 sp
sp HRL LTDE-SD experiments
HRL LTDE-SD experimentsSoler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-20-17, 71 Pages, 2021/07
Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Zheng, X.; Mandelli, D.*; Alfonsi, A.*; Smith, C.*; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
Proceedings of 30th European Safety and Reliability Conference and 15th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (ESREL 2020 and PSAM-15) (Internet), p.2176 - 2183, 2020/11
Watanabe, Tadashi*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Mano, Akihiro
International Journal of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (Internet), 13(11), p.516 - 519, 2019/10
The estimation of leak flow rates through narrow cracks in structures is of importance for nuclear reactor safety, since the leak flow could be detected before occurrence of loss-of-coolant accidents. The two-phase critical leak flow rates are calculated using the system analysis code, and two representative non-homogeneous critical flow models, Henry-Fauske model and Ransom-Trapp model, are compared. The pressure decrease and vapor generation in the crack, and the leak flow rates are found to be larger for the Henry-Fauske model. It is shown that the leak flow rates are not affected by the structural temperature, but affected largely by the roughness of crack surface.
Motegi, Kosuke; Trianti, N.; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.4324 - 4335, 2019/08
Soler, J. M.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; Svensson, U.*; Trinchero, P.*; Iraola, A.*; Ebrahimi, H.*; Molinero, J.*; et al.
SKB R-17-10, 153 Pages, 2019/01
The SKB Task Force is an international forum on modeling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing tracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A was the predictive modeling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modelling approaches, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modeling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable. The modeling results have also been finally compared to the measured breakthroughs.
 Zn
ZnKoizumi, Mitsuo; Seki, Akiyuki*; Toh, Yosuke; Osa, Akihiko; Utsuno, Yutaka; Kimura, Atsushi; Oshima, Masumi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Katakura, Junichi; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 730(1-2), p.46 - 58, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:73.04(Physics, Nuclear)Coulomb excitation experiment was carried out with a  Zn beam bombarding a
Zn beam bombarding a  Pb target. Two
Pb target. Two 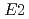 matrix elements and the quadrupole moment of the 2
matrix elements and the quadrupole moment of the 2
 state were newly derived with the least-squares search code GOSIA. The potential energy surface (PES) was calculated with the Nilsson-Strutinsky model, showing two shallow minima: the first minimum does not contain the
state were newly derived with the least-squares search code GOSIA. The potential energy surface (PES) was calculated with the Nilsson-Strutinsky model, showing two shallow minima: the first minimum does not contain the 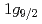 orbit below the Fermi surface, while the second minimum does. The ground state band and the intruder band seem to be constructed on the first and the second minimum, respectively. As for the ground state band, the asymmetric rotor model and the IBM in O(6) limit reproduced the experimental values rather well. The shallow PES may suggest unstability of the shape. The ground state band structure may be explained assuming a soft triaxial deformation.
orbit below the Fermi surface, while the second minimum does. The ground state band and the intruder band seem to be constructed on the first and the second minimum, respectively. As for the ground state band, the asymmetric rotor model and the IBM in O(6) limit reproduced the experimental values rather well. The shallow PES may suggest unstability of the shape. The ground state band structure may be explained assuming a soft triaxial deformation.
Kojima, Takao; Tachibana, Yukio; Fujimoto, Nozomu; Ishihara, Masahiro
Proceedings of 8th Annual International Conference on Composites Engineering (ICCE/8), p.479 - 480, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Teruyuki; Kato, Shohei
Radiation Risk Assessment Workshop Proceedings, p.140 - 150, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 4, p.2615 - 2622, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.59(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 3, p.7039 - 7046, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.84(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Soler, J. M.*; L fgren, M.*; Nilsson, K.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Gylling, B.*; Vidstrand, P.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; et al.
fgren, M.*; Nilsson, K.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Gylling, B.*; Vidstrand, P.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The GWFTS Task Force is an international forum in the area of modeling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing radiotracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A of Task Force was the predictive modeling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modeling approaches, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modeling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable.
Muramatsu, Ken; Kubo, Kotaro; Takada, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English