Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Ichiba, Yuta*
Radiation Measurements, 187, p.107486_1 - 107486_8, 2025/09
Birkholzer, J. T.*; Graupner, B. J.*; Harrington, J.*; Jayne, R.*; Kolditz, O.*; Kuhlman, K. L.*; LaForce, T.*; Leone, R. C.*; Mariner, P. E.*; McDermott, C.*; et al.
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100685_1 - 100685_17, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Kaburagi, Masaaki; Miyamoto, Yuta; Mori, Norimasa; Iwai, Hiroki; Tezuka, Masashi; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Tagawa, Akihiro; Takasaki, Koji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.308 - 316, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suzuki, Seiya; Katsube, Daiki*; Yano, Masahiro; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Terasawa, Tomoo; Ozawa, Takahiro*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; Kim, Y.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yuhara, Junji*; et al.
Small Methods, 9(3), p.2400863_1 - 2400863_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)Matsumura, Taichi; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kondo, Kazuhiro*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113791_1 - 113791_9, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) -,
-,  - and X-ray spectra
- and X-ray spectraOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Shen, H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The spectrum determination method (SDM) is the method to determine radioactivities by analyzing full spectral shape of  - or
- or  rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard
rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard  - and
- and  spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
Endo, Akira
Annals of the ICRP, 52(4), p.5 - 7, 2024/12
In its Publication 155, International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has developed data on the Specific Absorbed Fraction (SAF) for reference males and females at ages of newborn, 1 year, 5 years, 10 years, and 15 years. The SAF represents the fraction of energy emitted within a source region which is absorbed in a target region per mass of the target region and is essential for calculating absorbed doses in organs or tissues for internal exposure. By combining the data of Publication 155 with the SAF data for reference adult males and females already published as Publication 133, an SAF dataset for the calculation of age-dependent dose coefficients for members of the public for environmental intakes of radionuclides has been completed. This, together with revised biokinetic models and nuclear decay data, means that the key building blocks for calculating new dose coefficients are in place. The outcome will soon be available in a series of ICRP Publications of Dose Coefficients for Intakes of Radionuclides by Members of the Public.
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer and
ssbauer and  SR studies of Sm
SR studies of Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge
Tsutsui, Satoshi; Ito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jin*; Yoshida, Mio*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Koda, Akihiro*; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.55_1 - 55_9, 2024/12
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compounds
ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compoundsTsutsui, Satoshi; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Nakamura, Jin*; Ito, Takashi; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Sato, Hideyuki*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.9_1 - 9_10, 2024/12
Teshigawara, Makoto; Lee, Y.*; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Hartl, M.*; Aso, Tomokazu; Iverson, E. B.*; Ariyoshi, Gen; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)At Japanese Spallation Neutron Source in J-PARC, the para-hydrogen fraction was measured by using Raman spectroscopy in-situ for an integrated beam power of 9.4 MW h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW
h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
 = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
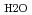 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and
, and  = 0
= 0
Walker, C. S.*; Arthur, R. C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106086_1 - 106086_17, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters of the hydrated (Si(OH) (aq), SiO(OH)
(aq), SiO(OH)
 and SiO
and SiO (OH)
(OH)
 ) and fictive dehydrated (SiO
) and fictive dehydrated (SiO (aq), HSiO
(aq), HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 ) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at
) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at  = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
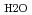 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100
, and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100 C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
Batsaikhan, M.; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Optics Express (Internet), 32(24), p.42626 - 42638, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Optics)Rochman, D.*; Minato, Futoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; 52 of others*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.9_1 - 9_83, 2024/10
Terada, Atsuhiko; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Nuclear Technology, 210(10), p.1871 - 1887, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to understand dispersion of H2 leaked in packed beds of non-porous/porous particles in a partially open space practically, the dispersion of H2 in the particle layers of glass beads and soil was analytically studied using a CFD code to be compared with the experiments and to elucidate the effects of particle layer. H2 flowed out from a single leak point in the particle layer of non-porous glass beads was affected by buoyancy around the leak point, and diffused directly above the leak point in an elliptical shape faster than in the horizontal direction. After that, when it reached the air layer in the head space above the particle layer, H2 spread horizontally, formed a large concentration gradient near the boundary between the particle layer and the air layer, and further diffused in the air layer until the H2 concentration became about 1/3 or less of the concentration near the surface of particle layer. The calculations largely reproduced the experimental concentration distributions. When the particle layer was porous decomposed granite soil, the diffusion behavior of H2 in the particle layer proceeded in the same manner as in the case of glass beads. However, a large concentration gradient was formed near the boundary between the particle layer and the air layer, and then H2 diffused in the air layer until the H2 concentration became below the lower combustion limit. It was suggested through sensitivity analysis that the air permeability coefficient had a large effect on the time course of H2 concentration distribution. Based on the above, we further simulated H2 behavior in the vessel containing the H2 leaked particle layer. By inserting multiple vent pipes without considering H2 generation distribution and particle properties in the particle layer, H2 accumulated from one pipe was discharged by buoyancy without depending on the H2 generation distribution and particle properties in the particle layer, and air flowed in from the other pipe.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wells, S. R.*; Yamamoto, Yuta*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In this study, triple and double resonance ionization schemes of atomic Ca were developed, aiming for the separation of odd isotopes by (i) laser polarization-dependent selection rules, and (ii) large isotope shifts of odd Ca isotopes in the Rydberg levels. Separation of odd isotopes was confirmed under the orthogonal condition. Suppression of non-resonant ionization of  Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of
Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of  Ca.
Ca.
Tian, Q.*; Feng, L.*; Wu, C.*; Wen, J.*; Qiu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Yu, Q.*
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 669, p.1006 - 1014, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:44.97(Chemistry, Physical)Licensing Application Group, Fuels and Materials Department
JAEA-Testing 2024-002, 20 Pages, 2024/08
The contamination accident occurred at Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) Oarai Research and Development Institute on June 6, 2017. During the work of opening the fuel storage container and checking the properties of the contents, the plastic bag that double-packed the inner container burst. The scattering of the fuels contaminated the work room and exposed the worker. The cause of the plastic bag burst was that the enclosed epoxy resin was decomposed by  -rays and the internal pressure increased due to the generated hydrogen gas. The 54 storage containers containing plutonium held at PFRF also at risk of increasing internal pressure. Therefore, an opening inspection was conducted to confirm the contents of the storage container in the hot cell. In addition, the contents of storage containers that may generate gas were stabilized. We are planning to transport the fuel storage containers out to another facility for the decommission of PFRF. The other 9 storage containers include oxide raw material powder: Pu +
-rays and the internal pressure increased due to the generated hydrogen gas. The 54 storage containers containing plutonium held at PFRF also at risk of increasing internal pressure. Therefore, an opening inspection was conducted to confirm the contents of the storage container in the hot cell. In addition, the contents of storage containers that may generate gas were stabilized. We are planning to transport the fuel storage containers out to another facility for the decommission of PFRF. The other 9 storage containers include oxide raw material powder: Pu +  U in excess of 220 g. In order to decrease to less than 220 g (the limit of transport cask), the metal inner containers in the storage container were taken out and repacked in another storage container. This report describes advance measures such as permit application and the details of about storage container opening inspection and metal inner container repacking.
U in excess of 220 g. In order to decrease to less than 220 g (the limit of transport cask), the metal inner containers in the storage container were taken out and repacked in another storage container. This report describes advance measures such as permit application and the details of about storage container opening inspection and metal inner container repacking.
Tanaka, Takuro*; Fukuoka, Masafumi*; Toda, Kanako*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Niwano, Yuma*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Kobayashi, Natsuko*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; et al.
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 4(8), p.3579 - 3586, 2024/08
Terada, Atsuhiko; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(8), p.1135 - 1154, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to elucidate ventilation and exhaust of hydrogen leaked in a partially open space practically, the effects of outer wind on them were studied analytically by using a CFD code in the room of experimental Half-size Hallway model, which has a H release hole on the bottom, one vent on the roof and another vent on the side: external air flowed in the room from the Door vent and then H
release hole on the bottom, one vent on the roof and another vent on the side: external air flowed in the room from the Door vent and then H was discharged outside from the Roof vent. The H
was discharged outside from the Roof vent. The H concentration distribution in the room was divided into two layers at the height of Door vent, with a high concentration layer above it and a low concentration layer below it, forming a stratified interface. When the wind speed blown into the room increased, the combination of the Realizable k-e; turbulence model and the turbulence Schmidt number of 1.0 improved the reproducibility of the analysis results of H
concentration distribution in the room was divided into two layers at the height of Door vent, with a high concentration layer above it and a low concentration layer below it, forming a stratified interface. When the wind speed blown into the room increased, the combination of the Realizable k-e; turbulence model and the turbulence Schmidt number of 1.0 improved the reproducibility of the analysis results of H concentration distribution. The trial analysis suggested that the concern that wind would increase the indoor H
concentration distribution. The trial analysis suggested that the concern that wind would increase the indoor H concentration could be reduced by using the plate with a simple structure in which two plates were crossed on the Roof vent.
concentration could be reduced by using the plate with a simple structure in which two plates were crossed on the Roof vent.