Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Micheau, C.; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; 阿久津 和宏*; 山田 悟史*; 山田 雅子*; Moussaoui, S. A.*; Makombe, E.*; Meyer, D.*; Berthon, L.*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 401, p.124372_1 - 124372_12, 2024/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:65.57(Chemistry, Physical)Supramolecular organization of amphiphilic extractant molecules is involved in metal cation selectivity and separation kinetics during solvent extraction. The relationship between extractant associates/aggregates formed in the organic bulk phase and at the liquid-liquid interface is poorly understood even though it affects the extraction mechanism. The nanoscopic structures of the extraction systems N,N,N',N'-tetrahexylmalonamide (THMA) in toluene and N,N'-dibutyl-N,N'-dimethyl-2-tetradecylmalonamide (DBMA) in n-heptane, used for either Pd(II) or Nd(III) selective extraction from an acidic aqueous phase, were examined. These systems present markedly different affinity for Pd(II) and Nd(III), and extraction kinetics. Extractant organization in the organic bulk phase and at the interface were compared by small-angle X-ray scattering, interfacial tension, and neutron reflectivity. THMA in toluene forms small associates in the organic bulk phase and accumulates in a diffuse layer at the interface, decreasing Pd(II) coordination probability and resulting in slow extraction. DBMA in n-heptane forms large aggregates and a compact, dense interfacial layer, resulting in rapid Pd(II) and Nd(III) extraction. Thus, Pd(II) extraction is driven by interfacial coordination alone, whereas the incorporation of Nd(III) into the core of large aggregates governs Nd(III) extraction in the interfacial layer. These results suggest that the interface should be described as a nanoscale interphase containing a high extractant concentration compared with the organic bulk phase.
藤原 悟*; 松尾 龍人*; 杉本 泰伸*; 柴田 薫
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 10(23), p.7505 - 7509, 2019/12
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:17.65(Chemistry, Physical)無秩序なポリペプチド鎖のダイナミクスの特性評価は、本質的に無秩序状態なタンパク質およびフォールディングプロセスに関連する非ネイティブ状態下のタンパク質の挙動を解明するために必要である。本研究では、小角X線散乱測定データと動的光散乱測定データと組み合わせて準弾性中性子散乱測定データから、タンパク質のセグメント運動と分子全体の拡散および局所側鎖運動を評価する方法を独自に開発した。そしてこの方法を、非フォールディング状態およびメルトグロビュール(MG)状態のタンパク質RNase Aに適用し、セグメント運動から生じる拡散係数を評価し、非フォールディング状態とMG状態で異なる値をとることを明らかにした。またこの方法で得られた値は、蛍光現象を用いた別の測定技術を使用して得られた値と一致していることも確認できた。これらの研究成果は、この方法の、さまざまな無秩序状態でのタンパク質の挙動を特徴付ける実行可能性だけでなく、有用性も示している。
 -synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formation藤原 悟*; 河野 史明*; 松尾 龍人*; 杉本 泰伸*; 松本 友治*; 成田 哲博*; 柴田 薫
Journal of Molecular Biology, 431(17), p.3229 - 3245, 2019/08
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:49.83(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)パーキンソン病発症には、脳細胞中の「 -シヌクレイン」というタンパク質が線維状に集合した状態(「アミロイド線維」と呼ばれる)となることが関係すると考えられており、どのようなメカニズムでこのアミロイド線維が形成されるのかに強い関心が寄せられている。そこで研究チームは、タンパク質分子の「動き」に着目し、アミロイド線維のできやすさが様々に異なった条件でのタンパク質の動きを、J-PARCの中性子準弾性散乱装置を用いて調べた。その結果、タンパク質分子の動きの違いによりアミロイド線維のできやすさが変わること、特にアミロイド線維ができるためには、タンパク質同士が集合しやすくなるような特定の動きが必要なことを明らかにした。
-シヌクレイン」というタンパク質が線維状に集合した状態(「アミロイド線維」と呼ばれる)となることが関係すると考えられており、どのようなメカニズムでこのアミロイド線維が形成されるのかに強い関心が寄せられている。そこで研究チームは、タンパク質分子の「動き」に着目し、アミロイド線維のできやすさが様々に異なった条件でのタンパク質の動きを、J-PARCの中性子準弾性散乱装置を用いて調べた。その結果、タンパク質分子の動きの違いによりアミロイド線維のできやすさが変わること、特にアミロイド線維ができるためには、タンパク質同士が集合しやすくなるような特定の動きが必要なことを明らかにした。
依田 修
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 17, p.337 - 343, 1984/00
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:63.21(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)全反射ガラスミラーと水晶モノクロメータを組み合わせて、X線を検出器位置に点状に収束させ、散乱強度を一次元位置敏感型検出器(PSPC)によって測定する高分解能小角散乱装置を試作した。この装置の設計、性能を詳述した。

 Si
Si

土井 健治; 茅野 秀夫*; 増本 健*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 11(5), P. 605, 1978/00
非晶質合金Pd
 Si
Si
 をJMTRの速中性子により5
をJMTRの速中性子により5 10
10
 /cm
/cm のフルエンスに照射した試料のX線小角散乱を測定した。X線広角散乱には照射による変化は殆ど認められないことはすでに報告した(登録No.A-7199)。CuK
のフルエンスに照射した試料のX線小角散乱を測定した。X線広角散乱には照射による変化は殆ど認められないことはすでに報告した(登録No.A-7199)。CuK 線を用い散乱角15'~5°の範囲の測定を行ったところ、照射によりこの範囲の散乱強度が著しく増大していることを見た。未照射試料についてはこの範囲での散乱強度は殆ど0である。この散乱強度分布より、中性子照射により数10
線を用い散乱角15'~5°の範囲の測定を行ったところ、照射によりこの範囲の散乱強度が著しく増大していることを見た。未照射試料についてはこの範囲での散乱強度は殆ど0である。この散乱強度分布より、中性子照射により数10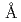 程度の構造のゆらぎが生じたことを結論した。前報の結果と併せて非晶質物質の照射損傷の様子が結晶性物質のそれとどのように異なるかについて一般的な考察を行なう。
程度の構造のゆらぎが生じたことを結論した。前報の結果と併せて非晶質物質の照射損傷の様子が結晶性物質のそれとどのように異なるかについて一般的な考察を行なう。