Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Seiya*; Kawahara, Jun*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Sugihara, Kenta; Takase, Shinsuke*; Moriguchi, Shuji*; Hashimoto, Hirotada*
Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 17(1), p.2211143_1 - 2211143_23, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:81.62(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In tsunami inundations or slope disasters of heavy rain, a lot of floating debris or driftwood logs are included in the flows. The damage to structures from solid body impacts is more severe than the damage from the water pressure. In order to study free-surface flows that include floating debris, developing a high-accurate simulation code of free-surface flows with high performance for large-scale computations is desired. We propose the single-phase free-surface flow model based on the cumulant lattice Boltzmann method coupled with a particle-based rigid body simulation. The discrete element method calculates the contact interaction between solids. An octree-based AMR (Adaptive Mesh Refinement) method is introduced to improve computational accuracy and time-to-solution. High-resolution grids are assigned near the free surfaces and solid boundaries. We conducted two kinds of tsunami flow experiments in the 15 and 70 m water tanks at Hachinohe Institute of Technology and Kobe University to validate the accuracy of the proposed model. The simulation results have shown good agreement with the experiments for the drifting speed, the number of trapped wood pieces, and the stacked angles.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Ina, Takuya; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 13th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Heterogeneous Systems (ScalAH22) (Internet), p.10 - 17, 2022/00
The ensemble data assimilation of computational fluid dynamics simulations based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) is implemented and optimized on a GPU supercomputer based on NVIDIA A100 GPUs. To connect the LBM and LETKF parts, data transpose communication is optimized by overlapping computation, file I/O, and communication based on data dependency in each LETKF kernel. In two dimensional forced isotropic turbulence simulations with the ensemble size of 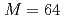 and the number of grid points of
and the number of grid points of 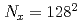 , the optimized implementation achieved
, the optimized implementation achieved 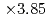 speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of
speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of 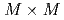 real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and
real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and 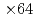 speedup was achieved.
speedup was achieved.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Aoki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Hiromichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Parallel Computing, 108, p.102851_1 - 102851_12, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.00(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)The aerodynamics simulation code based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) using forest-of-octrees-based block-structured local mesh refinement (LMR) was implemented, and its performance was evaluated on GPU-based supercomputers. We found that the conventional Space-Filling-Curve-based (SFC) domain partitioning algorithm results in costly halo communication in our aerodynamics simulations. Our new tree cutting approach improved the locality and the topology of the partitioned sub-domains and reduced the communication cost to one-third or one-fourth of the original SFC approach. In the strong scaling test, the code achieved maximum 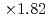 speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
Ishikawa, Hirotaku*; Kai, Tetsuya; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(2), p.221 - 227, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ebihara, Kenichi
JAERI-Research 2005-004, 121 Pages, 2005/03
This report is the JAERI's report version of the doctor thesis by the author. In this report, first, the validity and usefulness of the application of the two-phase fluid model of the lattice-gas method and the lattice Boltzmann method(LBM) are examined. On the basis of the examination, next, the horizontal stratified two-phase flow that is the fundamental and important flow is simulated by the HCZ model which is one of the two-phase fluid model of the LBM. It is seen that the interfacial growth of the HCZ model satisfies the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability theory and reproduces the theoretical two-phase flow regime map of Taitel and Dukler(T-D map). It is found that more superficial flow velocity of the rare phase is necessary in the channel with the narrow width. The HCZ model can also simulate the droplet generation accompanying more complex interfacial phenomena and reproduce the experimental correlation of Ishii and Grolmes in the range of the distribution of the experimental data.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Watanabe, Tadashi
Proceedings of 2004 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition (IMECE '04) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2004/11
This paper describes the numerical simulation of the interfacial growth of the stratified wavy two-phase flow in the horizontal rectangular channel. The influence of the channel width upon the growth of the interfacial wave was evaluated by the several simulations for the different channel width. The numerical simulation model adopted in this paper is a one-component two-phase fluid model of the lattice Boltzmann method. The wave growth was observed and the dimensionless numbers that characterize the two-phase flow state were measured during the computations. The relation between the wave growth and the dimensionless numbers, which characterize the flow state, was compared with that in the flow pattern map proposed by Taitel and Dukler. It was verified in the case of the wide channel width that the simulated relation was almost in agreement with that in the flow pattern map. It was shown that the narrower the channel width became, the more mass flow rate of the rare phase the interfacial growth needed and the obtained relation deviated from that in the flow pattern map.
Ebihara, Kenichi
Tsukuba Daigaku Daigakuin Shisutemu Joho Kogaku Kenkyuka Hakase Gakui Rombun, 134 Pages, 2004/09
In this thesis, first the liquid-gas models of the lattice method are examined by applying them to two-phase flow simulations. Next the liquid-gas model(the HCZ model) of the lattice Boltzmann method is applied to the three-dimensional simulation of the horizontal stratified two-phase flow. The following results are obtained. (1)The two- and three- dimensional interface simulated by the HCZ model satisfies the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability theory. (2)In the simulation of the interfacial growth in the rectangular channel, it is found that the relation between the interfacial growth and the flow state is in agreement with the flow regime map proposed theoretically by Taitel and Dukler. (3)It is also found that the three dimensionality becomes remarkable and the interfacial growth needs more flow rate of the rare phase than that of the theoretical flow regime map when the channel width is narrower. (4)In the droplet creation simulation, it is found that the relation between the droplet creation and the flow state simulates the experimental correlation proposed by Ishii and Grolmes.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Watanabe, Tadashi
Nagare, 23(4), p.253 - 261, 2004/08
The lattice Boltzmann method for one-component two-phase fluid is applied to the simulation of the droplet creation in the horizontal stratified two-phase flow. It is observed in several flow states that the droplet tears from the interface wave. The dimensionless numbers that characterize the flow state are also measured during the simulations. After checking the influence of the lattice length and width to the simulation result, the relation between the droplet creation and the measured dimensionless numbers is compared with the inception criteria of the droplet creation that was proposed on the basis of experimental data by Ishii and Grolmes. It was found that the simulation results are included in the devitation of experimental data from the correlation of Ishii-Grolmes.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Watanabe, Tadashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 70(694), p.1393 - 1399, 2004/06
The horizontal stratified two-phase flow in the rectangular pipe whose width in smaller than the height is simulated by the one-component two-phase lattice Boltzmann method. The interfacial growth between two phases is measured for three cases with the different pipe width and the measured dimensionless number charactering the two-phase flow is compared with the flow regime map proposed by Taitel and Dukler. It is found that the boundary separating the interfacical growth from the non-growth which is obtained by the simulations is larger in the flow regime map when the pipe width is narrower.
Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; Yamakawa, Koichi; Faenov, A. Y.*; Magunov, A. I.*; et al.
Physical Review A, 68(6), p.063201_1 - 063201_8, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:86.61(Optics)The Boltzmann Equation and a detailed collisional radiative model are solved simultaneously as a function of time to model the time integrated X-ray spectra of the transient plasma produced by a high intensity ultrafast laser source. The results are in agreement with highly resolved F-like to He-like K-shell emission spectra recorded recently during ultrashort laser experiments with argon cluster targets in Japan.
Watanabe, Tadashi; Ebihara, Kenichi
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (SNA 2000) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Computational Fluid Dynamics Journal, 8(1), p.135 - 141, 1999/04
no abstracts in English
; Yokokawa, Mitsuo;
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu, 1(1), p.101 - 104, 1996/05
no abstracts in English
; ; Yokokawa, Mitsuo
JAERI-Data/Code 96-013, 25 Pages, 1996/03
no abstracts in English
PNC TN9410 94-111, 42 Pages, 1994/04
Thermal striping phenomena are characterized by stationaly random temperature fluctuations and observed in the region immediately above the core exit of LMFBRs due to the interactions of cold and hot sodium. To evaluate the phenomena, it is neccessary to consider a time-dependent heat transfer coefficient to structures from fluid, in the same manner as a evaluation of a stationaly temperature fluctuation in fluid. For this purpose, a computer program THEMIS (Time-dependent Heat transfer Evaluation by Monte Carlo Direct Simulation) has been developed for the thermohydraulic analysis based on the Boltzmann equation. A two-dimensional duct flow problem has been solved to check the fundamental performance of the THEMIS code. The main results are as follows: (1)Axial distribution of molecular velocity U has shown good agreement with the solution of the Navier-Stokes equation under the condition of Kn=0.0002. (2)An acceleration on the VP-2600 vector processor is about 12 times as the VP-2600 scalar processor. Future works of the THEMIS code development are (1)investigation of the applicabilities in a non-isothermal fluid system and in a complex geometry system and (2)verification with detailed experimental results.
Sato, Kazuyoshi; Akiba, Masato; Araki, Masanori; ; ; I.Smid*; A.Cardella*; R.Duwe*; E.D.Pietro*
JAERI-M 93-058, 22 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Kenji*; Yokokawa, Mitsuo; ;
JAERI-M 90-192, 32 Pages, 1990/11
no abstracts in English
; ; ; Shiraishi, K.
ASTM Special Technical Publication 725, p.247 - 268, 1981/00
no abstracts in English
 O pellets
O pellets; Kurasawa, T.; ; ; ;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 80(2), p.249 - 252, 1979/00
Times Cited Count:4no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 5(7), p.374 - 376, 1968/00
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English