Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(18), p.184903_1 - 184903_10, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Eichler, R.*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Chiera, N. M.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Dressler, R.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07005_1 - 07005_7, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:71.33(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In recent years gas-phase chemical studies assisted by physical pre-separation allowed for the productions and investigations of fragile single molecular species of superheavy elements. The latest highlight is the formation of very volatile hexacarbonyl compound of element 106, Sg(CO) . Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO)
. Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO) , W(CO)
, W(CO) , and Sg(CO)
, and Sg(CO) .
.
 and W(CO)
and W(CO)
Usoltsev, I.*; Eichler, R.*; Wang, Y.*; Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 104(3), p.141 - 151, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:94.43(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Conditions of the production and decomposition of hexacarbonyl complexes of short-lived Mo and W isotopes were investigated to study thermal stability of the heaviest group 6 hexacarbonyl complex Sg(CO) . A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO)
. A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO) and W(CO)
and W(CO) , indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO)
, indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO) could be determined with this technique.
could be determined with this technique.
Ozawa, Kazumi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Morisada, Yoshiaki*; Fujii, Hidetoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.2054 - 2057, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)Reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel, as typified by F82H, is a promising candidate for structural material of DEMO fusion reactors. To prevent plasma sputtering, tungsten (W) coating was essentially required. This study aims to examine the irradiation effects on hardness and microstructure of vacuum-plasma-spray coated W-F82H steel, with a special emphasis on the impacts of grain-refining induced by frictional stir processing (FSP). It was revealed that the hardness of the VPS-FSP W after ion-irradiation to 5.4 dpa at 800 C were not remarkably changed, where bulk W usually exhibited significant irradiation hardening.
C were not remarkably changed, where bulk W usually exhibited significant irradiation hardening.
Nakano, Tomohide; Shumack, A.*; Maggi, C. F.*; Reinke, M.*; Lawson, K.*; Coffey, I.*; P tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; et al.
tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; et al.
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 48(14), p.144023_1 - 144023_11, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:83.02(Optics)The 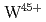 and
and 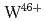 3p-4d inner shell excitation lines in addition to
3p-4d inner shell excitation lines in addition to 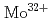 2p-3s lines have been identified from the spectrum taken by an upgraded high-resolution X-ray spectrometer. It is found from analysis of the absolute intensities of the
2p-3s lines have been identified from the spectrum taken by an upgraded high-resolution X-ray spectrometer. It is found from analysis of the absolute intensities of the 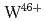 and
and 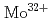 lines that W and Mo concentrations are in the range of
lines that W and Mo concentrations are in the range of 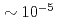 and
and 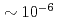 , respectively, with a ratio of
, respectively, with a ratio of  5% for ELMy H-mode plasmas with a plasma current of 2.0- 2.5 MA, a toroidal magnetic field of 2.7 T and a neutral beam injection power of 14-18 MW. For the purpose of checking self-consistency, it is confirmed that the W concentration determined from the
5% for ELMy H-mode plasmas with a plasma current of 2.0- 2.5 MA, a toroidal magnetic field of 2.7 T and a neutral beam injection power of 14-18 MW. For the purpose of checking self-consistency, it is confirmed that the W concentration determined from the 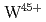 line is in agreement with that from the
line is in agreement with that from the 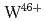 line within 20% and that the plasma effective charge determined from the continuum of the first order reflection spectrum is also in agreement with that from the second order within 50%. Further, the determined plasma effective charge is in agreement with that determined from a visible spectroscopy, confirming that the sensitivity of the X-ray spectrometer is valid and that probably the W and the Mo concentrations are also valid.
line within 20% and that the plasma effective charge determined from the continuum of the first order reflection spectrum is also in agreement with that from the second order within 50%. Further, the determined plasma effective charge is in agreement with that determined from a visible spectroscopy, confirming that the sensitivity of the X-ray spectrometer is valid and that probably the W and the Mo concentrations are also valid.
Shimizu, Yusuke*; Fujita, Takaaki*; Arimoto, Hideki*; Nakano, Tomohide; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hayashi, Nobuhiko
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10(Sp.2), p.3403062_1 - 3403062_4, 2015/07
Suzuki, Satoshi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hirose, Takanori; Sato, Kazuyoshi; Yoshida, Hajime; Enoeda, Mikio; Akiba, Masato
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.93 - 103, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents an R&D activity on the plasma facing components (PFCs), such as first wall and divertor, for the fusion power plant. The PFCs of the power plant will be subjected to heavy neutron irradiation and high heat/particle flux from plasma during the continuous operation. In the present design of the PFCs, the candidate structural material is a reduced activation ferritic-martensitic steel, F82H, from the viewpoints of low activation and high robustness against neutron irradiation, and the candidate armor material is tungsten from the low sputtering yield and low tritium retention points of view. To realize the PFCs using such materials, JAERI has bee extensively conducting R&Ds on; (1) high performance cooling tube, (2) tungsten armor materials, (3) selection of a bonding technique for F82H and tungsten materials and (4) evaluation of structural integrity. Recent achievements on these R&Ds are presented.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.957 - 962, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:96.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of blistering on deuterium retention in W was investigated using the newly established plasma generator with controllable incident energies ranging from 100 eV down to around 10 eV and incident flux of 1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5
/s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5  C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850
C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850  C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 347(1-2), p.111 - 117, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:98.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Polycrystalline tungsten samples have been irradiated at room temperature by high flux (1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7
/s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7  98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering
98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering 
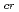 was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies
was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies  20 eV/D,
20 eV/D, 
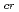 increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of
increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of 
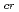 may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2
may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2 m.
m.
Sato, Kazuyoshi; Ezato, Koichiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Suzuki, Satoshi; Akiba, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(7), p.643 - 650, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.73(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Satoshi
Koon Gakkai-Shi, 30(5), p.243 - 247, 2004/09
Selection and the development of plasma facing materials for fusion devices, mainly ITER, are presented. For the divertor, CFC (Carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite) materials are utilized as plasma facing materials in the lower part of vertical targets in ITER. Since the design maximum heat flux to the vertical targets is 20 MW/m , CFC materials, which have higher thermal conductivity than pure copper, are preferable from a heat removal point of view. On the other hand, a plasma facing material of a dome and a liner is tungsten because tungsten has low sputtering yield and has relatively high thermal conductivity among metals. First wall covers 80% of the plasma facing area of ITER. The plasma facing material of the first wall should have good compatibility with plasma. Therefore, beryllium is utilized as a plasma facing material from the low contamination and the minimization of the oxygen impurity to the plasma points of view.
, CFC materials, which have higher thermal conductivity than pure copper, are preferable from a heat removal point of view. On the other hand, a plasma facing material of a dome and a liner is tungsten because tungsten has low sputtering yield and has relatively high thermal conductivity among metals. First wall covers 80% of the plasma facing area of ITER. The plasma facing material of the first wall should have good compatibility with plasma. Therefore, beryllium is utilized as a plasma facing material from the low contamination and the minimization of the oxygen impurity to the plasma points of view.
Sugie, Tatsuo; Kasai, Satoshi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Nagatsu, Masaaki*; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(2), p.1481 - 1485, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:85.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In ITER, the effect of lower energy particle bombardment is important for mirrors located near the divertor where the low temperature plasma is formed. The test pieces of molybdenum mirrors and a tungsten mirror were irradiated by high flux and low energy (67-80 eV) deuterium ions using SLEIS (Super Low Energy Ion Source with High Ion Flux) facility at the temperature of around 100  C. The molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering and melting the thin layer of the surface by electron beam in order to eliminate holes on the surface has a higher reflectivity before irradiation than the mirrors without melting the surface, but the reflectivity decreases rapidly with the irradiation fluence due to the generation of blisters on the mirror surface. The reflectivity of molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering only did not decrease so significantly (less than 10 % at the fluence of 1.3
C. The molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering and melting the thin layer of the surface by electron beam in order to eliminate holes on the surface has a higher reflectivity before irradiation than the mirrors without melting the surface, but the reflectivity decreases rapidly with the irradiation fluence due to the generation of blisters on the mirror surface. The reflectivity of molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering only did not decrease so significantly (less than 10 % at the fluence of 1.3  10
10 m
m ). The molybdenum and tungsten mirrors manufactured by sintering without melting the surface have a potential for plasma facing mirrors in ITER.
). The molybdenum and tungsten mirrors manufactured by sintering without melting the surface have a potential for plasma facing mirrors in ITER.
Kikuchi, Kenji; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of 6th International Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerator Technology (AccApp '03) (CD-ROM), p.17 - 25, 2004/00
Spallation target being developed for high intensity neutron source of MW incident proton power. Mercury is a primary target material in pulsed spallation neutron sources, lead-bismuth is a candidate target material in the accelerator-driven system (ADS) for nuclear transmutation, and tungsten is a back-up solid target for pulsed spallation neutron sources and a candidate for ADS target. Current status of these project and materials issues are stated.
Ando, Masaki; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okajima, Shigeaki; Kawasaki, Kenji
JAERI-Research 2003-029, 72 Pages, 2003/12
The objectives of this study is to clarify calculation accuracy for the Doppler effect of the resonance materials; erbium (Er), tungsten (W) and thorium (ThO ). Doppler effect measurements were carried out in a fast neutron spectrum (XX-2 core) and in an intermediate neutron spectrum (XXI-1D2 core) by the sample-heated and reactivity worth measurement method up to 800
). Doppler effect measurements were carried out in a fast neutron spectrum (XX-2 core) and in an intermediate neutron spectrum (XXI-1D2 core) by the sample-heated and reactivity worth measurement method up to 800 C using FCA. The experiment was analyzed with the standard analysis method for fast reactor cores at FCA with the use of the JENDL-3.2. The SRAC system was also used to investigate the calculation accuracy of the system and to compare it with that of the FCA standard analysis method. The standard analysis method underestimated for the XX-2 core and agreed the experiments within the experimental errors for the XXI-1D2 core. The analysis with the SRAC system gave smaller values by 3%
C using FCA. The experiment was analyzed with the standard analysis method for fast reactor cores at FCA with the use of the JENDL-3.2. The SRAC system was also used to investigate the calculation accuracy of the system and to compare it with that of the FCA standard analysis method. The standard analysis method underestimated for the XX-2 core and agreed the experiments within the experimental errors for the XXI-1D2 core. The analysis with the SRAC system gave smaller values by 3% 10% for the Er sample and bigger values by 2%
10% for the Er sample and bigger values by 2% 5% for the W sample than the standard analysis method.
5% for the W sample than the standard analysis method.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka
JAERI-Research 2003-024, 24 Pages, 2003/11
Re-evaluation of tritium permeation through vertical target of divertor under the ITER operation condition was carried out using tritium transport properties in the candidate materials such as the diffusion coefficient and the trapping factors in tungsten for armor, and the surface recombination coefficient on copper for the heat sink obtained by authors' recent investigation (authors' data), which simulated the plasma-facing conditions of ITER. Evaluation with the data set of previous evaluation was also carried out for comparison (previous data). The permeation analysis was carried out individually by classifying into the armor region (Carbon Fiber Composites and tungsten) and the slit region without armor (3% of armor surface area) assuming the incident flux and temperature for each region. As the results of the permeation analysis, estimated permeation amount with the authors' data was one order less than that with the previous data at the end of lifetime of the divertor due to authors' small diffusion coefficient of tritium in tungsten. It also indicated the possibility that permeation through the slit region of the armor tiles could dominate total permeation through the vertical target, since tritium permeation amount through tungsten armor with the authors' data was estimated to be reduced drastically smaller than that with the previous evaluation data. The result of a little tritium permeation amount through the vertical target with the authors' data ensured the conservatism of the current evaluation of tritium concentration in the primary cooling water in ITER divertor, as it indicated the possibility of direct drainage of the divertor primary cooling water.
Li, J.-F.*; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Kikuchi, Kenji; Igarashi, Tadashi*; Kurishita, Hiroaki*; Watanabe, Ryuzo*; Kawasaki, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 321(2-3), p.129 - 134, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)For the development of tantalum-clad tungsten targets for spallation neutron sources, the bonding strength of tantalum-tungsten interface was investigated by means of an easy-to-use and miniaturized small punch (SP) test, in which a punching load is vertically applied to the center of a jointed disk. Cracks initiated and propagated in the tungsten side for all the samples hot-isostatically pressed (HIPed) at temperatures from 1673 to 2073 K, whereas nocrack and debonding were observed in the interface, indicating that the jointed interface is strongly bonded. The re-crystallization of tungsten occurs and results in its strength reduction, consequently the crack-initiating load decreases with HIPing temperature. The finite element analysis of the measured SP testing results shows that the maximum bonding strength can exceed 1000 MPa. The present study shows that SP test is suitable for the strength evaluation of jointed tantalum-tungsten interfaces.
Suzuki, Satoshi; Ueda, Yoshio*; Tokunaga, Kazutoshi*; Sato, Kazuyoshi; Akiba, Masato
Fusion Science and Technology, 44(1), p.41 - 48, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:86.30(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kawai, Masayoshi*; Furusaka, Michihiro; Li, J.-F.*; Kawasaki, Akira*; Yamamura, Tsutomu*; Mehmood, M.*; Kurishita, Hiroaki*; Kikuchi, Kenji; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.1087 - 1096, 2003/07
In order to establish the technique fabricating a thin target slab with a real size, thin tantalum-clad tungsten slab with a hole for a thermocouple was fabricated with the high-precision machinery techniques and the HIP'ing method. The ultrasonic diagnostic showed that tantalum and tungsten bond was perfect. The HIP optimum condition was certified by means of the small punch test as already reported. The electrolytic coating technique in a molten salt was developed to make a thinner tantalum cladding on a tungsten target with a complicated shape, in order to reduce radioactivity from tantalum in an irradiated target.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Harada, Masahide; Teraoku, Takuji*; Maekawa, Fujio
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.1175 - 1180, 2003/07
It is important to monitor the proton beam for the high intensity pulse spallation target. Especially for the beam halo, which may irradiate the bulk surrounding the target, it is important to be observed to prevent causing heat spot in the shielding bulk. At JSNS, a proton beam monitors are located at front of the target. These monitors are assembled with the proton beam window. Since this scheme increases the radiation on the monitor due to the beam loss at the windows, it may arise heat deposition on the monitor. Therefore, heat deposition is calculated with NMTC/JAM. It is found that the heat deposition for normal operation is less than 0.1 W/cc.
Ando, Masaki; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okajima, Shigeaki; Kawasaki, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 319, p.126 - 130, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Doppler effect experiments on resonance materials for ROX fuels were carried out to examine the calculation accuracy in the intermediate neutron spectrum using Fast Critical Assembly (FCA) at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute. This study is the second phase of a series of the Doppler effect experiments on the resonance materials, which is following the measurements in the fast neutron spectrum. The Doppler effect was measured as the sample reactivity change between the heated and unheated samples. The cylindrical samples of the resonance materials such as erbium (Er), tungsten (W) and thorium (ThO ) were used. The sample was heated up to 800
) were used. The sample was heated up to 800 C at the center of the FCA core. The Doppler effect measurements were analyzed using the SRAC 95 code system with the use of JENDL 3.2. The calculated values agreed with the experiment within the experimental error for the W and ThO
C at the center of the FCA core. The Doppler effect measurements were analyzed using the SRAC 95 code system with the use of JENDL 3.2. The calculated values agreed with the experiment within the experimental error for the W and ThO samples, while the calculation overestimated the experiment for the Er sample about 10 %.
samples, while the calculation overestimated the experiment for the Er sample about 10 %.