Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wada, Yuki; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hibiki, Takashi*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 249, p.127219_1 - 127219_16, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Ichiba, Yuta*
Radiation Measurements, 187, p.107486_1 - 107486_8, 2025/09
Takei, Hayanori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45 Pages, 2025/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is working on the research and development of an accelerator-driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS) for transmuting minor actinides. This system combines a subcritical nuclear reactor with a high-power superconducting proton linear accelerator (JADS-linac). One of the factors limiting the advancement of the JADS-linac is beam trips, which often induce thermal cycle fatigue, thereby damaging the components in the subcritical core. The average beam current of the JADS-linac is 32 times higher than that of the linear accelerator (linac) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Therefore, according to the development stage, comparing the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac with the allowable beam trip frequency (ABTF) is necessary. Herein the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac was estimated through a Monte Carlo program using the reliability functions based on the operational data of the J-PARC linac. The Monte Carlo program afforded the distribution of the beam trip duration, which cannot be obtained using traditional analytical methods. Results show that the frequency of the beam trips with a duration exceeding 5 min must be reduced to 27% of the current J-PARC linac level to be below the ABTF.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Hayano, Akira; Ono, Hirokazu; Tachi, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
, 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency launched the Horonobe International Project (HIP) utilizing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The main objectives of this project are to develop and demonstrate advanced technologies to be used in repository design, operation and closure and a realistic safety assessment in deep geological disposal, and to encourage and train the next generation of engineers and researchers. In this review, an overview of the HIP is presented.
Toyota, Kodai; Onizawa, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi*
Research & Development in Material Science (Internet), 21(5), p.2632 - 2637, 2025/06
Wada, Yuki; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hibiki, Takashi*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 239, p.126598_1 - 126598_18, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:21.83(Thermodynamics)
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Uchihara, Takeru*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Ishii, Yuta*; Nakao, Hironori*; Takehana, Kanji*; Imanaka, Yasutaka*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sawahata, Yoshiro*; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-022, 170 Pages, 2025/03
On March 11, 2011, the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake caused a tsunami that led to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, releasing radioactive material into the environment. Since then, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) using manned helicopters has been employed to measure radiation distribution. As a commissioned project from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) utilizes this technology for emergency monitoring during nuclear facility accidents, aiming to provide prompt results by pre-arranging information on background radiation, topography, and control airspaces around nuclear power plants nationwide. In fiscal year 2023, the commissioned project included conducting ARM around the Sendai Nuclear Power Station and preparing related information. To enhance effectiveness during emergencies, ARM and the first domestic training flight of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) were conducted during the FY2023 Nuclear Energy Disaster Prevention Drill. Furthermore, UAVs radiation monitoring technology was advanced by selecting UAVs and investigating their performance. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified providing insights to improve emergency preparedness.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Nagakubo, Azusa; Sawahata, Yoshiro*; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-021, 232 Pages, 2025/03
The 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on March 11, 2011, caused a tsunami that led to the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident, releasing a large amount of radioactive material into the surrounding environment. Since the accident, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) has been used to quickly and widely measure radiation distribution. As a commissioned project from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has continuously conducted ARM around FDNPS using manned and unmanned helicopters. This report summarizes the monitoring results for fiscal year 2023, evaluates changes in dose rate from past results, and discusses the factors contributing to these changes. Additionally, an analysis considering terrain undulation was conducted to improve accuracy for converting ARM data into dose rate. Furthermore, a method to discriminate airborne radon progeny was applied for ARM results to evaluate its impact. Moreover, to perform wide-area monitoring more efficiently, we advanced the development of unmanned airplane monitoring technology.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) and -MOX lattice calculations
and -MOX lattice calculationsFujita, Tatsuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study estimated the influence of implicit effect on the k-infinity uncertainty in the PWR-UO and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n,
and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n, ) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO
) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For
and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For  Pu and
Pu and  Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.
Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.
Tanigawa, Masafumi; Seya, Kazuhito*; Asakawa, Naoya*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Horigome, Kazushi; Mukai, Yasunobu; Kitao, Takahiko; Nakamura, Hironobu; Henzlova, D.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-014, 63 Pages, 2025/02
The liquid waste treatment process generated sludge items at the plutonium conversion development facility. They are highly heterogeneous and contain large amounts of impurities (Na, Fe, Ni etc.). Therefore, the sludge items have very large sampling uncertainty and so the total measurement uncertainty is very large (approximately 24%). The plutonium scrap multiplicity counter (PSMC) measurement technique for sludge items was developed by joint research between the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). The technical validity for sludge items using the PSMC was evaluated using various types of sample measurements and Monte Carlo N-Particle transport code calculations. The PSMC measurement parameters were found to be valid for use with sludge items and the validity of multiplicity analysis was confirmed and demonstrated through comparisons with standard MOX powder and a standard sludge. As a result, the PSMC measurement values were shown to be consistent and reasonable and the large amount of impurity (Fe, Ni etc.) did not impact the results. Therefore, the measurement uncertainty of the improved nuclear material accountancy (NMA) procedure by combined PSMC and high-resolution gamma spectrometry was shown to be 6.5%. In addition, an acceptance test was conducted using PSMC/HRGS and IAEA benchmark equipment. Measured Pu mass by both equipment agrees within the measurement uncertainty of each method, and so the validity for Pu mass measurement by PSMC/HRGS was confirmed. The above results confirm the applicability of PSMC/HRGS as an additional NMA method for sludge and a newly designed NDA procedure based on this study is applied to sludge for NMA in PCDF.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez Espinoza, V.*; Stakhanova, A.*; Groudev, P.*; Petrova, P.*; Vryashkova, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.110962_1 - 110962_16, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:94.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suetake, Koya*; Ogata, Sho*; Yasuhara, Hideaki*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Inui, Toru*; Kishida, Kiyoshi*
Dai-16-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.304 - 309, 2025/01
It is very important to predict the extent of EDZ (excavation disturbed zone) and the behavior of hydraulic conductivity after excavation of shafts and tunnels for geological disposal of radioactive waste. In this study, we attempted to reproduce the in-situ tunnel excavation test and the subsequent permeability test at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) using a three-dimensional tunnel excavation simulator. As a result, similar results to the in-situ tests were obtained for the extent of EDZ propagation by excavation and the results of permeability tests. The simulator is effective in predicting the mechanical effects of excavation, coupled phenomena such as deformation and seepage, and hydraulic conductivity in deep mudstones in Japan.
Fujita, Tatsuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.470 - 479, 2025/01
This study confirmed the efficiency of a combined approach of the control variates (CV) and the Latin hypercube sampling (LHS), which enhanced the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification due to cross-section (XS) covariance data, by considering the effect of statistical variation and also performed the sensitivity analyses on the influence due to the selection of alternative parameter to apply CV. The convergence performance for the uncertainty of infinite multiplication factor (k-infinity) during the random sampling was compared between several efficient sampling techniques such as the antithetic sampling (AS), LHS, CV, and the combined approaches of them in the PWR-UO fuel assembly geometry. The k-infinity uncertainty was evaluated by statistically processing several times Serpent2 calculations using perturbed ACE-formatted XS files based on ENDF/B-VIII.0. CV+LHS was more efficient than AS, LHS, and CV+AS. In addition, sensitivity analyses were performed to select alternative parameters used in CV. The 3
fuel assembly geometry. The k-infinity uncertainty was evaluated by statistically processing several times Serpent2 calculations using perturbed ACE-formatted XS files based on ENDF/B-VIII.0. CV+LHS was more efficient than AS, LHS, and CV+AS. In addition, sensitivity analyses were performed to select alternative parameters used in CV. The 3 3 mini fuel lattice calculation can improve the efficiency of CV+LHS. The reason was qualitatively considered that this calculation can capture the influence of XS covariance data for Gd isotopes. Consequently, the applicability of CV+LHS for the improvement of convergence performance to evaluate the k-infinity uncertainty during the random sampling was confirmed.
3 mini fuel lattice calculation can improve the efficiency of CV+LHS. The reason was qualitatively considered that this calculation can capture the influence of XS covariance data for Gd isotopes. Consequently, the applicability of CV+LHS for the improvement of convergence performance to evaluate the k-infinity uncertainty during the random sampling was confirmed.
Maeda, Mizuho*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kimura, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(2), p.024707_1 - 024707_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Maruyama, Shuhei; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)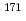 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) -,
-,  - and X-ray spectra
- and X-ray spectraOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Shen, H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The spectrum determination method (SDM) is the method to determine radioactivities by analyzing full spectral shape of  - or
- or  rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard
rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard  - and
- and  spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Yada, Hiroki
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 147, p.031901_1 - 031901_9, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)After the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, very strict safety measures were implemented for nuclear power plants in Japan. It thus becomes a crucial issue if the safety of a plant is maintained or not at beyond design basis events. In this study, head plates and bellows were examined as components that compose the parts of the boundary of vessels that contain the primary coolant of a prototype fast breeder reactor. The behaviors of buckling, post-buckling deformation, and penetration failure, that is, loss of boundary function of these components with increasing pressure were investigated. The series of this research program started in FY2013 and the research proceeded step by step. The new result in this paper is the application of the proposed criteria to head plates and bellows, and a conservative estimation of penetration failure of these components is obtained.