Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*
Nuclear Technology, 210(8), p.1427 - 1443, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The retention of hydrogen (H ) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H
) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H
retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H
O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H
O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H
bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H observed with and without stirring the slurry after
observed with and without stirring the slurry after  Co
Co  -irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H2 bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.
-irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H2 bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.
Nakashio, Nobuyuki*; Osugi, Takeshi; Kurosawa, Shigenobu; Ishikawa, Joji; Hemmi, Ko; Iketani, Shotaro; Yokobori, Tomohiko
JAEA-Technology 2022-016, 47 Pages, 2022/08
The Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started operation of the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities (AVWF) for production of waste packages for disposal of low-level radioactive solid wastes (LLW). To clarify the operating conditions for homogenization of non-metallic LLW, preliminary tests were carried out using the plasma melting furnace of the non-metal melting unit. The fluidity of molten waste influences homogenization conditions of solidified products. It was clarified that the viscosity, which is determined by the chemical composition and the melting temperature, influence the fluidity of molten waste greatly through previous literature review and the small-scale melting tests. In the preliminary tests, the simulated waste with a cold tracer loaded in 200 L drums were melted. Using the waste chemical components (basicity, iron oxide concentration) as an experimental parameter, the homogeneity of the chemical components of the solidified product was investigated and the homogenization conditions of melting tests were examined. The retention ratio of the tracer in the molten bath was also confirmed. The viscosity of the molten wastes was measured and the correlation with homogeneity was examined. In addition, the technical requirements that should be concerned in advance for future actual operation were discussed.
Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Sakuma, Hiroshi*
Nendo Kagaku, 58(1), p.8 - 25, 2019/00
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were conducted to investigate physical properties of water and cations in montmorillonite interlayer nanopores. The swelling behaviors and hydration states were firstly evaluated as functions of interlayer cations and layer charge. The diffusion coefficients of water and cations in interlayer nanopores were decreased in comparison with those in bulk water and came closer to those in bulk water when basal spacing increased. The viscosity coefficients of interlayer water estimated indicated a significant effect of viscoelectricity at 1- and 2-layer hydration states and higher layer charge of montmorillonite. These trends from MD calculations were confirmed to be consistent with existing measured data and previous MD simulation. In addition, model and parameter related to viscoelectric effect used in the diffusion model was refined based on comparative discussion between MD simulations and measurements. The series of MD calculations could provide atomic level understanding for the developments and improvements of the diffusion model for compacted montmorillonite.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Miyahara, Shinya; Uno, Masayoshi*
Netsu Sokutei, 45(1), p.2 - 8, 2018/01
Liquid sodium (Na) has been used as the coolant of fast reactors for the various merits, such as the high thermal conductivity. On the other hand, it is postulated that a steel liner may fail and lead to a sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) during the Na-leak accident. Because of concrete ablation and release of hydrogen gas due to the chemical reactions between Na and concrete components, the SCR is one of the important phenomena in the Na-leak accident. In the study, fundamental experiments related to the SCR were performed using Na and concrete powder. Here, the used concrete powder is milled siliceous concrete which is usually used as the structural concrete in Japanese nuclear power plants. The obvious temperature changes at 3 temperature regions were observed for the reaction process such as Na-melt, NaOH-SiO and Na-H
and Na-H O-SiO
O-SiO reaction, which occurred around 100, 300 and 500
reaction, which occurred around 100, 300 and 500 C, respectively. Especially, the violent reaction around 500
C, respectively. Especially, the violent reaction around 500 C caused the temperature peak to
C caused the temperature peak to 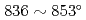 C, and the reaction heat of
C, and the reaction heat of 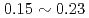 kW/g was estimated under the Na-concrete mixing ratio such as
kW/g was estimated under the Na-concrete mixing ratio such as 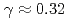 . The main components of the reaction products was identified as Na
. The main components of the reaction products was identified as Na SiO
SiO with X-ray diffraction technique. Moreover, the measured thermophysical properties such as melting point, density, specific heat, thermal conductivity and viscosity were similar to those of
with X-ray diffraction technique. Moreover, the measured thermophysical properties such as melting point, density, specific heat, thermal conductivity and viscosity were similar to those of  Na
Na O-
O-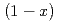 SiO
SiO (
(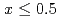 ).
).
Otani, Eiji*; Suzuki, Akio*; Ando, Ryota*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Advances in High-Pressure Technology for Geophysical Applications, p.195 - 209, 2005/09
This paper summarizes the techniques for the viscosity and density measurements of silicate melt and glasses at high pressure and temperature by using the X-ray radiography and absorption techniques in the third generation synchrotron radiation facility, SPring-8, Japan. The falling sphere method using in situ X-ray radiography makes it possible to measure the viscosity of silicate melts to the pressures above 6 GPa at high temperature. We summarize the details of the experimental technique of the viscosity measurement, and the results of the measurements of some silicate melts such as the albite and diopside-jadeite systems. X-ray absorption method is applied to measure the density of the silicate glasses such as the basaltic glass and iron sodium disilicate glass up to 5 GPa at high temperature. A diamond capsule, which is not reactive with the glass, is used for the density measurement of the glasses. The present density measurement of the glasses indicates that this method is useful for measurement of the density of silicate melts at high pressure and temperature.
Konovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Tsypin, V. S.*; Kovalishen, E. A.*; Shirokov, M. S.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori
Physics Letters A, 318(4-5), p.429 - 434, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Kiminori*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku
Geophysical Research Letters, 29(8), p.68_1 - 68_3, 2002/05
The in situ viscosity measurements of the pure molten Fe under high pressures were made by falling sphere X-ray radiography method. Viscosity coefficients at about 2000 K were 15-24 mPa s at 2.7-5.0 GPa, and 4-9 mPa s at 5.0-7.0 GPa. Drastic decrease was found at around 5 GPa, at which stable solid phase below the melting temperatures change from delta (bcc) to gamma (fcc) phases. The observation indicates the possibility that the structural change in the molten Fe occurs in a narrow pressure interval (1 GPa) at the similar condition with the phase transformation in the solid.
Idesaki, Akira; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Morita, Yosuke; Seguchi, Tadao; Ito, Masayoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 36(23), p.5565 - 5569, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:77.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A very fine silicon carbide (SiC) fiber with diameter of 6  m, about a half of that of a commercially available SiC fiber, was synthesized from a polymer blend of polycarbosilane (PCS) and polyvinylsilane (PVS). The fine SiC fiber was obtained by optimizing the composition and the spinning temperature of PCS-PVS polymer blends. In order to determine these optimum conditions, the relationship between temperature and melt viscosities of the polymer blends was investigated. As a result, it was found that the optimum spinning temperature range was within a temperature range where the melt viscosity is 5-10Pa
m, about a half of that of a commercially available SiC fiber, was synthesized from a polymer blend of polycarbosilane (PCS) and polyvinylsilane (PVS). The fine SiC fiber was obtained by optimizing the composition and the spinning temperature of PCS-PVS polymer blends. In order to determine these optimum conditions, the relationship between temperature and melt viscosities of the polymer blends was investigated. As a result, it was found that the optimum spinning temperature range was within a temperature range where the melt viscosity is 5-10Pa s. Moreover, by blending PVS with PCS, the spinning temperature of the polymer blends was lowered, the spinnability of polymer system was improved, and finer polymer fiber was obtained compared with PCS. The optimum content of PVS in the polymer blend was 15-20wt%.
s. Moreover, by blending PVS with PCS, the spinning temperature of the polymer blends was lowered, the spinnability of polymer system was improved, and finer polymer fiber was obtained compared with PCS. The optimum content of PVS in the polymer blend was 15-20wt%.
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku; Maeda, Makoto*; Sato, Jin*; Kubo, Tomoaki*; Kasai, Shizu*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 190(1-2), p.93 - 101, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:69.18(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Fe-FeS melt is thought to be the major candidate of the outer core material. Its viscosity is one of the most important physical properties to study the dynamics of the convection in the outer core. We performed the in situ viscosity measurement of the Fe-FeS melt under high pressure using X-ray radiography falling sphere method with a novel sample assembly. Viscosity was measures in the temperature, pressure, and compositional conditions of 1233-1923 K, 1.5-6.9 GPa, and Fe-Fe 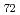 S
S 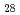 (wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm
(wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm  /mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe
/mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe 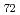 S
S 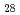 melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
;
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 67(12), p.4302 - 4303, 1998/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.98(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English

Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Ogawa, Toru
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 205-207(PT.1), p.139 - 142, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Hada, Kazuhiko
JAERI-M 93-029, 99 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English

Ono, Hideo;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 27(1), p.45 - 48, 1990/01
no abstracts in English
Nakanishi, Hiroshi*; Arakawa, Kazuo; Hayakawa, Naohiro; Machi, Sueo; Yagi, Tetsuya*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 26(8), p.718 - 724, 1984/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Arakawa, Kazuo; ; Hayakawa, Naohiro
JAERI-M 83-060, 29 Pages, 1983/04
no abstracts in English
Nakanishi, Hiroshi*; Arakawa, Kazuo; Hayakawa, Naohiro; Machi, Sueo; Yagi, Tetsuya*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 25(3), p.217 - 224, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Kazuo;
Trans.JIM, 19(19), p.553 - 561, 1978/00
no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Kazuo;
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 41(5), p.450 - 457, 1977/05
no abstracts in English
; Yamaguchi, Koichi; ; ; ; Takehisa, Masaaki
JAERI-M 5477, 44 Pages, 1973/12
no abstracts in English
Matsuoka, Seikichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Satake, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
When non-axisymmetric magnetic perturbations are imposed in axisymmetric tokamaks, broken axisymmetry induces the neoclassical viscosity, and affects momentum transport and resulting plasma rotation profiles. In this work, we estimate the neoclassical toroidal viscosity using full-f gyrokinetic simulations, and verify calculation methods and obtained results. We discuss the parameter dependency of the neoclassical toroidal viscosity in the presence of small resonant magnetic perturbations, based on comparisons against analytic theories and neoclassical transport codes.