Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maurer, C.*; Galmarini, S.*; Solazzo, E.*; Ku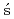 mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar
mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar , J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
, J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.106968_1 - 106968_27, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.52(Environmental Sciences)After performing multi-model exercises in 2015 and 2016, a comprehensive Xe-133 atmospheric transport modeling challenge was organized in 2019. For evaluation measured samples for the same time frame were gathered from four International Monitoring System stations located in Europe and North America with overall considerable influence of IRE and/or CNL emissions. As a lesion learnt from the 2nd ATM-Challenge participants were prompted to work with controlled and harmonized model set ups to make runs more comparable, but also to increase diversity. Effects of transport errors, not properly characterized remaining emitters and long IMS sampling times (12 to 24 hours) undoubtedly interfere with the effect of high-quality IRE and CNL stack data. An ensemble based on a few arbitrary submissions is good enough to forecast the Xe-133 background at the stations investigated. The effective ensemble size is below five.
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 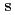 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 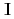 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 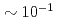 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (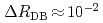 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki*; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Ishii, Toshiaki; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 140, p.209 - 214, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.93(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Kai, Tetsuya; Uchida, Toshitsugu; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Oi, Motoki; Wakui, Takashi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Takada, Hiroshi
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1021(1), p.012042_1 - 012042_4, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Bakhtiari, M.; Kramer, G. J.*; Takechi, Manabu; Tamai, Hiroshi; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kamada, Yutaka
Physical Review Letters, 94(21), p.215003_1 - 215003_4, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:84.17(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Bremsstrahlung radiation of runaway electrons is found to be an energy limit for runaway electrons in tokamaks. The minimum and maximum energy of runaway electron beams is shown to be limited by collisions and Bremsstrahlung radiation, respectively. It is also found that a massive injection of a high-Z gas such as Xenon can terminate a disruption-generated runaway current before the runaway electrons hit the walls.
Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Harada, Hiro; Murata, Isao; Shindo, Ryuichi;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 30(3), p.249 - 260, 1993/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; Iwai, Takashi; Saito, Junichi; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Oyamada, Rokuro; Saito, Minoru
JAERI-M 93-016, 0, p.259 - 267, 1993/02
no abstracts in English
Baba, Yuji; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Teikichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 63, p.391 - 394, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:60.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 kernels in Cracked Particles and its Effect on Xenon Release
kernels in Cracked Particles and its Effect on Xenon ReleaseTobita, Tsutomu; Ikawa, Katsuichi
JAERI-M 84-096, 16 Pages, 1984/05
no abstracts in English
; Abe, Shinichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 212, p.533 - 537, 1983/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ;
Hoken Butsuri, 17, p.427 - 436, 1982/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; Ikawa, Katsuichi; Iwamoto, K.; Yamamoto, Katsumune
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 19(11), p.889 - 902, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 24(5), p.381 - 389, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:21.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 powders
powdersShiba, Koreyuki; ; Ugajin, Mitsuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 96(3), p.255 - 260, 1981/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:62.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 23(11), p.843 - 850, 1981/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 --U
--U O
O system with emphasis on radiation damage
system with emphasis on radiation damageShiba, Koreyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 57(3), p.271 - 279, 1975/03
no abstracts in English
; Shinohara, Yoshikuni
JAERI-M 5712, 36 Pages, 1974/05
no abstracts in English
Ikezoe, Yasumasa; ; Shimizu, Saburo; ;
JAERI-M 5498, 10 Pages, 1973/12
no abstracts in English
;
Measurement and Analysis of Xenon Oscillations, p.761 - 762, 1969/00
no abstracts in English