Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -CsOH
-CsOHRizaal, M.; Luu, V. N.; 中島 邦久; 三輪 周平
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
Thermochemistry prevailing between gaseous CsOH and concrete main chemical phase CaCO at temperatures up to 570
at temperatures up to 570 C was investigated with various scenarios using the thermogravimetric method. The aim was to elucidate the decreasing behavior of cesium (Cs) trapping on CaCO
C was investigated with various scenarios using the thermogravimetric method. The aim was to elucidate the decreasing behavior of cesium (Cs) trapping on CaCO observed in the transpiration method. A quasi-two-compartment platinum crucible was developed to realize co-measurements of both CsOH and CaCO
observed in the transpiration method. A quasi-two-compartment platinum crucible was developed to realize co-measurements of both CsOH and CaCO during thermal treatment. Post-test X-ray diffraction was conducted to identify the chemical compound formed on the CaCO
during thermal treatment. Post-test X-ray diffraction was conducted to identify the chemical compound formed on the CaCO precursor. The early presence (timely sensitivity) of CsOH near the heated surface of CaCO
precursor. The early presence (timely sensitivity) of CsOH near the heated surface of CaCO was found to play a key role in the trapping (in the form of Cs
was found to play a key role in the trapping (in the form of Cs CO
CO ). Such a factor is crucial because, otherwise, the Ca(OH)
). Such a factor is crucial because, otherwise, the Ca(OH) would predominate the surface upon CaCO
would predominate the surface upon CaCO decomposition where leading to no reaction with CsOH.
decomposition where leading to no reaction with CsOH.
 at temperature range 170 - 290
at temperature range 170 - 290 C
CLuu, V. N.; 中島 邦久
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 426, p.113402_1 - 113402_7, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A field assessment at the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station revealed high radioactivity on the concrete shield plugs, which is estimated above 20 PBq for Cs-137 at units 2 and 3. This leads to significant interest in the retention of Cs on concrete during severe accidents (SA). However, the interaction of CsOH, as one of the main Cs forms released in SA, with concrete surfaces at elevated temperatures remains poorly researched. In this study, we have experimentally investigated the deposition behavior of CsOH on CaCO , which is the primary phase existing on the surface of concrete, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate (N), and increased linearly with CsOH concentration (C
, which is the primary phase existing on the surface of concrete, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate (N), and increased linearly with CsOH concentration (C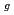 ), as following expression: N(
), as following expression: N( g/cm
g/cm
 s) = v
s) = v C
C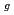 , where v
, where v is temperature-dependent deposition velocity as given by ln v
is temperature-dependent deposition velocity as given by ln v (cm/s) = -3785.8/T + 3.766, for T in the range of 170 and 290
(cm/s) = -3785.8/T + 3.766, for T in the range of 170 and 290  C. This empirical model can be integrated into severe accident codes to quantify the chemical trapping of cesium on concrete surfaces during ex-vessel release. Moreover, it can contribute to understanding the reasons behind the high dose rate on concrete shield plugs at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear power stations and aid in developing effective decommissioning practices for concrete structures.
C. This empirical model can be integrated into severe accident codes to quantify the chemical trapping of cesium on concrete surfaces during ex-vessel release. Moreover, it can contribute to understanding the reasons behind the high dose rate on concrete shield plugs at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear power stations and aid in developing effective decommissioning practices for concrete structures.
 at temperature range 170 - 290
at temperature range 170 - 290  C
CLuu, V. N.; 中島 邦久
no journal, ,
A recent field survey revealed extremely high radioactivity on the concrete shield plugs, exceeding 20 PBq for Cs-137 at units 2, 3 of 1F. This leads to significant interest in the retention of Cs on concrete during severe accident. Despite this, the interaction of Cs vapors and/or aerosols in the gas phase with concrete surfaces at high temperatures remains inadequately explored. In this work, we investigated the deposition behavior of CsOH on CaCO , as a primary phase on the concrete surface, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate, and increased linearly with CsOH concentration.
, as a primary phase on the concrete surface, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate, and increased linearly with CsOH concentration.