Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Myagmarjav, O.; 田中 伸幸; 野口 弘喜; 上地 優; 小野 正人; 野村 幹弘*; 竹上 弘彰
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.235 - 242, 2025/05
Hydrogen plays an important role in the transition to clean energy and the achievement of net-zero emissions. Thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process, which uses nuclear heat to decompose water, is considered the most prospective method for producing large amounts of hydrogen without emitting carbon dioxide. The IS process consists of three coupled chemical reactions (Bunsen reaction, sulfuric acid decomposition, and hydrogen iodide decomposition). A major challenge for the practical application of the IS process is the efficient separation of hydrogen from the mixed corrosive gas of hydrogen iodide and iodine generated during hydrogen iodide decomposition (2HI H
H + I
+ I ). A membrane that can efficiently separate H
). A membrane that can efficiently separate H while treating this corrosive HI gas has not yet been developed. In this study, a membrane with high separation performance and corrosion stability was developed by fabricating a three-layer structure consisting of a base
while treating this corrosive HI gas has not yet been developed. In this study, a membrane with high separation performance and corrosion stability was developed by fabricating a three-layer structure consisting of a base  -alumina support tube, a middle silica layer and a top H
-alumina support tube, a middle silica layer and a top H -selective silica layer. By selecting the dipping time and CVD time, which are critical to the properties of the resulting silica layers, the prepared membrane showed high separation performance. For instance, the H
-selective silica layer. By selecting the dipping time and CVD time, which are critical to the properties of the resulting silica layers, the prepared membrane showed high separation performance. For instance, the H /SF
/SF selectivity varied between 1622 and 1671 in the temperature range of 30-200
selectivity varied between 1622 and 1671 in the temperature range of 30-200  C. The result suggests that the developed membranes had no defects, especially existence of pinholes. HI stability tests also showed that these membrane were stable in corrosive environments.
C. The result suggests that the developed membranes had no defects, especially existence of pinholes. HI stability tests also showed that these membrane were stable in corrosive environments.
 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)SiH 八面体部位を特徴とするヒドリドケイ酸塩は、水素貯蔵と水素化物イオン伝導に関連する潜在的な性質を持つかなり新しい化合物のクラスである。ここでは、Zintl相水素化物BaSiH
八面体部位を特徴とするヒドリドケイ酸塩は、水素貯蔵と水素化物イオン伝導に関連する潜在的な性質を持つかなり新しい化合物のクラスである。ここでは、Zintl相水素化物BaSiH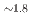 を4GPa以上の圧力でH
を4GPa以上の圧力でH 流体と反応させ、その後常圧まで減圧して得られた新しい代表的なBaSiH
流体と反応させ、その後常圧まで減圧して得られた新しい代表的なBaSiH について報告する。SiH
について報告する。SiH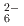 イオンはBa
イオンはBa 対イオンによって八面体に配位している。Ba原子とSi原子の配置は理想的なfcc NaCl構造からわずかにずれている。IRとラマンスペクトルからSiH
対イオンによって八面体に配位している。Ba原子とSi原子の配置は理想的なfcc NaCl構造からわずかにずれている。IRとラマンスペクトルからSiH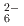 の屈曲と伸縮モードがそれぞれ800-1200と1400-1800cm
の屈曲と伸縮モードがそれぞれ800-1200と1400-1800cm の範囲で観測された。BaSiH
の範囲で観測された。BaSiH は95
は95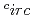 Cまで熱的に安定であり、それ以上ではBaH
Cまで熱的に安定であり、それ以上ではBaH とSiに分解する。DFT計算により、直接バンドギャップは2.5eVであることが示された。BaSiH
とSiに分解する。DFT計算により、直接バンドギャップは2.5eVであることが示された。BaSiH の発見により、ギガパスカル圧力(10GPa以下)のシリサイドの水素化反応からアクセス可能なヒドリドケイ酸塩の化合物クラスが固まった。BaSiH
の発見により、ギガパスカル圧力(10GPa以下)のシリサイドの水素化反応からアクセス可能なヒドリドケイ酸塩の化合物クラスが固まった。BaSiH の構造的性質は、超伝導ポリハイドライドBaSiH
の構造的性質は、超伝導ポリハイドライドBaSiH を予測されるより高い圧力で水素化するための中間体(あるいは前駆体)であることを示唆している。
を予測されるより高い圧力で水素化するための中間体(あるいは前駆体)であることを示唆している。
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
寺田 敦彦; Thwe Thwe, A.; 日野 竜太郎*
JAEA-Review 2024-049, 400 Pages, 2025/03
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)事故における水素爆発を鑑みて、原子力技術者が理解しておくべき水素安全技術の先端を示しつつ、原子力技術者に協力すべき燃焼、爆発専門家向けに原子力における水素安全の要点を示し、事故後廃棄物管理までを視野に入れて放射線分解水素に関する情報を加えた「原子力における水素安全対策高度化ハンドブック(第1版)」を2017年に刊行した。その後、水素安全対策の合理的な高度化や水素安全評価のさらなる信頼性の向上に向けて、原子力事故の解析に一般的に用いられている集中定数系(LP)コードを補完するうえで、原子炉格納容器(CV)内での局所的な水素濃度上昇の影響、着火後の火炎伝播加速による安全機器の健全性、水素処理対策の妥当性等をより精緻、かつ定量的に評価できる数値流体力学(CFD)解析への期待が高まっている。これは、さらなる水素挙動や爆発燃焼に対する安全性の向上を図ることが必要とされていることにもよる。そこで、加圧水型原子炉(PWR)を対象に、シビアアクシデント(SA)時の水素拡散から爆発燃焼、それによるCV及びCV内の安全機器への影響評価までを解析するCFDによる水素挙動統合解析システムを構築・整備してきた。ここで得られたSA安全対策、それによる水素安全向上、安全対策を踏まえた水素発生事故に対する安全性評価などについて、LP及びCFD解析の役割や活用例を本「原子力における水素安全対策高度化ハンドブック(第2版)」にまとめた。ハンドブックに記載した実機サイズの解析結果は解析モデル等を既存の代表的な小型、中型、大型試験による照合解析で確認した。
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; 服部 高典; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)飽和sp -カーボンナノスレッド(CNTh)は、その高いヤング率と熱伝導率が予測され、大きな関心を集めている。中心環へのヘテロ原子の導入がCNThの形成に影響を与え、化学的に均質な生成物が得られることが示されているが、ペンダント基が重合プロセスに与える影響については、まだ未解明である。本研究では、フェノールの圧力誘起重合を調べ、0.5GPaと4GPa以下で起こる2つの相転移を明らかにした。20GPa以上では、フェノールは水酸基とカルボニル基を持つ重合度4のCNTに重合する。ヒドロキシル基の水素移動は、重合度6のナノスレッドの形成を妨げることがわかった。この発見は、さらなるカラム内重合を阻止する水酸基の重要な役割を浮き彫りにし、今後のメカニズム研究やナノ材料合成に貴重な示唆を与えるものである。
-カーボンナノスレッド(CNTh)は、その高いヤング率と熱伝導率が予測され、大きな関心を集めている。中心環へのヘテロ原子の導入がCNThの形成に影響を与え、化学的に均質な生成物が得られることが示されているが、ペンダント基が重合プロセスに与える影響については、まだ未解明である。本研究では、フェノールの圧力誘起重合を調べ、0.5GPaと4GPa以下で起こる2つの相転移を明らかにした。20GPa以上では、フェノールは水酸基とカルボニル基を持つ重合度4のCNTに重合する。ヒドロキシル基の水素移動は、重合度6のナノスレッドの形成を妨げることがわかった。この発見は、さらなるカラム内重合を阻止する水酸基の重要な役割を浮き彫りにし、今後のメカニズム研究やナノ材料合成に貴重な示唆を与えるものである。
伊藤 辰也; 永石 隆二; 桑野 涼*; 神戸 正雄*; 吉田 陽一*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 226, p.112198_1 - 112198_5, 2025/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)近年、放射線照射実験や非密封放射性同位元素実験用の容器として、ポリイミドやポリエーテルエーテルケトンなどの耐放射線性樹脂の使用が増えている。しかし、水の分解生成物と樹脂との相互作用の可能性が見つかり、樹脂が放射線場における水中の反応に影響を及ぼすことが懸念された。その相互作用を明らかにするために、 線による水の放射線分解における重クロム酸イオン(Cr
線による水の放射線分解における重クロム酸イオン(Cr O
O
 )の還元と過酸化水素(H
)の還元と過酸化水素(H O
O )の生成を樹脂の有無で比較した。同一線量で樹脂ありの水溶液中のCr
)の生成を樹脂の有無で比較した。同一線量で樹脂ありの水溶液中のCr O
O
 還元量は樹脂なしの場合よりも大きくなり、樹脂によってCr
還元量は樹脂なしの場合よりも大きくなり、樹脂によってCr O
O
 還元が促進されることを示した。一方、電子捕捉剤の有無にかかわらず、純水中のH
還元が促進されることを示した。一方、電子捕捉剤の有無にかかわらず、純水中のH O
O 生成は樹脂の有無にほとんど依存しなかった。これらは、放射線場において水と接触した樹脂とヒドロキシルラジカルとの相互作用を示唆している。
生成は樹脂の有無にほとんど依存しなかった。これらは、放射線場において水と接触した樹脂とヒドロキシルラジカルとの相互作用を示唆している。
勅使河原 誠; Lee, Y.*; 達本 衡輝*; Hartl, M.*; 麻生 智一; Iverson, E. B.*; 有吉 玄; 池田 裕二郎*; 長谷川 巧*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)J-PARCの核破砕中性子源において、水酸化第二鉄触媒の機能性を評価するため、1MW運転時の積算ビーム出力9.4MW hの条件で、ラマン分光法を用いてパラ水素割合をその場測定した。その結果、1MW運転におけて触媒が十分に機能していることが分かった。また、触媒を通さないバイパスラインを用いて、中性子照射によるパラからオルソ水素への逆変換率を調べることを試みた。測定されたオルソ水素割合の増加は、500kW運転で積算ビーム出力2.4MW
hの条件で、ラマン分光法を用いてパラ水素割合をその場測定した。その結果、1MW運転におけて触媒が十分に機能していることが分かった。また、触媒を通さないバイパスラインを用いて、中性子照射によるパラからオルソ水素への逆変換率を調べることを試みた。測定されたオルソ水素割合の増加は、500kW運転で積算ビーム出力2.4MW hの場合に0.44%であった。しかしながら、この結果は、冷中性子モデレータ内で引き起こされた逆変換と、バイパスされた触媒容器中の温度上昇によって発生した準静的オルソ水素のメインループへの受動的滲出との合算であることが示された。
hの場合に0.44%であった。しかしながら、この結果は、冷中性子モデレータ内で引き起こされた逆変換と、バイパスされた触媒容器中の温度上昇によって発生した準静的オルソ水素のメインループへの受動的滲出との合算であることが示された。
土井 大輔
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 91, p.1245 - 1252, 2024/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:31.33(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrogen is a major nonmetallic impurity in the coolant of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) during normal operation. A higher hydrogen concentration than the gas-liquid equilibrium has been transiently detected in the gas space of actual SFR plants. The presence of several sodium compounds can increase hydrogen generation; however, a thorough understanding of the thermal behavior of candidate reactions is lacking. Herein, thermal analysis reveals the hydrogen release behavior of sodium hydride. Mass spectrometry indicates hydrogen generation with decreasing sample mass, indicating thermal decomposition. Detailed kinetic analysis based on master plot methods indicates that the hydrogen release reaction occurred through a mechanism involving random nucleation and growth of nuclei. Furthermore, the reaction rate was newly formulated based on a kinetic model function representing the above mechanism and the Arrhenius-type reaction rate constant comprising an activation energy of 119.0  0.8 kJ mol
0.8 kJ mol and a frequency factor of 1.8
and a frequency factor of 1.8  10
10 s
s . These findings will enable the numerical simulation of the hydrogen release behavior in SFRs.
. These findings will enable the numerical simulation of the hydrogen release behavior in SFRs.
守田 圭介; 青木 健; 清水 厚志; 佐藤 博之
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/11
High temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) is expected to use nuclear heat to wide range of industrial applications such as hydrogen production, which is capable of high temperature heat supply with inherent safe characteristics. JAEA started a High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) heat application test project to develop coupling technologies between HTGR and a hydrogen production plant necessary to achieve large-scale, carbon-free hydrogen production. One of the key technologies is a safety evaluation method which can simulate an impact of explosion hazards induced in the hydrogen production plant on reactor facility because HTGR hydrogen production system contains large amount of combustible gases such as hydrogen. A computational fluid dynamics code FLACS has been sufficiently validated for dispersion and explosion of combustible gases such as hydrogen and methane worldwide, however, only few attempts have been made for validation of analysis in closed area with small space. A leak of combustible gases to the piping in HTGR hydrogen production system may occur in case of abnormal condition in hydrogen production plant and therefore an explosion in the piping must be considered. This paper describes the validation of FLACS by analyzing explosion experiments in straight piping and complex piping aiming to establish a safety evaluation method for analyzing explosions of combustible gases in piping.
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Hydrogen embrittlement has long been an obstacle to the development of safe infrastructure. However, in contrast to hydrogen's embrittling effect, recent research has revealed that the addition of hydrogen improves both the strength and uniform elongation of AISI Type 310S austenitic stainless steel. A detailed understanding of how hydrogen affects the deformation mechanism of this steel could pave the way for the development of more advanced materials with superior properties. In the present study,  neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
柴山 由樹; 北條 智彦*; 小山 元道*; 秋山 英二*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 88, p.1010 - 1016, 2024/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:51.25(Chemistry, Physical)The effect of plastic deformation on the hydrogen embrittlement behavior of high-strength martensitic steels was investigated using a U-bend test. The hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility appeared to be enhanced with increasing plastic strain. Based on fractographic and stress-strain analyses, the maximum principal stress dominated the hydrogen embrittlement fracture. Although the apparent enhancement with increasing plastic deformation was observed, the origin of the enhancement was increased residual stress arising from the evolution of graded plastic strain during U-bending. We conclude that residual stress rather than plastic strain induced by plastic deformation strongly affects hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility in deformed high-strength steel components.
寺田 敦彦; 永石 隆二
Nuclear Technology, 210(10), p.1871 - 1887, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)表面の平滑なガラスビーズ層と細孔を有する真砂土層中に漏洩した水素の拡散挙動について、CFDによる実験結果の照合解析を行い、流れの特性を明らかにした。ガラスビーズ層と真砂土層において、漏洩点からの表層(空気層と粒子層の境界面)までの濃度の広がり方は同様な傾向を示すが、真砂土層の方が表層面近傍での空気層中の水素濃度は低下する傾向がみられた。真砂土層中の拡散挙動シミュレーションでは、透気係数や拡散係数の感度が実験結果の再現性に影響することが示唆された。また、空気層中に流出した水素の滞留を抑制する簡易な自然換気プロセスの検証を試計算し、見通しを示した。
井戸村 泰宏
Physics of Plasmas, 31(10), p.102504_1 - 102504_10, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)トカマクプラズマにおける水素同位体混合現象をfull-fジャイロ運動論シミュレーションを用いて解析した。モデルプラズマのパラメータは、重水素(D)ペレットを水素(H)プラズマに入射した後にエネルギー閉じ込め時間スケールで水素同位体混合が発生したJETの水素同位体ペレット実験に基づいて選択した。重水素ペレット入射前後のプラズマ分布を用いて2つの数値実験を行った。どちらの場合も、炉心の乱流揺動はイオン温度勾配駆動乱流によって特徴づけられるが、後者の場合、外側の領域に捕捉電子モード乱流が存在する。前者の場合、バルクHイオンの密度分布は準定常状態に保たれ、その粒子閉じ込め時間はエネルギー閉じ込め時間よりも一桁長い。後者の場合、バルクHイオンとペレットDイオンの密度分布は、エネルギー閉じ込め時間の時間スケールで過渡的な緩和を示し、早い水素同位体混合を示す。トロイダル角運動量バランスから、水素同位体混合はトロイダル電場応力によって駆動されることがわかった。
竹田 武司; 柴田 大受
JAEA-Review 2024-040, 29 Pages, 2024/09
日本の第6次エネルギー基本計画では、2050年までのカーボンニュートラルを目指したエネルギー政策の道筋を示すことが重要なテーマとなっている。2030年に向けた日本の原子力研究開発(R&D)への政策対応には、国際連携による2030年までの小型モジュール炉(SMR)技術の実証が盛り込まれている。これを踏まえ、脱炭素化と経済成長を同時に達成するGreen Transformation (GX)の実現に向けて、今後10年を見据えた取組の基本方針が取りまとめられた。海外に目を向けると、米国、カナダ、欧州、中国、ロシアを中心に、重工メーカーやR&D機関のみならずベンチャー企業も含めて、国際的にSMRのR&D活動が活発である。このような状況下で、原子力機関(NEA)の原子力施設安全委員会(CSNI)は、SMRの安全性への影響評価を支援するために、SMRに関する専門家グループ(EGSMR)を招集した。EGSMRの取組として、SMRの導入や研究活動に関する最新情報の収集を主目的とした数回にわたるアンケートへの回答の提出が求められた。これに対して、筆頭著者から、JAEAに加えて日立GEニュークリア・エナジー株式会社、三菱重工業株式会社からの情報に基づき回答した。アンケートに対する日本の回答の多くは、CSNI Technical Opinion Paper No.21 (TOP-21)のベースとなる情報である。本報告書では、整理した公開可能な日本のアンケート回答と付加情報を示し、TOP-21の記載内容の一部を補完した。これにより、EGSMRの活動(2022-2023年)を中心とした日本におけるSMRに関するR&Dの調査結果をまとめた。本報告書は、SMRに関する今後の国際協力の議論や国内外の原子力分野の人材育成に役立てることを目的としている。この中で、日本の革新炉のR&Dの主なトピックスとして、高温ガス炉(HTGR)とナトリウム冷却高速炉(SFR)に関して、実用化に必要な技術と現状のギャップを同定している。また、HTGRと水素製造施設の相互接続に関連して、水素製造施設からの可燃性ガスの漏洩と異常発生が安全性に与える影響等について整理している。
 /
/ /
/ 線ラジオリシス影響下における格納容器系統内広域防食の実現; ナノバブルを用いた新規防食技術の開発(委託研究); 令和4年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業
線ラジオリシス影響下における格納容器系統内広域防食の実現; ナノバブルを用いた新規防食技術の開発(委託研究); 令和4年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 東北大学*
JAEA-Review 2024-019, 102 Pages, 2024/09
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和4年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究および人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和2年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「 /
/ /
/ 線ラジオリシス影響下における格納容器系統内広域防食の実現:ナノバブルを用いた新規防食技術の開発」の令和2年度から令和4年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、デブリの本格的取り出し工程での閉じ込め機能(PCV、負圧維持系等)の経年劣化要因として重要と考えられる腐食を対象としたものである。1F 1
線ラジオリシス影響下における格納容器系統内広域防食の実現:ナノバブルを用いた新規防食技術の開発」の令和2年度から令和4年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、デブリの本格的取り出し工程での閉じ込め機能(PCV、負圧維持系等)の経年劣化要因として重要と考えられる腐食を対象としたものである。1F 1 3号機PCV内部における腐食環境の特殊性は、燃料デブリ由来の
3号機PCV内部における腐食環境の特殊性は、燃料デブリ由来の 線/
線/ 線放出核種の粒子やイオンと構造材料がPCV内の種々の部位で直接接触し得ることに在り、飛程の短い
線放出核種の粒子やイオンと構造材料がPCV内の種々の部位で直接接触し得ることに在り、飛程の短い 線/
線/ 線放出核種が接触する局所で、ラジオリシスにより生成する化学種(特にH
線放出核種が接触する局所で、ラジオリシスにより生成する化学種(特にH O
O )が局所的に高濃度となれば、当該箇所において鋼材の腐食が大きく加速する可能性が有る。対して、
)が局所的に高濃度となれば、当該箇所において鋼材の腐食が大きく加速する可能性が有る。対して、 /
/ ラジオリシスを考慮した腐食評価に関する知見が欠けていた。このような背景に鑑みて、本研究では以下の研究成果を得た。(1)
ラジオリシスを考慮した腐食評価に関する知見が欠けていた。このような背景に鑑みて、本研究では以下の研究成果を得た。(1) 線/
線/ 線/
線/ 線の影響を網羅したラジオリシス解析モデルを構築した。(2)
線の影響を網羅したラジオリシス解析モデルを構築した。(2) 線放出核種/
線放出核種/ 線放出核種を用いた電気化学試験(ホット試験)ならびにコールド条件での模擬環境腐食試験による系統的な腐食速度データを取得した。
線放出核種を用いた電気化学試験(ホット試験)ならびにコールド条件での模擬環境腐食試験による系統的な腐食速度データを取得した。
寺田 敦彦; 永石 隆二
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(8), p.1135 - 1154, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)天井と側面に換気口を設けた部屋の床面から漏洩した水素の挙動について、CFD解析を用いて実験結果との照合を行うことで、部屋周囲の風況による影響を明らかにした。室内の水素濃度の経時変化は、天井と床面付近の間で成層化がみられ、計算結果については局所的な流れ場の特性変化を反映できる乱流モデルと比較的大きな乱流シュミット数(1.0)を組み合わせた場合に実験結果の再現性が向上した。風況によって、室内に水素が滞留したケースについて、天井開口部にシンプルな板を設置することで換気の改善が図れることを示した。
比嘉 良太*; 藤原 比呂*; 戸田 裕之*; 小林 正和*; 海老原 健一; 竹内 晃久*
Materials Transactions, 65(8), p.899 - 906, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Al-Zn-Mg合金では、水素(H)によって機械的特性が著しく劣化することから、そのような合金の強度を向上させるためには、水素脆化(HE)と呼ばれるこの現象を抑制することが不可欠である。粒界破壊(IGF)は主にHE発生時に観察されるため、HEを抑制するためにはIGFの発生挙動を理解する必要がある。通常、応力、ひずみ、H濃度の不均一な分布は、多結晶材料におけるIGFの発生に影響を与える。本研究では、X線イメージング技術により得られた多結晶体の3次元微細構造データをもとに作成した3次元イメージベースモデルを用いた結晶塑性有限要素法とH拡散解析によるシミュレーションから、実際の破壊領域における応力、ひずみ、H濃度の分布を調べた。そして、シミュレーション結果とX線CTによる引張試験試料のその場観察を組み合わせ、実際のき裂発生挙動における応力、ひずみ、H濃度の分布を調べ、粒界き裂の発生条件を検討した。その結果、結晶塑性に起因する粒界垂直応力が粒界き裂の発生を支配することが明らかになった。一方、応力による内部Hの蓄積はき裂発生にほとんど影響しないことがわかった。
永塚 健太郎; 野口 弘喜; 長住 達; 野本 恭信; 清水 厚志; 佐藤 博之; 西原 哲夫; 坂場 成昭
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 425, p.113338_1 - 113338_11, 2024/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:93.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)高温ガス炉は固有の安全性を有し、二酸化炭素を排出することなく大量の水素や高温の熱供給が可能なことから、産業分野の脱炭素化に貢献できる。本報では、原子力機構で進めるHTTR(高温工学試験研究炉)を利用した炉心強制冷却喪失(LOFC)試験等の研究開発成果に加え、現在設計を進めるHTTRを用いた水素製造実証試験(HTTR-熱利用試験)の計画を紹介する。加えて、2030年代後半の運転開始に向け、基本設計が進められている高温ガス炉実証炉計画を紹介する。
伊藤 辰也; 永石 隆二; 桑野 涼*
Nuclear Technology, 210(8), p.1427 - 1443, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)福島第一原子力発電所の多核種除去設備における凝集沈殿(共沈)プロセスから排出される放射性廃棄物のような強アルカリ条件下で、水の放射線分解によって発生した水素(H )気泡の保持を、マグネシウムとカルシウムの混合沈殿物である懸濁物固体(SS)からなる炭酸塩スラリーの高粘度懸濁液中で定量的に研究した。親水性の異なる2種類の炭酸塩スラリー、親水性の「現行型」と疎水性の「返送型」についてH
)気泡の保持を、マグネシウムとカルシウムの混合沈殿物である懸濁物固体(SS)からなる炭酸塩スラリーの高粘度懸濁液中で定量的に研究した。親水性の異なる2種類の炭酸塩スラリー、親水性の「現行型」と疎水性の「返送型」についてH 保持特性を評価し、それらの特性を別の懸濁液であるベントナイトの粘土懸濁液の特性と比較した。SS粒子表面の化学吸着量とスラリー中のH
保持特性を評価し、それらの特性を別の懸濁液であるベントナイトの粘土懸濁液の特性と比較した。SS粒子表面の化学吸着量とスラリー中のH Oの量の比較から、SS粒子間でH
Oの量の比較から、SS粒子間でH O分子が共有されている必要があり、この共有により粘土懸濁液中で微細な粘土鉱物間の静電的な結合が形成する粘性とは異なる構造粘性が形成されることが確認された。スラリー中のH
O分子が共有されている必要があり、この共有により粘土懸濁液中で微細な粘土鉱物間の静電的な結合が形成する粘性とは異なる構造粘性が形成されることが確認された。スラリー中のH 気泡の保持は、
気泡の保持は、 Co
Co 線照射後のスラリーの撹拌前後で観測されたH
線照射後のスラリーの撹拌前後で観測されたH 発生量の差から評価した。親水性スラリー、疎水性スラリー、粘土懸濁液、処理水の保持特性の比較から、親水性スラリー中のH
発生量の差から評価した。親水性スラリー、疎水性スラリー、粘土懸濁液、処理水の保持特性の比較から、親水性スラリー中のH 気泡は構造粘性だけでなく立体障害によっても保持されると示唆された。
気泡は構造粘性だけでなく立体障害によっても保持されると示唆された。
山本 智彦; 加藤 篤志; 早川 雅人; 下山 一仁; 荒 邦章; 畠山 望*; 山内 和*; 江田 優平*; 由井 正弘*
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 56(3), p.893 - 899, 2024/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:57.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a secondary cooling system of a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), rapid detection of hydrogen due to sodium-water reaction (SWR) caused by water leakage from a heat exchanger tube of a steam generator (SG) is important in terms of safety and property protection of the SFR. For hydrogen detection, the hydrogen detectors using atomic transmission phenomenon of hydrogen within Ni-membrane were used in Japanese proto-type SFR "Monju." However, during the plant operation, detection signals of water leakage were observed even in the situation without SWR concerning temperature up and down in the cooling system. For this reason, the study of a new hydrogen detector has been carried out to improve stability, accuracy and reliability. In this research, the authors focus on the difference in composition of hydrogen and the difference between the background hydrogen under normal plant operation and the one generated by SWR and theoretically estimate the hydrogen behavior in liquid sodium by using ultra-accelerated quantum chemical molecular dynamics (UA-QCMD). Based on the estimation, dissolved H or NaH, rather than molecular hydrogen (H ), is the predominant form of the background hydrogen in liquid sodium in terms of energetical stability. On the other hand, it was found that hydrogen molecules produced by the sodium-water reaction can exist stably as a form of a fine bubble concerning some confinement mechanism such as a NaH layer on their surface. In parallel, we observed experimentally that the fine bubbles of H
), is the predominant form of the background hydrogen in liquid sodium in terms of energetical stability. On the other hand, it was found that hydrogen molecules produced by the sodium-water reaction can exist stably as a form of a fine bubble concerning some confinement mechanism such as a NaH layer on their surface. In parallel, we observed experimentally that the fine bubbles of H stably existed in the liquid sodium than expected before. This paper describes the comparison between the theoretical estimation and experimental results based on hydrogen form in sodium in the development of the new hydrogen detector in Japan.
stably existed in the liquid sodium than expected before. This paper describes the comparison between the theoretical estimation and experimental results based on hydrogen form in sodium in the development of the new hydrogen detector in Japan.