Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-005, 106 Pages, 2025/06
JAEA has been creating input data for pressurized water reactor (PWR) analysis with RELAP5/MOD3.3 code, mainly based on design information for the four-loop PWR's Tsuruga Power Station Unit-2 as the reference reactor of the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF). The cold leg large-break loss-of-coolant accident (LBLOCA) calculation in the flamework of the BEMUSE program is cited as a representative OECD/NEA activity related to the PWR analysis. The new regulatory requirements for PWRs in Japan include the event of loss of recirculation functions from emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in the cold leg LBLOCA. This event should be evaluated the effectiveness of measures against severe core damage. The input data for this study were made preparations to analyze the PWR LBLOCA, which is one of the design basis accidents that should be postulated in the safety design. This report describes the main features of the input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis. The PWR model comprised a reactor vessel, pressurizer (PZR), hot legs, steam generators (SGs), SG secondary-side system, crossover legs, cold legs, and ECCS. A four-loop PWR was simulated by two loops in the LBLOCA calculation. Specifically, loop-A attached with the PZR corresponded to three loops, and loop-B mounted with the break was equal to one loop. The nodalization schemes of the PWR components were referred to those of the LSTF components. Moreover, interpretations were added to the main input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis, and further information such as the basis for determining the input data was provided. In addition, transient analysis was performed employing the prepared input data for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event. The present transient analysis was confirmed to be appropriate generally by comparing with the calculation in the previous study using the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code. Furthermore, sensitivity analyses were executed exploiting the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code to clarify the effects of a discharge coefficient through the break and water injection flow rate of the alternative recirculation on the fuel rod cladding surface temperature. This report explains the results of the sensitivity analyses within the defined ranges, which complement some of the content of the previous study's calculation for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event.
 -eigenvalue perturbation in Monte Carlo calculation
-eigenvalue perturbation in Monte Carlo calculationTuya, D.; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 169, p.108919_1 - 108919_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Estimating an effect of a perturbation in a fissile system on its  -eigenvalue requires special technique called perturbation theory when the considered perturbation is small. In this study, we develop an adjoint-weighted correlated sampling (AWCS) method based on the exact perturbation theory without any approximation by combining the correlated sampling (CS) method with iterated-fission probability (IFP) based adjoint-weighting method. With the advantages of the CS method being good at providing very small uncertainty for small perturbations and the IFP-based adjoint-weighting method being suitable for continuous-energy Monte Carlo calculation, the developed AWCS method based on the exact perturbation theory offers a new rigorous approach for perturbation calculations. The obtained results by the developed AWCS method for verification problems involving Godiva and simplified STACY density perturbations showed good agreement with the reference calculations.
-eigenvalue requires special technique called perturbation theory when the considered perturbation is small. In this study, we develop an adjoint-weighted correlated sampling (AWCS) method based on the exact perturbation theory without any approximation by combining the correlated sampling (CS) method with iterated-fission probability (IFP) based adjoint-weighting method. With the advantages of the CS method being good at providing very small uncertainty for small perturbations and the IFP-based adjoint-weighting method being suitable for continuous-energy Monte Carlo calculation, the developed AWCS method based on the exact perturbation theory offers a new rigorous approach for perturbation calculations. The obtained results by the developed AWCS method for verification problems involving Godiva and simplified STACY density perturbations showed good agreement with the reference calculations.
Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Clavel, J.-B.*; Duhamel, I.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.51 - 61, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The new critical assembly STACY will be able to contribute to the validation of criticality calculations related to the fuel debris. The experimental core designs are in progress in the frame of JAEA/IRSN collaboration. This paper presents the method applied to optimize the design of the new STACY core to measure the criticality characteristics of pseudo fuel debris that simulated Molten Core Concrete Interaction (MCCI) of the fuel debris. To ensure that a core configuration is relevant for code validation, it is important to evaluate the reactivity worth of the main isotopes of interest and their k sensitivity to their cross sections. In the case of the fuel debris described in this study, especially for the concrete composition, silicon is the nucleus with the highest k
sensitivity to their cross sections. In the case of the fuel debris described in this study, especially for the concrete composition, silicon is the nucleus with the highest k sensitivity to the cross section. For this purpose, some parameters of the core configuration, as for example the lattice pitches or the core dimensions, were adjusted using optimization algorithm to find efficiently the optimal core configurations to obtain high sensitivity of silicon capture cross section. Based on these results, realistic series of experiments for fuel debris in the new STACY could be defined to obtain an interesting feedback for the MCCI. This methodology is useful to design other experimental conditions of the new STACY.
sensitivity to the cross section. For this purpose, some parameters of the core configuration, as for example the lattice pitches or the core dimensions, were adjusted using optimization algorithm to find efficiently the optimal core configurations to obtain high sensitivity of silicon capture cross section. Based on these results, realistic series of experiments for fuel debris in the new STACY could be defined to obtain an interesting feedback for the MCCI. This methodology is useful to design other experimental conditions of the new STACY.
Sugita, Yutaka; Taniguchi, Naoki; Makino, Hitoshi; Kanamaru, Shinichiro*; Okumura, Taisei*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 19(3), p.121 - 135, 2020/09
A series of structural analysis of disposal containers for direct disposal of spent fuel was carried out to provide preliminary estimates of the required pressure resistance thickness of the disposal container. Disposal containers were designed to contain either 2, 3 or 4 spent fuel assemblies in linear, triangular or square arrangements, respectively. The required pressure resistance thickness was evaluated using separation distance of the housing space for each spent fuel assembly as a key model parameter to obtain the required thickness of the body and then the lid of the disposal container. This work also provides additional analytical technical knowledge, such as the validity of the setting of the stress evaluation line and the effect of the model length on the analysis. These can then be referred to and used again in the future as a basis for conducting similar evaluations under different conditions or proceeding with more detailed evaluations.
 for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo technique
for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo techniqueIwamoto, Hiroki; Stankovskiy, A.*; Fiorito, L.*; Van den Eynde, G.*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 4, p.42_1 - 42_7, 2018/11
This paper presents a nuclear data sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of the effective delayed neutron fraction  for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The
for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The  sensitivities are calculated by the modified
sensitivities are calculated by the modified  -ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the
-ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the  sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors
sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors  introduced by Chiba shows that a value of
introduced by Chiba shows that a value of 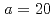 is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of
is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of  . Using the calculated
. Using the calculated  sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the
sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the  uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2
uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2  0.2% and 2.0
0.2% and 2.0  0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of
0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of  Pu and
Pu and  U.
U.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
In the accidents at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station, Tsunami caused loss of electric power supply and this event led to core melt and failure of Containment vessel. Finally, fission products were released to the environment. Currently, the activities for understanding of accident progressions are carried out based on the measured data during the accident, accident progression analysis using integrated severe accident analysis codes and investigation of inside of reactor buildings and containment vessels. On the other hand, there are some research activities with combination of accident progression analysis and accident consequence analysis. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the research project of combination of these analyses using the computational simulation codes has been started. The results obtained from the combination analysis are expected to have broad width of uncertainty because of many uncertainty factors in this combined analysis. In order to perform the analysis efficiently, sensitivity analysis for failure location on containment vessel and its failure size were carried out by THALES2/KICHE developed by JAEA at first. This analysis was performed on unit 1, since it was the first plant to release radioactive materials to the environment during the accident and its consequence had no effect from other plants. The authors focused on the failure of containment vessel head flange, penetration seal and vacuum breaker pipe, and possibility of partial open of vent valve based on the investigations of reactor building inside performed by TEPCO. This paper presents the results obtained from this sensitivity analysis.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2017/11
no abstracts in English
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Itoi, Tatsuya*; Takada, Tsuyoshi*; Furuya, Osamu*; Muta, Hitoshi*; Muramatsu, Ken
Proceedings of 13th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-13) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2016/10
In this study, we address epistemic uncertainty in structure fragility estimation of nuclear power plants (NPPs). In order to identify and quantify dominant factors in fragility assessment, sensitivity analyses of seismic analysis results are conducted for a target NPP building using a three-dimensional finite element model and a conventional lumped mass model (embedded sway rocking model), and the uncertainty caused by the major factors is then evaluated. The results are used to classify epistemic uncertainty levels in a fragility estimation workflow for NPPs in several stages, and a graded knowledge tree technique, which can be used for future fragility estimations, is proposed.
Zheng, X.; Ito, Hiroto; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Maruyama, Yu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.333 - 344, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zheng, X.; Ito, Hiroto; Kawaguchi, Kenji; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Maruyama, Yu
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 138, p.253 - 262, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:39.87(Engineering, Industrial)Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nishihara, Tetsuo
JAERI-Tech 2005-033, 206 Pages, 2005/07
In this report, we investigated the effects of jet for the dispersion and explosion analysis of leaked gas, obstacles, position of an ignition point and cell size for the gas explosion analysis, and atmospheric stability for the dispersion analysis of the leaked gas, with PHOENICS, AutoReaGas, and AUTODYN. Then, we carried out two accident analyses about combustible fluid leakage based on the investigation results of these effects. As a result, it was shown that important buildings related to safety was hardly affected by the explosion of the leaked gas.
Kasahara, Seiji; Hwang, G.*; Nakajima, Hayato; Choi, H.*; Onuki, Kaoru; Nomura, Mikihiro
Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 36(7), p.887 - 899, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:70 Percentile:88.20(Engineering, Chemical)Thermal efficiency of the IS thermochemical hydrogen production process was evaluated. Sensitivities of operation conditions (HI conversion ratio, pressure and reflux ratio at HI distillation and concentration of HI after EED) and nonidealities of the process (electric energy loss in EED, loss at heat exchangers and loss of waste heat recovery as electricity) were investigated. Concentration of HI after EED had the most significant effect of 13.3 % on thermal efficiency in operation conditions. Nonidealities had importance on thermal efficiency. Thermal efficiency was 56.8 % with optimized operation conditions and no nonidealities.
Nagai, Haruyasu
Journal of Applied Meteorology, 41(2), p.160 - 176, 2002/02
no abstracts in English
Homma, Toshimitsu; Inoue, Yoshihisa*; Tomita, Kenichi*
JAERI-Research 2000-049, 101 Pages, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Homma, Toshimitsu; Liu, X.; Tomita, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM-5), p.2753 - 2758, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Yamazawa, Hiromi; Furuno, Akiko; Chino, Masamichi
Atmospheric Environment, 32(24), p.4343 - 4349, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.13(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Yamazawa, Hiromi; Chino, Masamichi; Furuno, Akiko
ETEX Symp. on Long-Range Atmospheric Transport,Model Verification and Emergency Response, p.191 - 194, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Homma, Toshimitsu; A.Saltelli*
Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf., 52, p.1 - 17, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:1451 Percentile:99.97(Engineering, Industrial)no abstracts in English
Homma, Toshimitsu; A.Saltelli*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(11), p.1164 - 1173, 1995/11
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:92.17(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
A.Saltelli*; T.H.Andres*; Homma, Toshimitsu
Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 20, p.387 - 407, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:89.87(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)no abstracts in English